Inverse Trigonometric Functions (OCR A Level Maths A): Revision Note
Exam code: H240
Did this video help you?
Inverse trigonometric functions
What are the inverse trigonometric functions?
These functions are the inverse functions of sin, cos and tan
sin (arcsin x) = x
cos (arccos x) = x
tan (arctan x) = x
The domains of sin, cos, and tan must first be restricted to make them one-to-one functions (only one-to-one functions have inverses)
What are the restricted domains?
domain of sin x is restricted to -π/2 ≤ x ≤ π/2 (-90° ≤ x ≤ 90°)

domain of cos x is restricted to 0 ≤ x ≤ π (0° ≤ x ≤ 180°)

domain of tan x is restricted to -π/2 < x < π/2 (-90° < x < 90°)

How do I sketch the graph of y = arcsin x?
The graph of y = arcsin x looks like this:
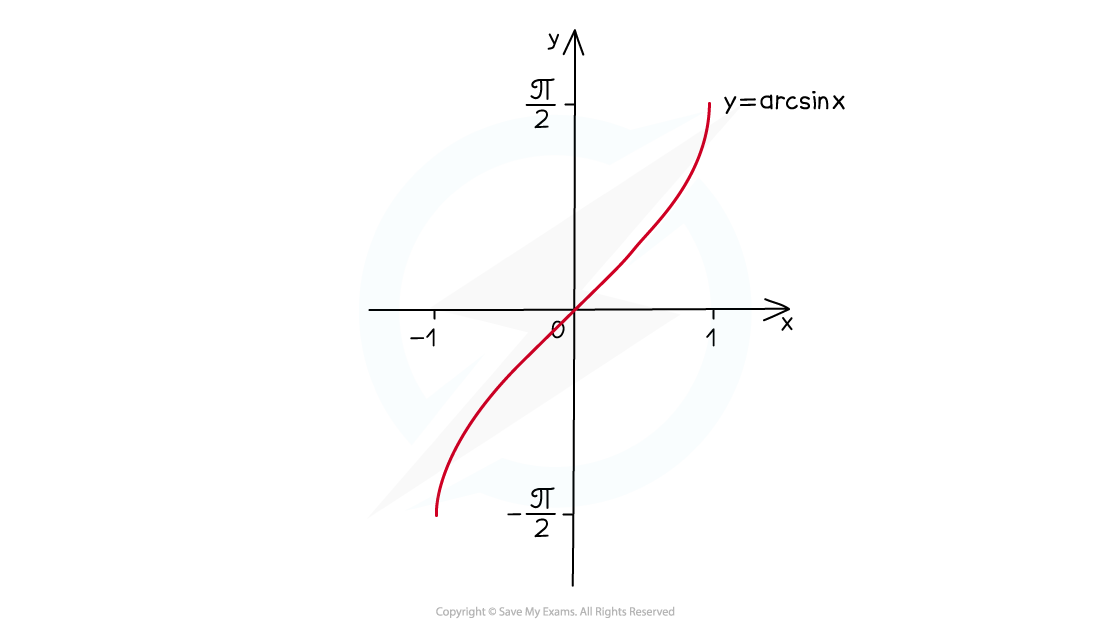
the domain is -1 ≤ x ≤ 1
the range is -π/2 ≤ arcsin x≤ π/2 (-90° ≤ arcsin x ≤ 90°)
How do I sketch the graph of y = arccos x?
The graph of y = arccos x looks like this:
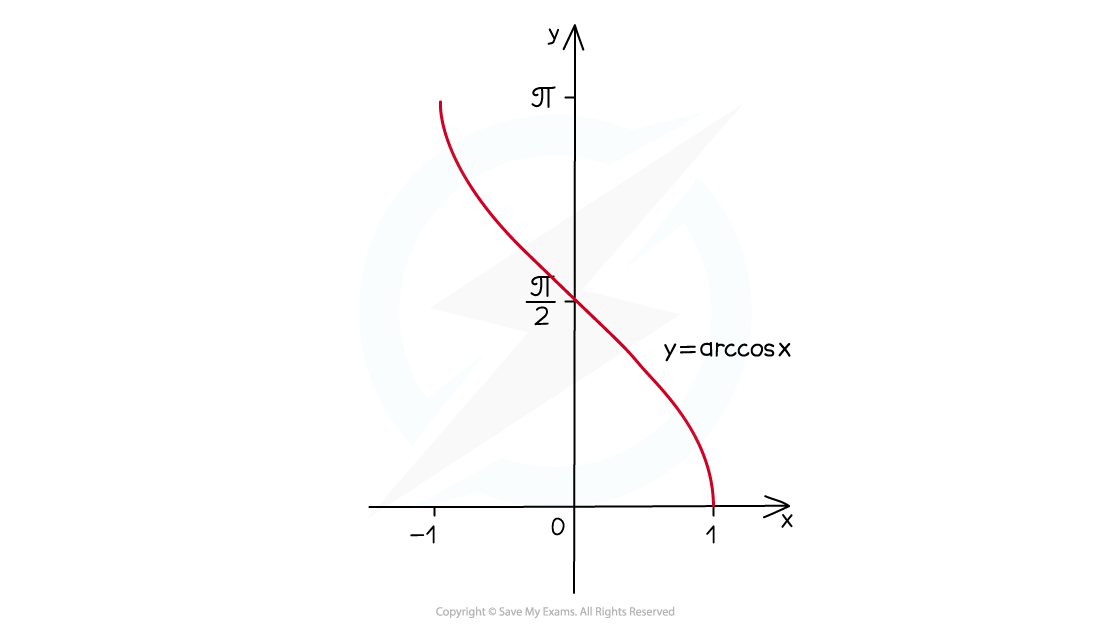
the domain is -1 ≤ x ≤ 1
the range is 0 ≤ arccos x ≤ π (0° ≤ arccos x ≤ 180°)
How do I sketch the graph of y = arctan x?
The graph of y = arctan x looks like this:
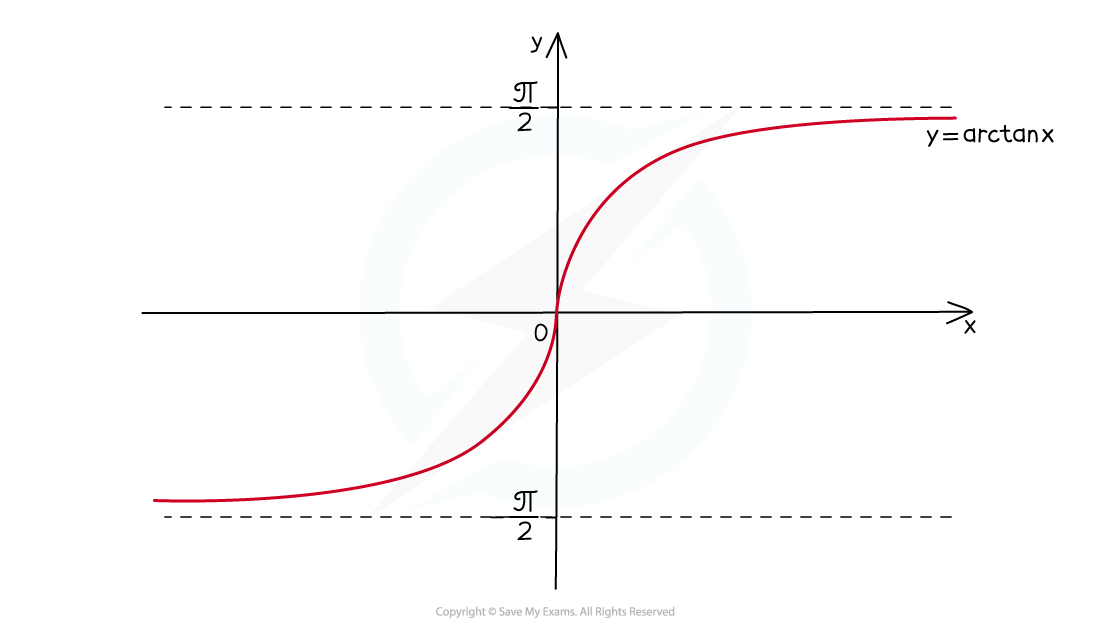
the domain is x ∈ ℝ (ie arctan x is defined for all real number values of x)
the range is -π/2 < arctan x < π/2 (-90° < arctan x < 90°)
horizontal asymptotes at y= - π/2 and y = -π/2
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you know the shapes of the graphs for sin, cos and tan.
As inverses, the graphs of arcsin, arccos and arctan are reflections of sin, cos and tan in the line y = x.
The values returned by the sin-1, cos-1 and tan-1 keys on your calculator are the values from the ranges of arcsin, arccos and arctan.
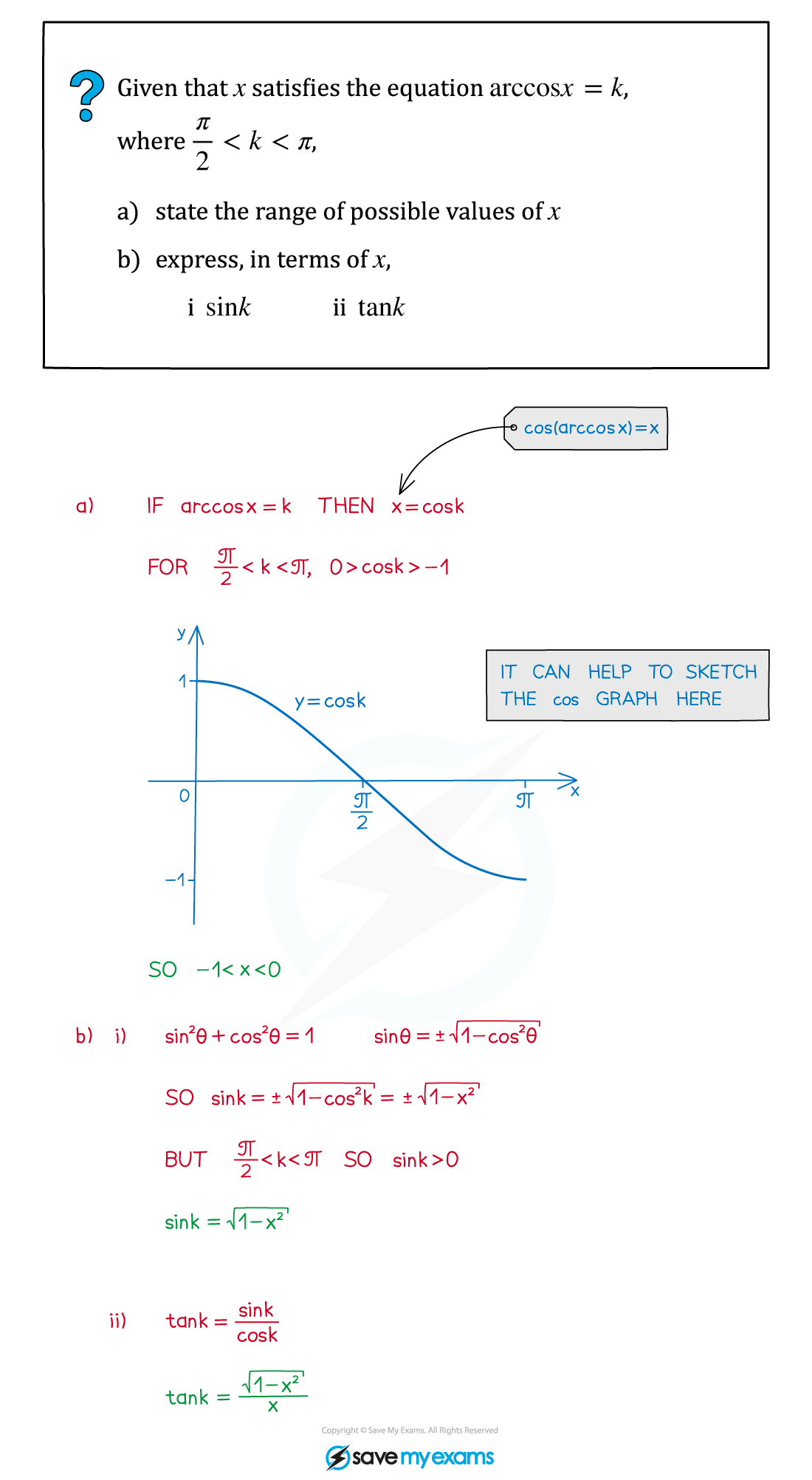
Worked Example

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?