Fibre Optics & Endoscopy (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
Written by: Dan Mitchell-Garnett
Updated on
Fibre Optics in Medicine
What does 'Fibre Optics' Mean?
Fibre optics refers to the use of light travelling along a flexible fibre to produce an image
This is particularly useful in medicine, as it allows medics to view internal structures with the flexible fibre, without the need for surgery
What is an Endoscope?
The piece of equipment used to do this is called an endoscope
Endoscopes contain bundles of optical fibres along which light is transmitted to an eyepiece
An optical fibre is a flexible fibre, or core, along which light is transmitted
The core is surrounded by cladding
This protects the core - light escapes if it is unclean or if it makes contact with neighbouring fibres
It also has a slightly lower refractive index than the core, allowing light in the core to be totally internally reflected
Cross-section of an optical fibre

Light passing through the core is internally reflected with a large critical angle, θc
The core's refractive index is slightly higher than the cladding's refractive index
This makes the critical angle large
A large critical angle means that only light entering the fibre at shallow angles to the axis will be totally internally reflected
These shallow-angle rays travel in straighter paths and undergo fewer reflections
Therefore, the light transmitted by the fibre experiences very little loss of information, as some energy is absorbed at each reflection
Light entering at steep angles does not meet the condition for TIR and instead escapes into the cladding
Worked Example
The core of an endoscope has a refractive index of 1.46. The critical angle is 80°.
Calculate the refractive index of the cladding.
Answer:
Step 1: Recall Snell's Law for the critical angle:
Step 2: Rearrange this for the index of the cladding, n2 :
Step 3: Insert the core's refractive index and the critical angle:
Operation of the Endoscope
Optical fibres are utilised in medicine in order to see within the human body
The piece of equipment using these optical fibres is called an endoscope
In an endoscope, fibre optics can be bundled together as
Coherent bundles
Incoherent bundles
Coherent Bundles
A coherent bundle of optical fibres is:
A bundle of optical fibres with fixed positions relative to each other at each end and along its length
This type of bundle is used for transmitting an image to the viewer of the endoscope
The optical fibres are grouped together in a regular pattern
Each fibre is in a fixed position relative to its neighbours
Each fibre receives and transmits a portion of the image to the endoscope's eyepiece
Collectively, the fibres make the whole image
The fibres in a coherent bundle have a diameter of ~10 μm
This is small, for a high resolution
Any smaller than this, however, and diffraction affects the image quality
Incoherent Bundles
An incoherent bundle of optical fibres is:
A bundle of optical fibres grouped together in a random arrangement
This type of bundle is used to transmit light from a source to the endoscope's target
The optical fibres do not keep their position relative to their neighbours in the bundle
No image needs to be transmitted, this bundle only transmits light to illuminate the target tissue
The light reflected by the tissue is transmitted by the coherent bundle to produce an image
Optical fibres in this bundle have a diameter range of 50 - 100 μm
These bundles are cheaper to produce than coherent bundles
Cross-Sections of Coherent and Incoherent Bundles

Fibres in a coherent bundle are regularly spaced. The diameters and spacing of fibres in an incoherent bundle are less crucial, as their role is illumination rather than transmitting a clear image.
Features of an Endoscope
An endoscope features a long flexible shaft connected to an eyepiece
Within this shaft is contained:
An aperture (hole along the length of the endoscope) through which to operate medical instruments
A channel for air or water
An incoherent bundle for illumination
A coherent bundle for transmitting an image
Uses of an Endoscope
Endoscopes can be used simply for viewing an internal system, e.g. looking for a tumour in the digestive system
They can also be used to perform small medical procedures, using tools through the aperture e.g. taking tissue samples for further study
Some examples of procedures using an endoscope:
Gastroscopy (examining the upper digestive system, see the diagram below)
Colonoscopy (examining the lower digestive system)
Arthroscopy (examining joints for issues such as arthritis, through a small incision)
Basic Structure and Use of an Endoscope
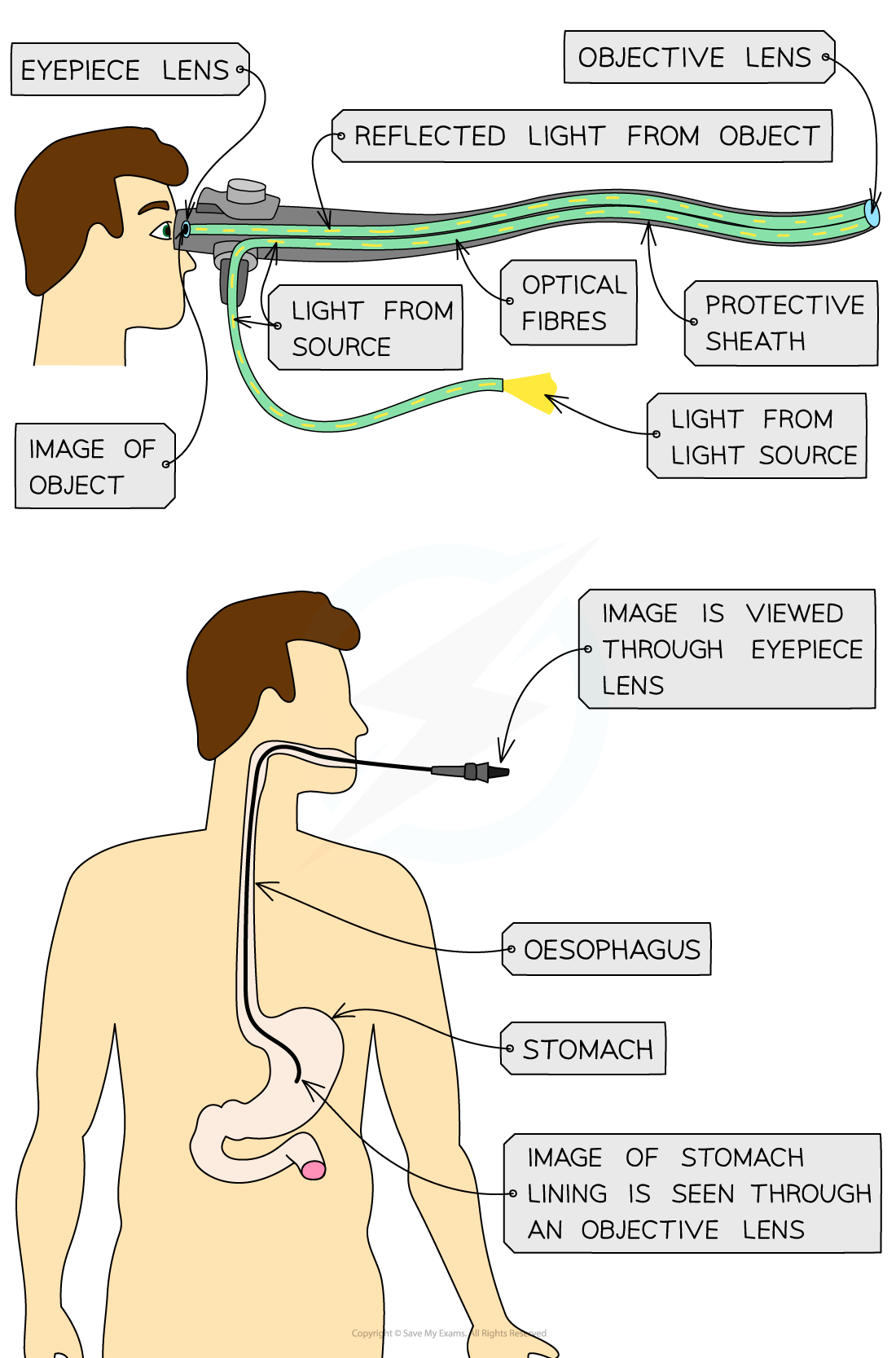
The structure of an endoscope allows internal organs to be viewed or sampled. The lower image shows a gastroscopy, in which the upper digestive system can be viewed.
Endoscopy is commonly used instead of surgery because:
Endoscopy is less painful than surgery
There is a lower infection risk than surgery
The recovery time is faster than that of surgery
Of course, endoscopy is limited to small procedures and certain systems - sometimes surgery, magnetic resonance scans or other forms of imaging are more appropriate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When studying this topic, make sure you are building on a strong foundation of knowledge about total internal reflection. You may have to refer to this to form part of your descriptions and explanations of endoscopy in your exam. For example, an endoscope can only bend a certain amount before light can no longer undergo total internal reflection in the core, because it doesn't strike the interface at (or above) the critical angle.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
