Snell's Law (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Snell's Law
Snell’s law relates the angle of incidence to the angle of refraction at a boundary between two media and is given by:
n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2
Where:
n1 = the refractive index of material 1
n2 = the refractive index of material 2
θ1 = the angle of incidence of the ray in material 1
θ2 = the angle of refraction of the ray in material 2
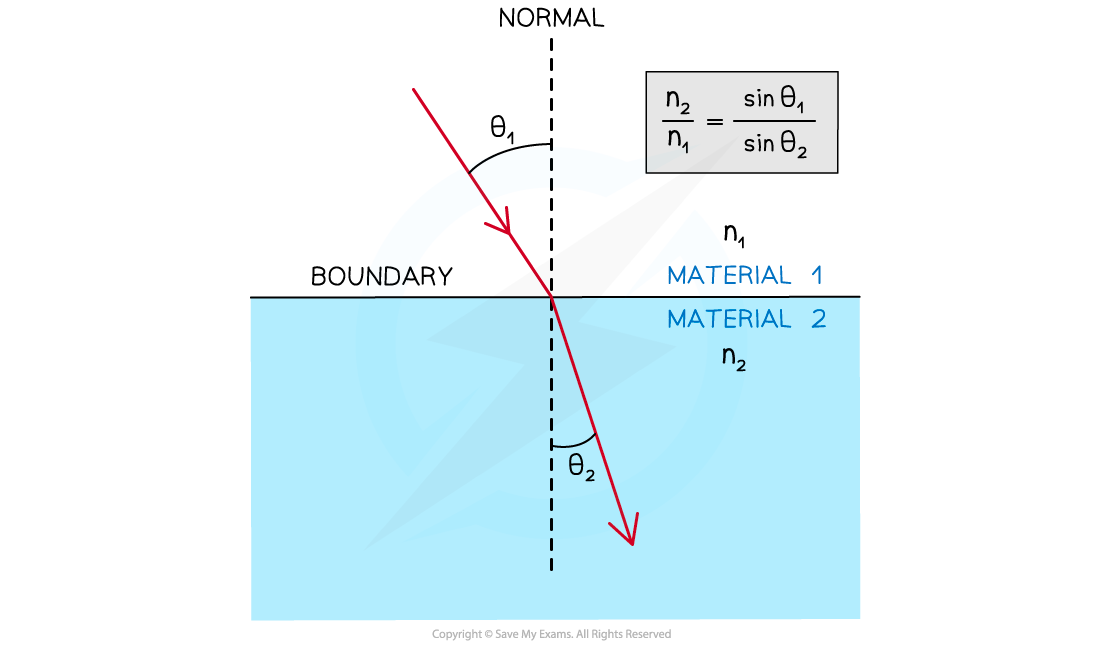
θ1 and θ2 are always taken from the normal
Material 1 is always the material in which the ray goes through first
Material 2 is always the material in which the ray goes through second
Worked Example
A light ray is directed at a vertical face of a glass cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram.
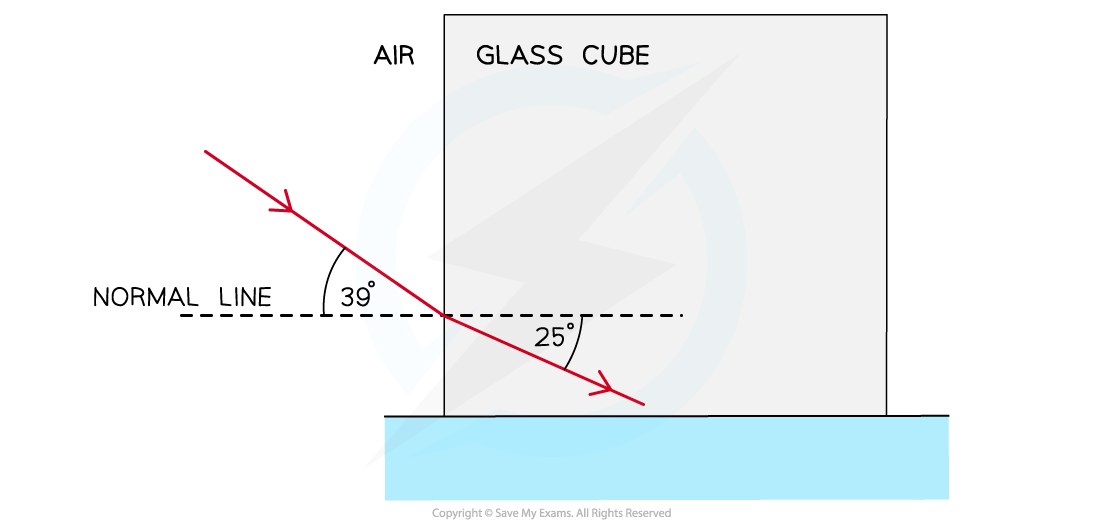
Show that the refractive index of the glass is about 1.5.
Answer:


Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always check that the angle of incidence and refraction are the angles between the normal and the light ray. If the angle between the light ray and the boundary is calculated instead, calculate 90 – θ (since the normal is perpendicular to the boundary) to get the correct angle.
Also check that your calculator is in degrees and not radians.
Keeping track of which angles are θ1 and which are θ2 can be tricky. To help label each angle as the angle for the material
Total Internal Reflection
Critical Angle (θc)
The larger the refractive index of a material, the smaller the critical angle
For a larger n then θC is smaller
When light is shone at a boundary between a denser and a less dense material, different angles of incidence result in different angles of refraction
As the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases
Until the angle of incidence reaches the critical angle
When the angle of incidence = critical angle then:
Angle of refraction = 90°
The refracted ray is refracted along the boundary between the two materials
When the angle of incidence < critical angle then:
the ray is refracted and exits the material
When the angle of incidence > critical angle then:
the ray undergoes total internal reflection
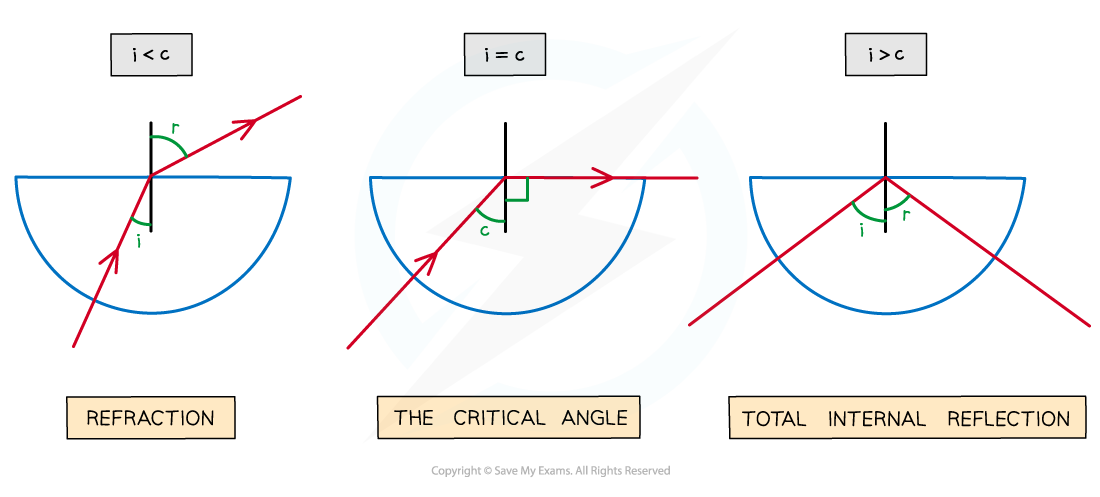
As the angle of incidence increases it will eventually exceed the critical angle and lead to the total internal reflection of the light
Critical Angle Equation
The critical angle of material 1 is found using the equation:
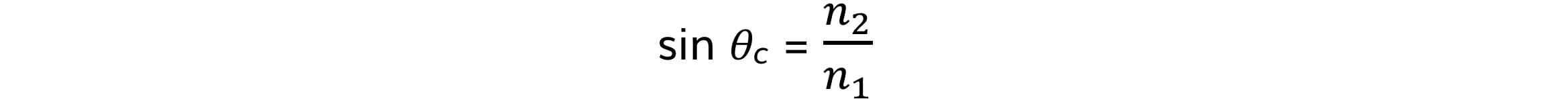
Where:
n1 = refractive index of material 1
n2 = refractive index of material 2
θc = critical angle of material 1
The formula finds the critical angle of the denominator of the fraction
The critical angle can also be calculated using the angles of incidence and refraction:
Total Internal Reflection
Total internal reflection is a special case of refraction that occurs when:
The angle of incidence within the denser medium is greater than the critical angle (I > θc)
The incident refractive index n1 is greater than the refractive index of the material at the boundary n2 (n1 > n2)
Total internal reflection follows the law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
A denser medium has a higher refractive index
For example, the refractive index of glass, ng > the refractive index of air, na
Light rays inside a material with a higher refractive index are more likely to be totally internally reflected
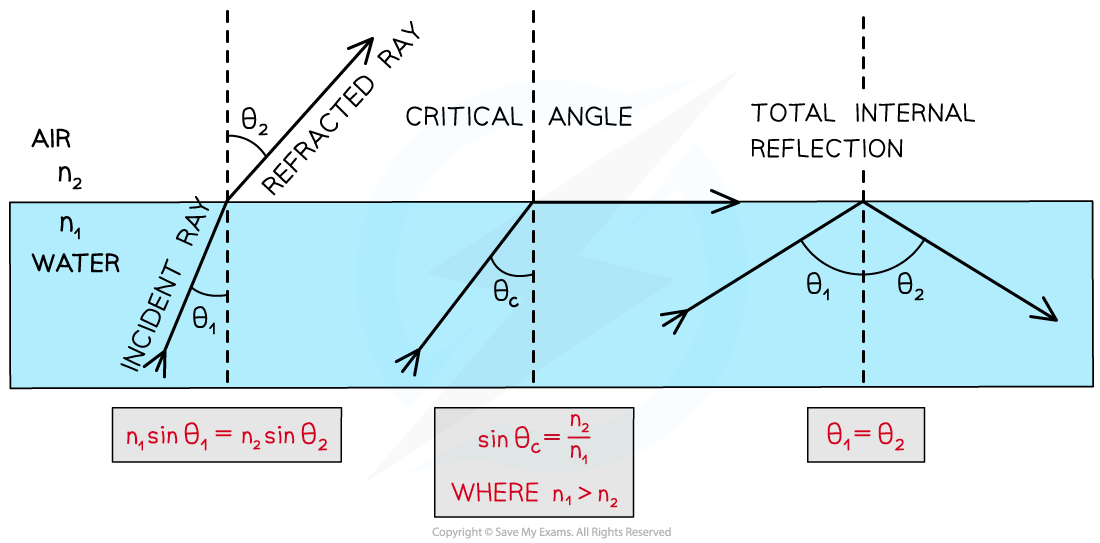
Angles of incidence, reflection and refraction to satisfy the conditions for total internal reflection
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at the vertical face of the cube. When the angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram, the light ray is totally internally reflected at X for the first time.
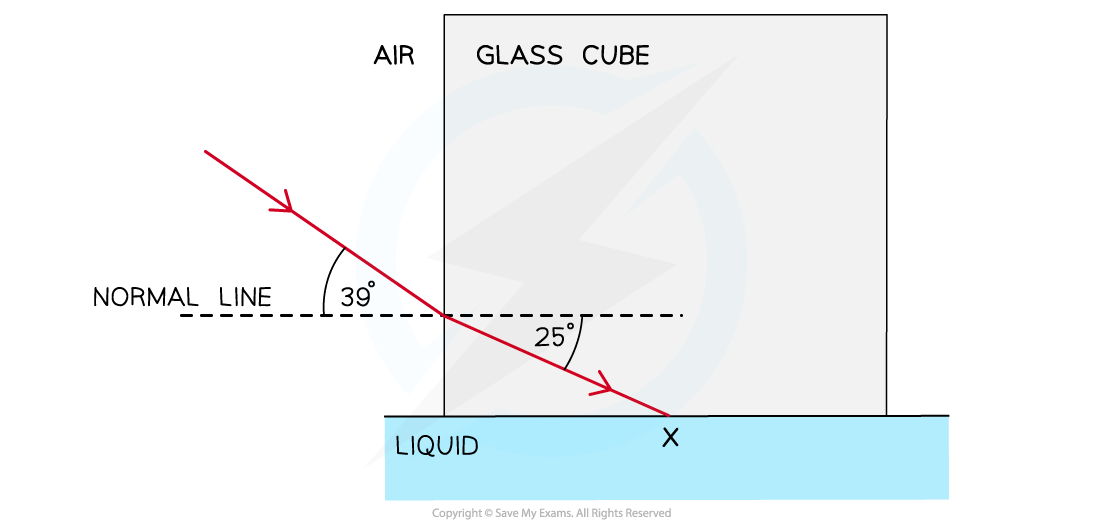
(i) Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond X to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.
(ii) The refractive index of the glass is 1.489.
Calculate the refractive index of the liquid.
Answer:
(i)
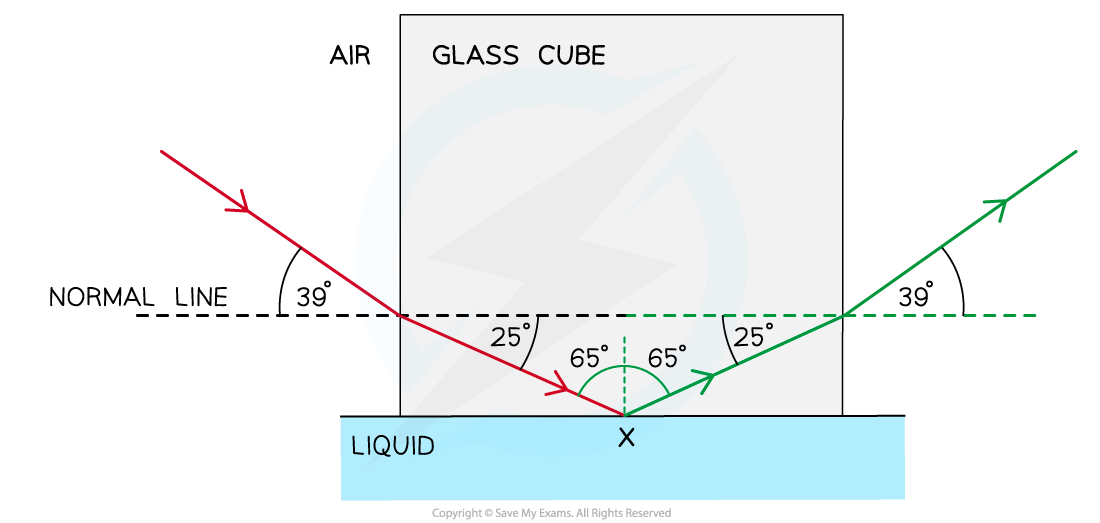
Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
Therefore, the angle of incidence (or reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts away from the normal when the ray leaves to air (as air is less dense)
Due to the reflection, the light rays are symmetrical on either side of the glass (39o)
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary
The question states the ray is “totally internally reflected for the first time” meaning that this is the smallest angle at which TIR occurs
Therefore, 65° is the critical angle
(ii) Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Refractive index of glass, n1 = 1.489
Refractive index of liquid = n2
Angle of incidence / critical angle, θ1 = θc = 65°
Angle of refraction, θ2 = 90°
Step 2: Write out Snell’s Law or the equation for critical angle
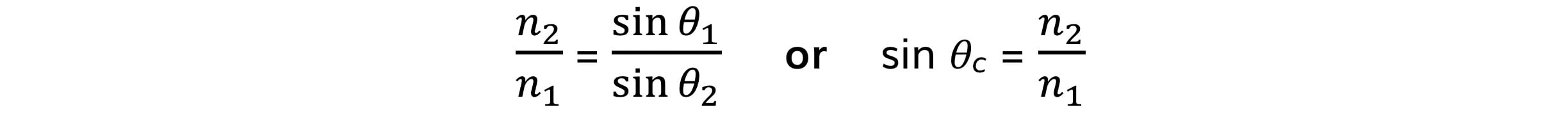
Step 3: Calculate the refractive index of the liquid


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?