Longitudinal & Transverse Waves (AQA A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Defining Transverse & Longitudinal Waves
In mechanical waves, particles oscillate about fixed points
There are two types of waves:
Transverse waves
Longitudinal waves
Each type of wave can be distinguished by its direction of vibration relative to its direction of travel
Transverse Waves
A transverse wave is defined as:
A wave in which the particles oscillate perpendicular to the direction of the wave travel (and energy transfer)
Transverse waves show areas of crests (peaks) and troughs

Diagram of a transverse wave
Examples of transverse waves are:
Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV
Vibrations on a guitar string
Transverse waves can be shown on a rope
Transverse waves can be polarised
Longitudinal Waves
A longitudinal wave is defined as:
A wave in which the particles oscillate parallel to the direction of the wave travel (and energy transfer)
Longitudinal waves show areas of compressions and rarefactions
Compressions are regions of increased pressure
Rarefactions are regions of decreased pressure

Diagram of a longitudinal wave
Examples of longitudinal waves are:
Sound waves
Ultrasound waves
Longitudinal waves can be shown on a slinky spring
Longitudinal waves cannot be polarised
Energy is transmitted through the wave
The particles in the medium vibrate as they are given energy
The compressions cause the nearby particles to also vibrate with more energy
This produces a compression further along in the medium

A wavelength on a longitudinal wave is the distance between two compressions or two rarefactions
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The definitions of transverse and longitudinal waves are often asked as exam questions so ensure you have them memorised!
Examples of Transverse Waves & Longitudinal Waves
Energy is transferred through moving oscillations or vibrations
This can be demonstrated visually using ropes or springs
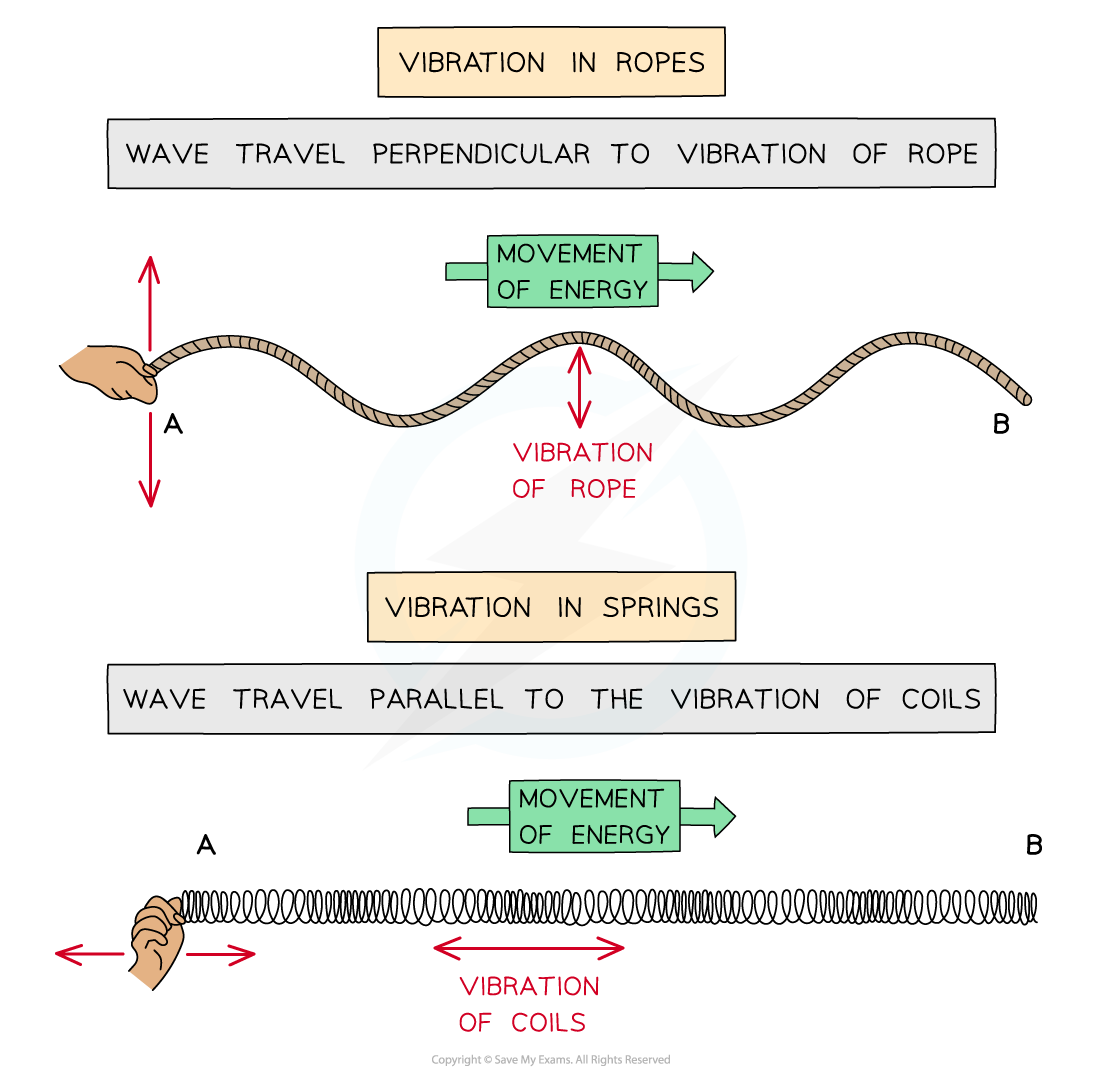
Waves can be shown through vibrations in ropes or springs
The oscillations, or vibrations, can be perpendicular or parallel to the direction of wave travel:
Waves which oscillate in a perpendicular direction are transverse waves
Waves which oscillate in a parallel direction are longitudinal waves
Examples of transverse waves are:
Electromagnetic waves e.g. radio, visible light, UV
Vibrations on a guitar string
Waves on a string
Seismic (S) waves
Examples of longitudinal waves are:
Sound waves
Ultrasound waves
Waves through a slinky coil
Seismic (P) waves

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
