Progressive Waves (AQA A Level Physics) : Revision Note
Properties of Oscillations
A progressive wave is defined as:
A wave that transfers energy from one point to another without transferring the medium itself
Properties of a Progressive Wave
Displacement (x) of a wave is the distance of a point on the wave from its equilibrium position
It is a vector quantity; it can be positive or negative
Amplitude (A) is the maximum displacement of a particle in the wave from its equilibrium position
Wavelength (λ) is the distance between points on successive oscillations of the wave that are in phase
These are all measured in metres (m)
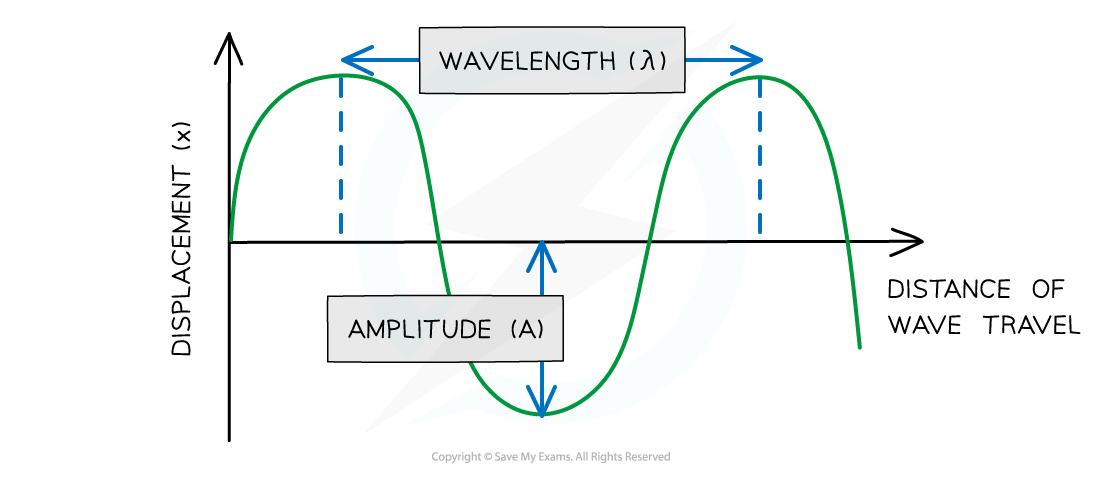
Diagram showing the amplitude and wavelength of a wave
Period (T) or time period, is the time taken for one complete oscillation or cycle of the wave
Measured in seconds (s)
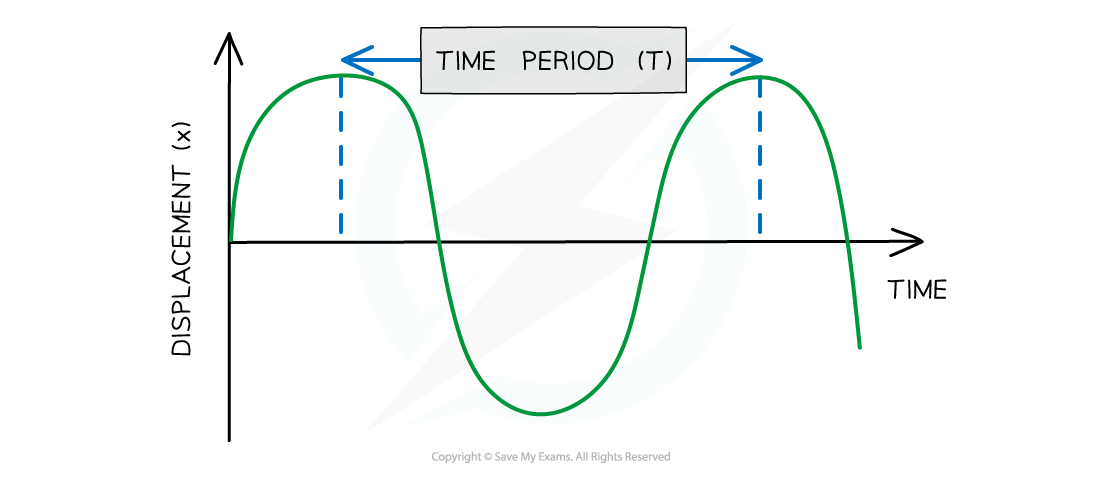
Diagram showing the time period of a wave
Frequency (f) is the number of complete oscillations per unit time. Measured in Hertz (Hz) or s-1

Frequency-period equation
Speed (v) is the distance travelled by the wave per unit time
Measured in metres per second (m s-1)
The wave equation links the speed, frequency and wavelength of a wave
This is relevant for both transverse and longitudinal waves

The Wave Equation
The wave equation shows that for a wave of constant speed:
As the wavelength increases, the frequency decreases
As the wavelength decreases, the frequency increases
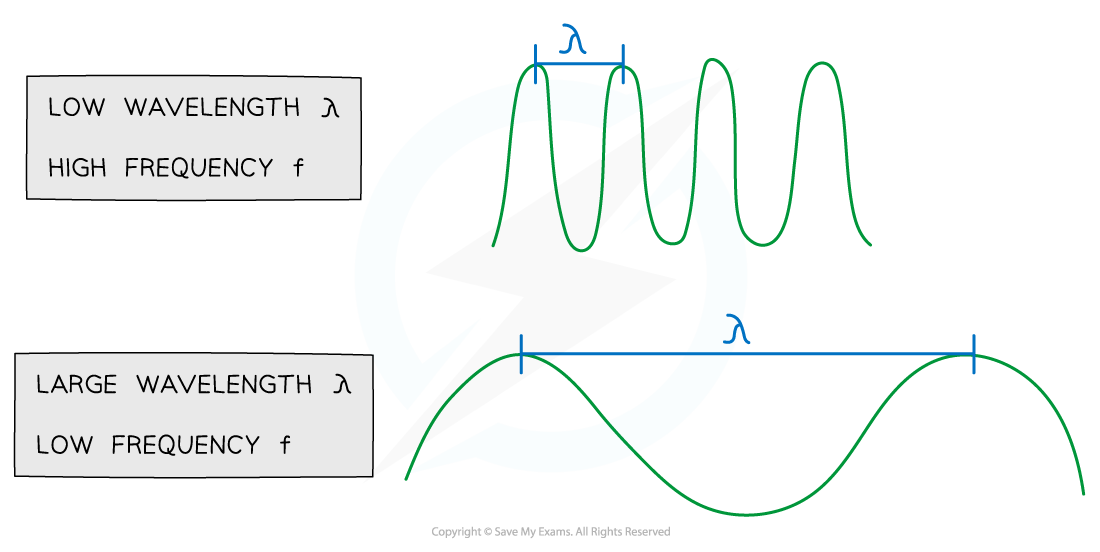
The relationship between frequency and wavelength of a wave
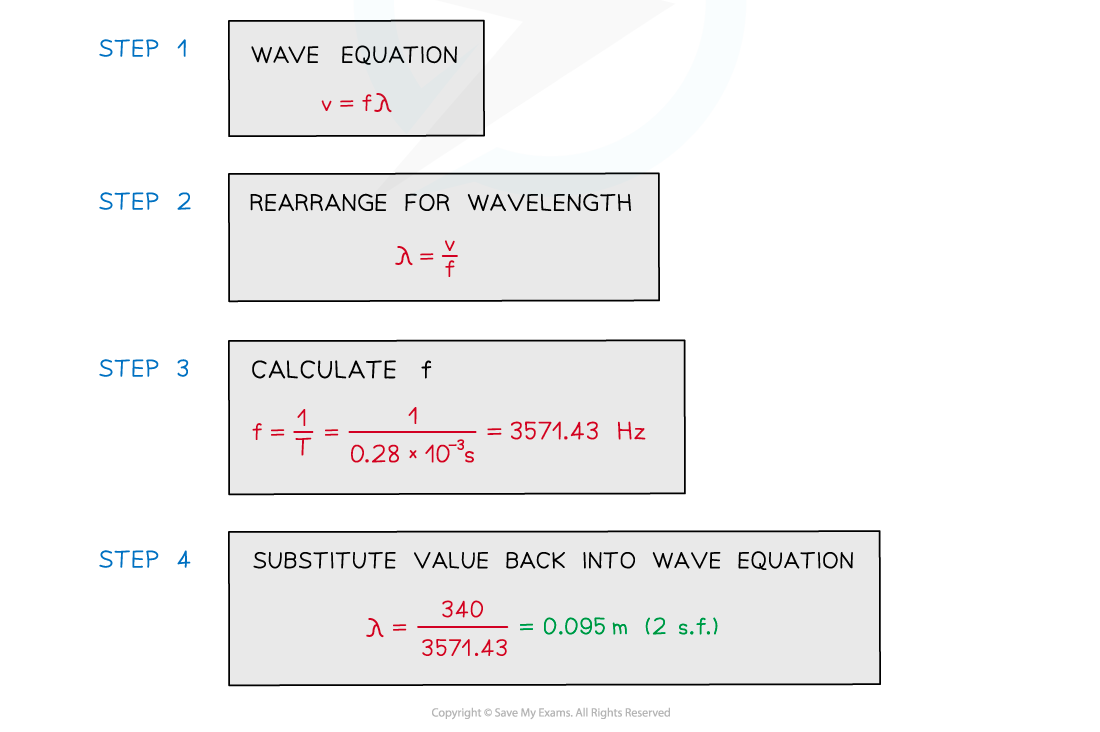
Worked Example
The wave in the diagram below has a speed of 340 m s–1.
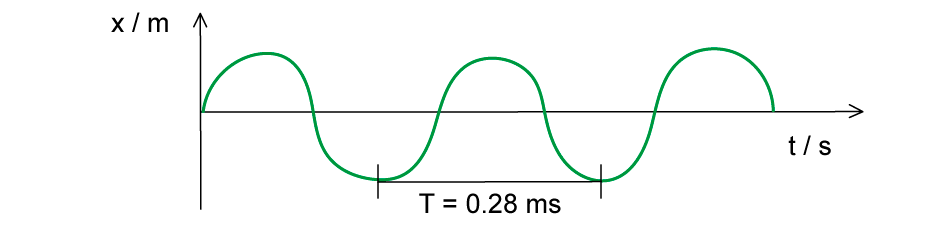
What is the wavelength of the wave?
Answer:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may also see the wave equation be written as c = fλ where c is the wave speed. However, c is often used to represent a specific speed ー the speed of light (3 × 108 m s–1). Only electromagnetic waves travel at this speed, therefore it’s best practice to use v for any speed that isn’t the speed of light instead.
Phase Difference
The phase difference between two waves is a measure of how much a point or a wave is in front or behind another
This can be found from the relative positive of the crests or troughs of two different waves of the same frequency
When the crests or troughs are aligned, the waves are in phase
When the crest of one wave aligns with the trough of another, they are in antiphase
The diagram below shows two waves with the same wavelength and frequency, but they are not in phase
The green wave reaches the same point in the cycle (e.g. a peak) earlier than the purple wave — it is shifted to the left
This means the green wave leads the purple wave by ¼ λ
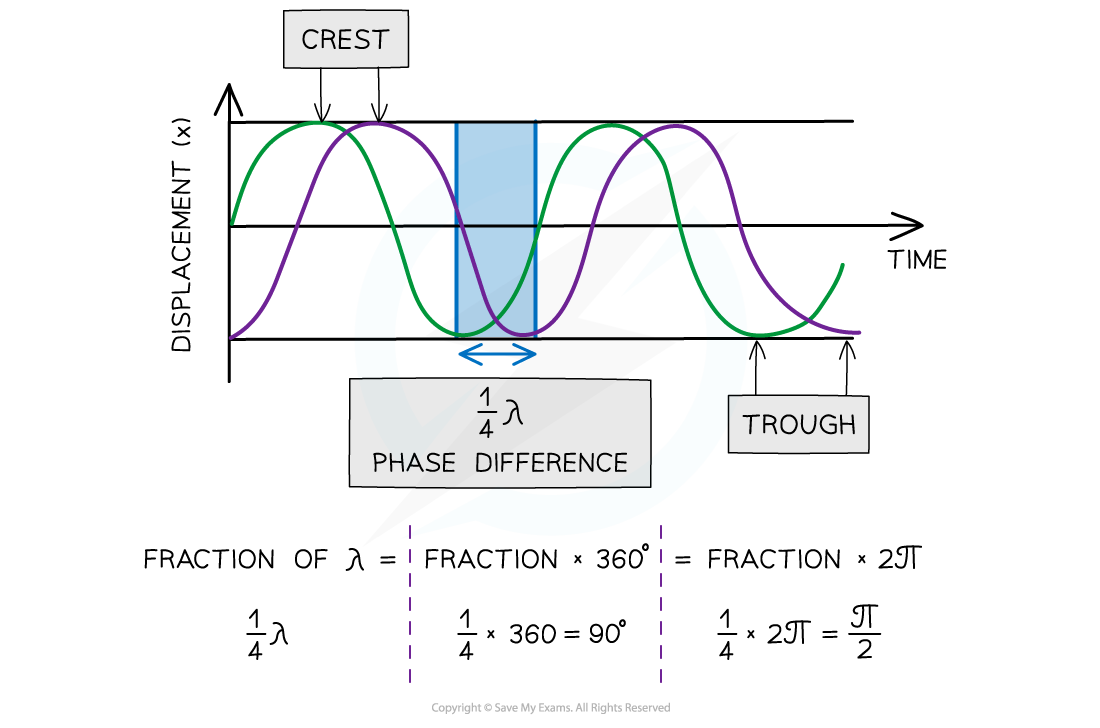
Two waves ¼ λ out of phase
In contrast, the purple wave is said to lag behind the green wave by ¼ λ
Phase difference is measured in fractions of a wavelength, degrees or radians
The phase difference can be calculated from two different points on the same wave or the same point on two different waves
The phase difference between two points can be described as:
In phase is 360o or 2π radians
In anti-phase is 180o or π radians
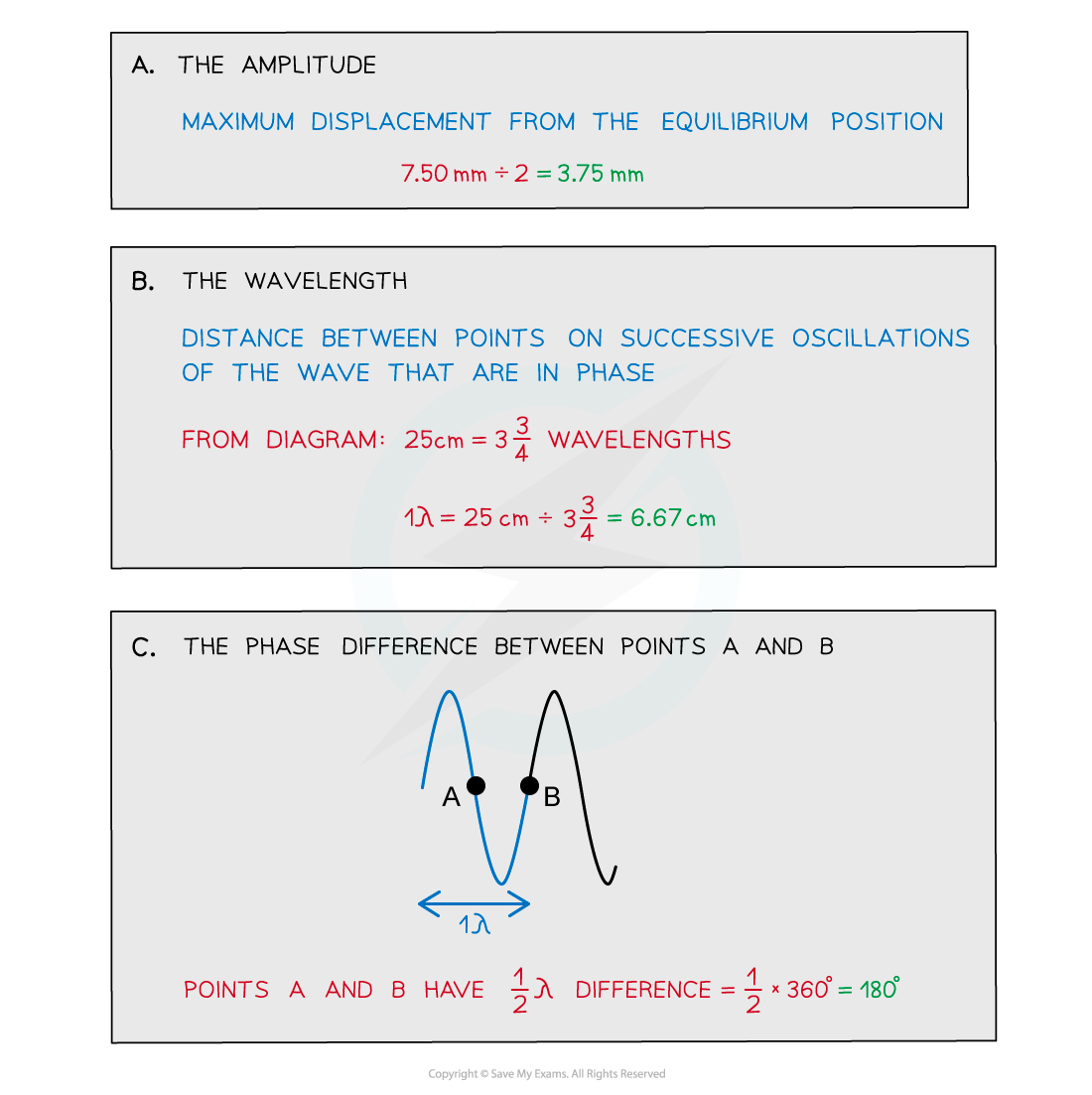
Worked Example
Plane waves on the surface of water at a particular instant are represented by the diagram below.

The waves have a frequency of 2.5 Hz. Determine:
a) The amplitude
b) The wavelength
c) The phase difference between points A and B
Answer:
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When labelling the wavelength and time period on a diagram:
Make sure that your arrows go from the very top of a wave to the very top of the next one
If your arrow is too short, you will lose marks
The same goes for labelling amplitude, don’t draw an arrow from the bottom to the top of the wave, this will lose you marks too.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
