Nucleon & Proton Number (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
AZX Notation
A nucleus can be described using
notation
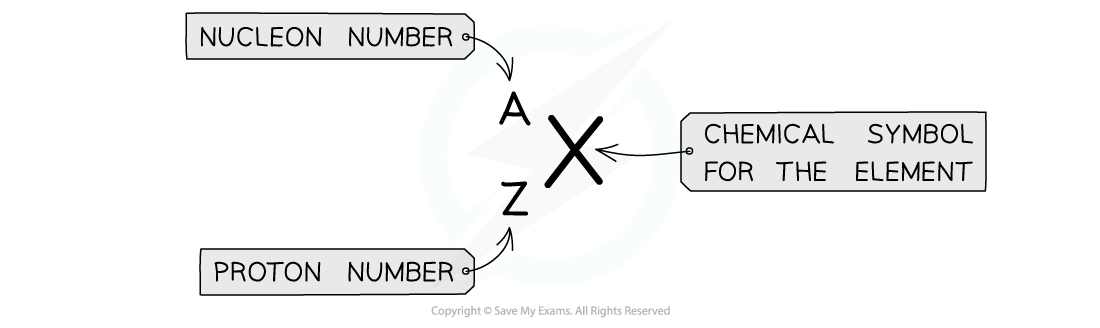
notation is used to describe the constituents of a nucleus
The top number A represents the nucleon number or the mass number
Nucleon number (A) = total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus
The lower number Z represents the proton or atomic number
Proton number (Z) = total number of protons in the nucleus
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In Chemistry, you may see nucleon number referred to as mass number and proton number as atomic number. Both of these are valid, just make sure you don't mistake mass number for atomic number, or vice versa.
Make sure you know that the periodic table is ordered by atomic number
Isotopes
Elements are defined by a fixed number of protons in their atoms
For example, all hydrogen atoms have 1 proton, and all carbon atoms have 6 protons
However, atoms of an element can have different numbers of neutrons
These different versions of elements are called isotopes
An isotope is defined as:
Nuclei that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
For example, hydrogen has two isotopes, deuterium and tritium
All three isotopes contain 1 proton, but different numbers of neutrons
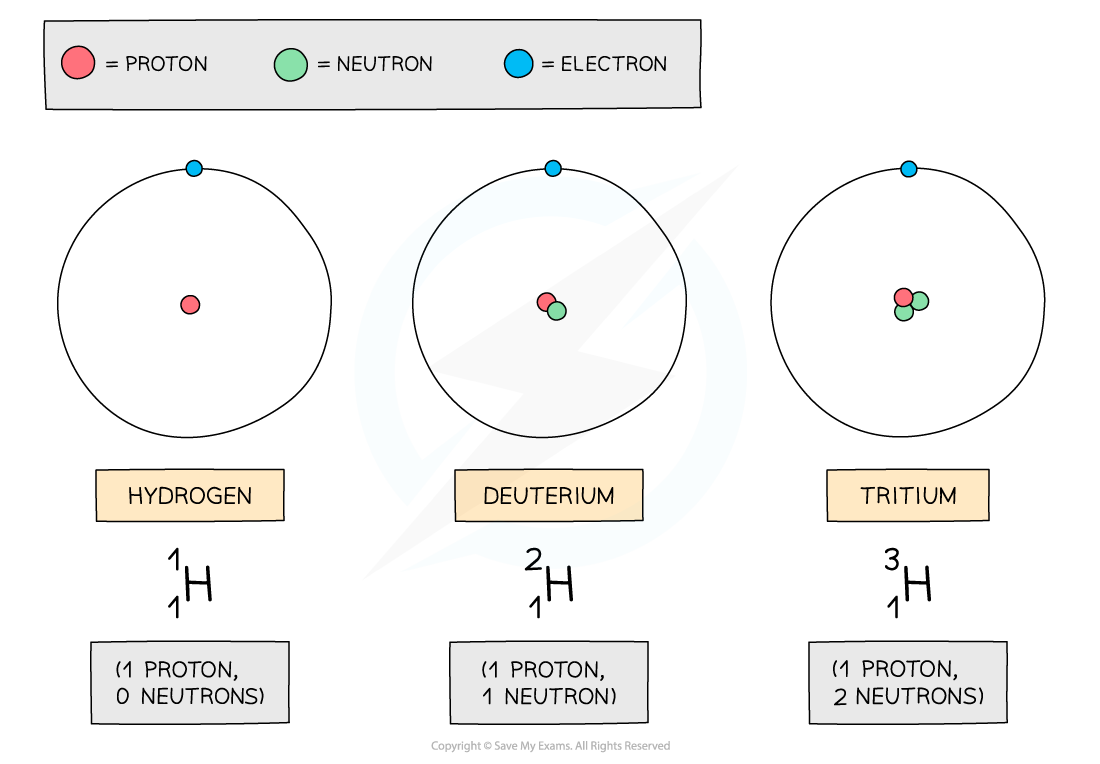
The three atoms shown above are all forms of hydrogen, but they each have different numbers of neutrons
Since nucleon number A includes the number of protons and neutrons, an isotope of an element will have
A fixed proton number, Z
A different nucleon number, A
Some isotopes have an imbalance of neutrons and protons which makes them unstable
This means they constantly decay and emit radiation to achieve a more stable form
This can happen from anywhere between a few nanoseconds to 100,000 years
Isotopic Data
Isotopic data is defined as:
The relative amounts of different isotopes of an element present within a substance
The mass of an element is often given as relative atomic mass
The relative atomic mass of an element can be calculated using the relative abundance values
The percentage abundance of different isotopes in a sample can be obtained using a mass spectrometer
Table of isotopic data for a sample of oxygen
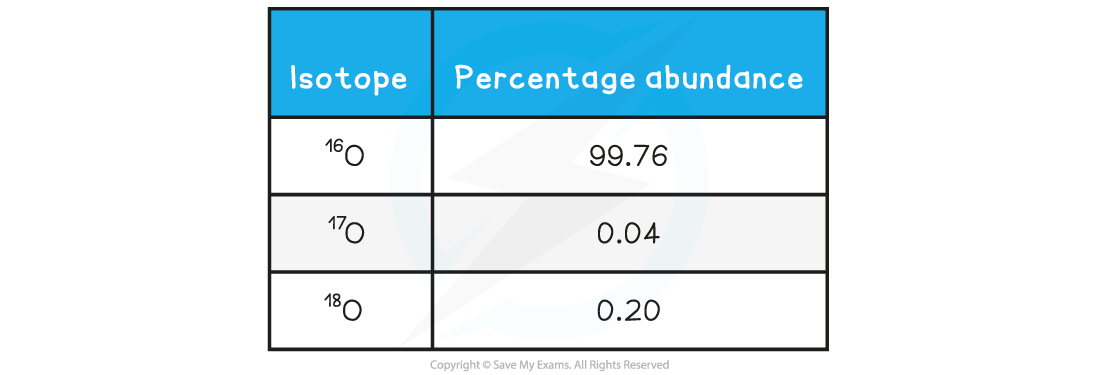
For example, a sample of oxygen may contain three isotopes:
,
and
The relative atomic mass of this sample of oxygen can be calculated using:
(16 × 0.9976) + (17 × 0.0004) + (18 × 0.002) = 16.0044
To two decimal places, the relative atomic mass of the sample of oxygen is 16.00
A common use of isotopic data is carbon dating of archaeological artefacts
This involves using the ratio of the amount of stable isotope carbon-12, to the amount of unstable isotope, carbon-14
The age of a sample of dead tissue can be determined by comparing the ratio of these isotopes to the ratio in a sample of living tissue
Worked Example
One of the rows in the table shows a pair of nuclei that are isotopes of one another.

Which row is correct?
Answer: B
Step 1: Properties of isotopes
Isotopes are nuclei with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
The nucleon number is the sum of the protons and neutron
Therefore, an isotope has a different nucleon number too
Step 2: Calculate protons in the first nucleus
Nucleon number: 37
Neutrons: 20
Protons = 37 − 20 = 17
Step 3: Calculate protons in the second nucleus
Nucleon number: 35
Neutrons: 18
Protons = 35 − 18 = 17
Step 4: Conclusion
Therefore, they have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons and are isotopes of each other
The correct answer is therefore option B

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?