Stationary Waves (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Stationary Waves
Standing waves are produced by the superposition of two waves of the same frequency and amplitude travelling in opposite directions
This is usually achieved by a travelling wave and its reflection
The superposition produces a wave pattern where the peaks and troughs do not move
Stationary waves store energy, unlike progressive waves which transfer energy
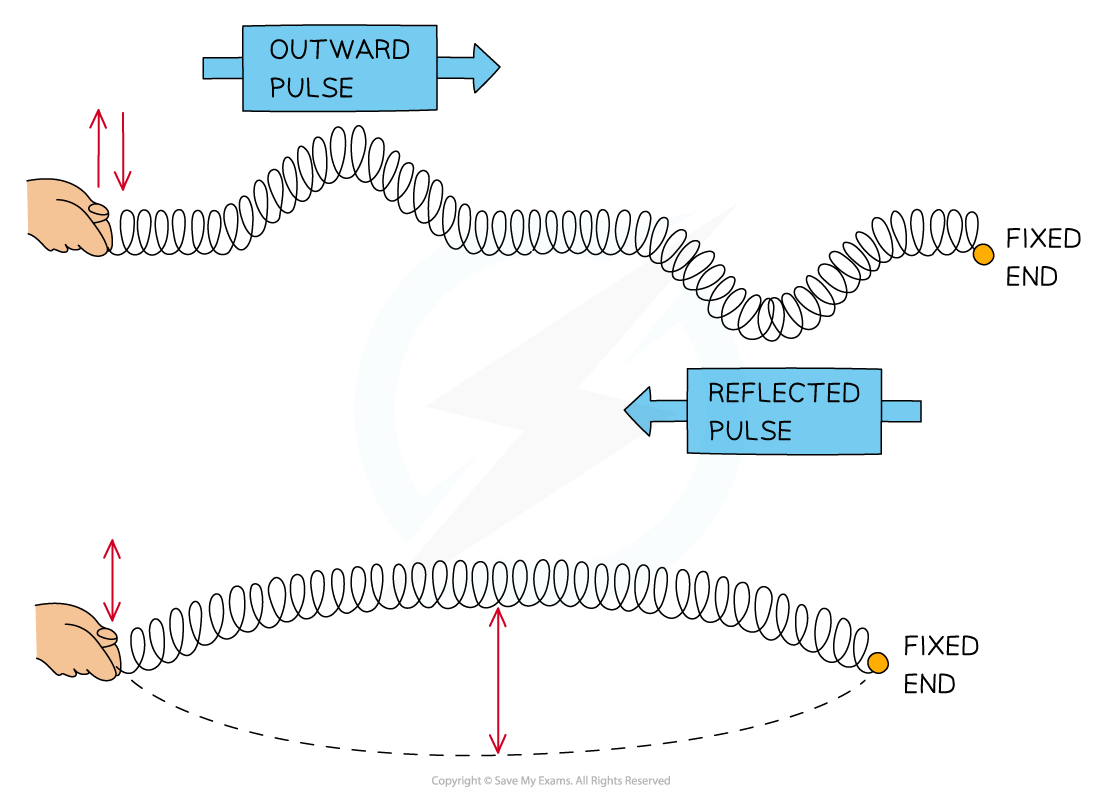
Formation of a stationary wave on a stretched spring fixed at one end
Comparing Progressive & Stationary Waves

Nodes & Antinodes
A stationary wave is made up nodes and antinodes
Nodes are regions where there is no vibration
Antinodes are regions where the vibrations are at their maximum amplitude
The nodes and antinodes do not move along the string
Nodes are fixed and antinodes only move in the vertical direction
The phase difference between two points on a stationary wave are either in phase or out of phase
Points between nodes are in phase with each other
Points that have an odd number of nodes between them are out of phase
Points that have an even number of nodes between them are in phase
The image below shows the nodes and antinodes on a snapshot of a stationary wave at a point in time
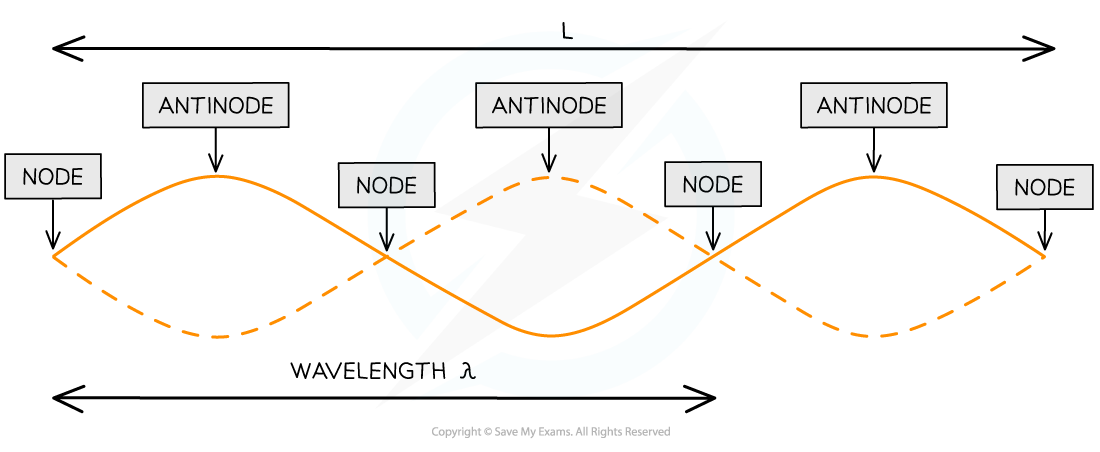
Where:
L is the length of the string
One wavelength λ is only a portion of the length of the string
Worked Example
A stretched string is used to demonstrate a stationary wave, as shown in the diagram.

Which row in the table correctly describes the length of L and the name of X and Y?
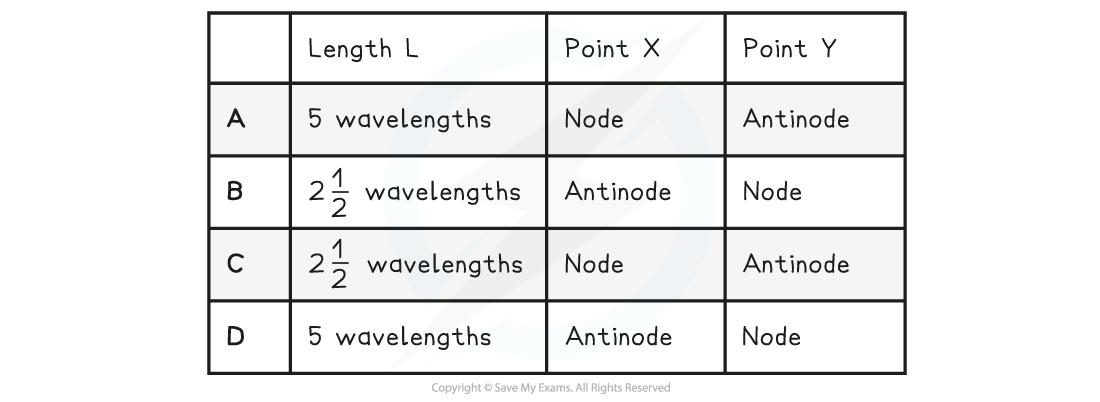
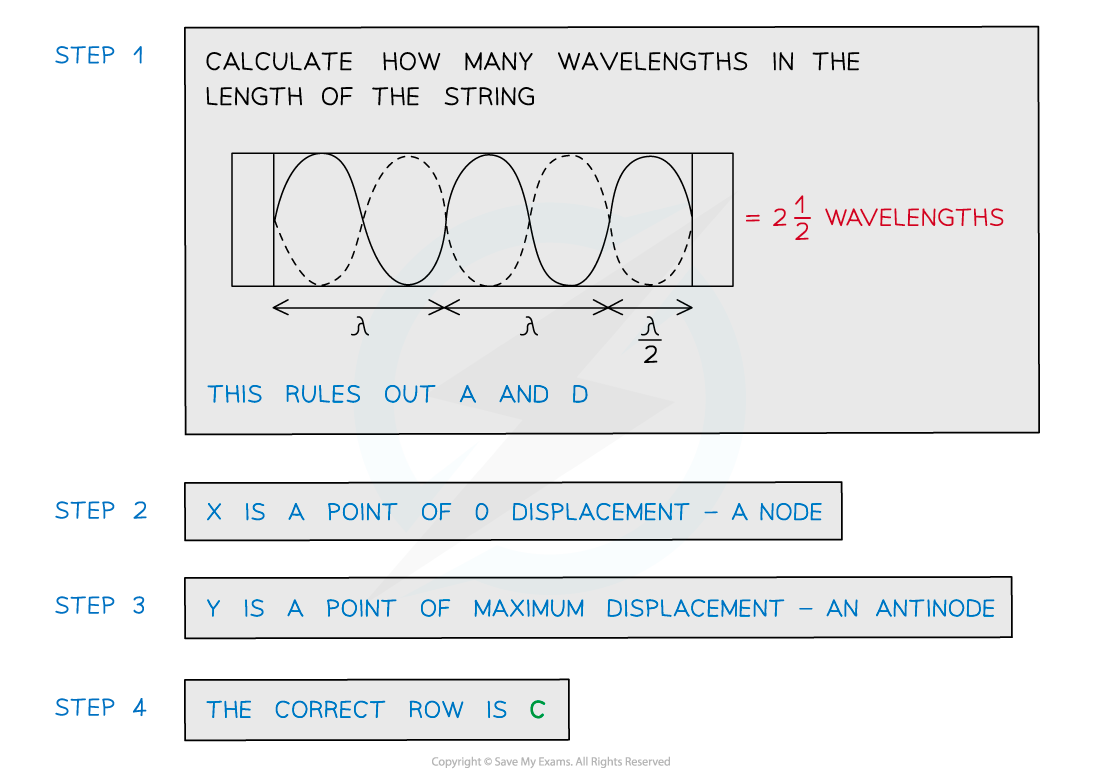
Answer: C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you learn the definitions of node and antinode:
Node = A point of no vibration
Antinode = A point of maximum amplitude
In exam questions, the lengths of the strings will only be in whole or half wavelengths. For example, a wavelength could be made up of 3 nodes and 2 antinodes or 2 nodes and 3 antinodes.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
