The Second Law of Thermodynamics (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Second Law of Thermodynamics
A heat engine is a system that converts heat to usable energy which is then used to do mechanical work
The second law of thermodynamics states that:
A heat engine requires a source and a sink to operate
A source is a high-temperature reservoir
It has a high temperature TH and the heat energy from it is QH
A sink is a low-temperature reservoir
It has a low temperature TC and the heat energy going into it is QC
Other ways of stating the second law are:
Thermal energy cannot spontaneously transfer from a region of lower temperature to a region of higher temperature
OR
When extracting energy from a heat reservoir, it is impossible to convert it all into work
If the engine reached the temperature of the source, no heat would flow as they would have reached thermal equilibrium
Therefore, no work would be done
This means it is impossible for a heat engine to work solely on the First Law of Thermodynamics
If a heat engine only obeyed the First Law (there is no friction), the source-sink diagram would look like:
Source-Sink Diagrams

Source-sink diagram that obeys only the First Law of Thermodynamics
It is assumed that TH remains at a constant temperature
This engine is 100% efficient however, it is not possible to make this type of engine, due to frictional losses in real life
Therefore, all engines obey the Second Law of Thermodynamics, and a source-sink diagram for an actual heat engine is
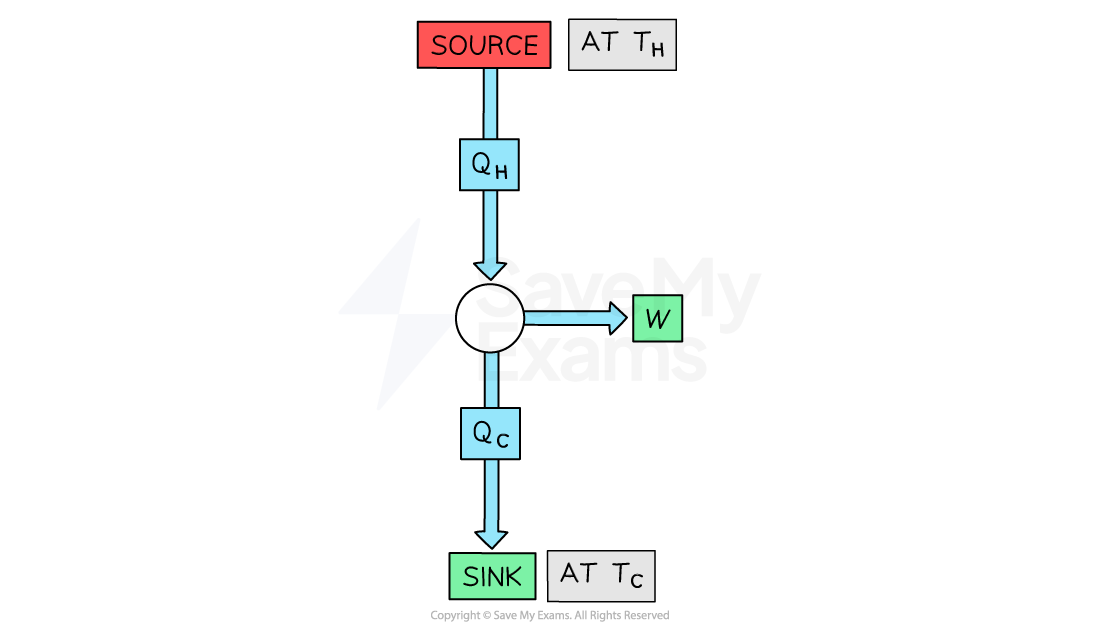
Actual source-sink diagram for a heat engine that obeys the First and Second Law of Thermodynamics
Heat energy (QH) is transferred from the source at temperature TH
Some of this energy is transferred into work, W
The remaining energy (QC), is transferred to the sink at temperature TC
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that heat can only flow from a hot place to cold. Therefore, if you're sketching source-sink diagrams, take care with the arrows and make sure you have all the components included (especially the work done, otherwise, the engine wouldn't work!).
Take care of your terminology:
Heat engines convert thermal energy into mechanical work (as above)
Heat pumps transfer heat energy from low temperature to high temperature (this is explored later)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
