Coefficient of Friction & F = ma (AQA A Level Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Coefficient of Friction - F = ma
How do we apply Newton’s Second Law (F = ma) in problems involving friction?
The coefficient of friction combined with F = ma allows you to determine an object's motion where friction is involved in a problem
For problems where the surface is horizontal:
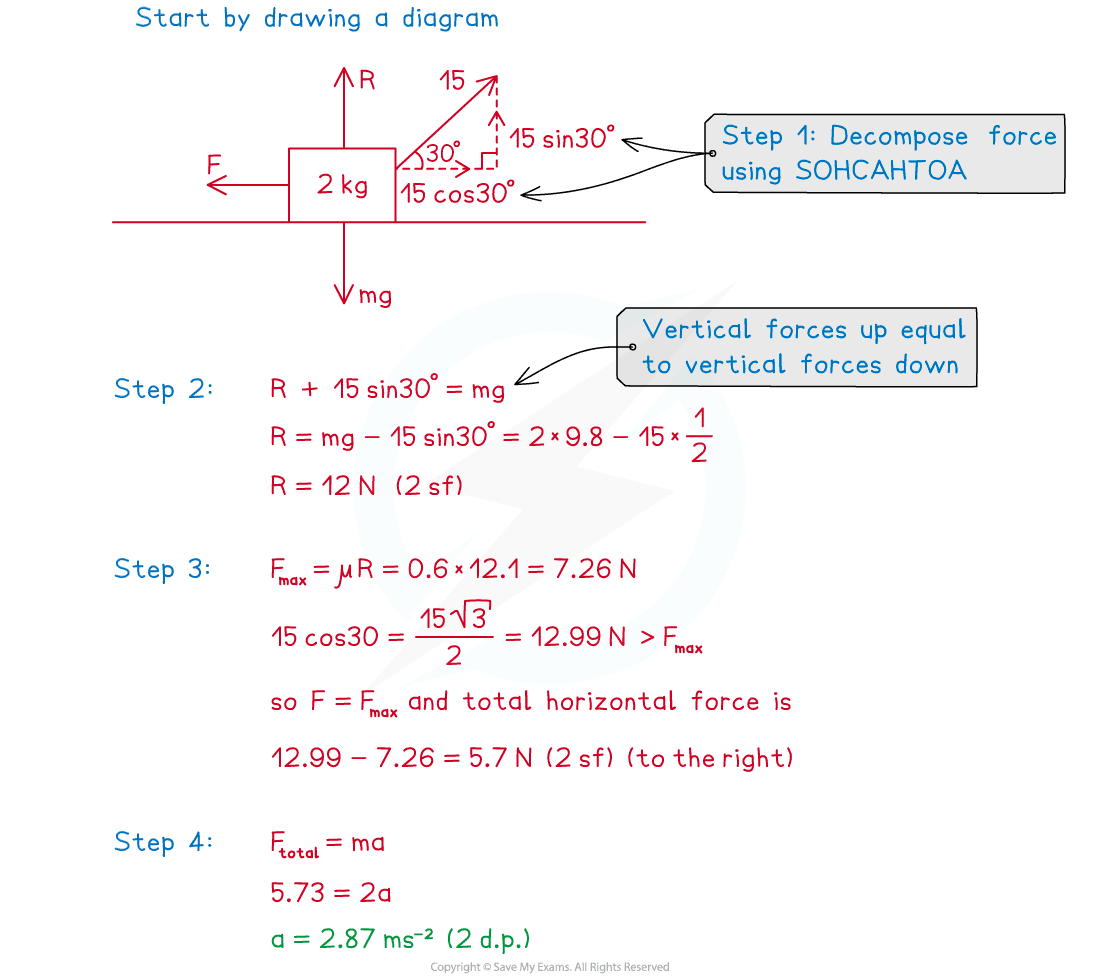
Step 1. If necessary, resolve any angled forces into vertical and horizontal components
Step 2. Calculate the normal reaction force R
Be careful – if there are vertical forces other than gravity these will affect the value of R
with a horizontal surface R will always be directed vertically upwards
the magnitude of R will be such as to make the total vertical force on the object zero
Step 3. Calculate FMAX= μR and find the resultant (total force) of all the horizontal forces on the object
Remember – if the resultant of the other horizontal forces is less than or equal to FMAX then friction will exactly balance those forces out and the object will remain stationary
Step 4. Use F = ma to determine the acceleration of the object
For non-horizontal surfaces see the notes on inclined planes
Worked Example
A wooden block of mass 2 kg is at rest on a rough horizontal floor, where the coefficient of friction between the block and the floor is 0.6. A constant force of 15 N is applied to the block at an angle of 30o to the horizontal, as shown in the diagram below.

Find the acceleration of the block.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Always draw a force diagram and label it clearly. Look out for the words smooth and rough in mechanics problems involving an object moving (or potentially moving) along a surface:
If the surface is described as smooth then you can ignore friction in the problem (ie μ= 0)
If the surface is described as rough than you need to include the force of friction in solving the problem
Be aware of whether the question is on a horizontal surface or an inclined plane.
If g = 9.8 m s-2 has been used within a calculation then round that answer to 2 significant figures.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
