Did this video help you?
F = ma - Vector Notation (AQA A Level Maths: Mechanics): Revision Note
F = ma - Vector Notation
How is Newton’s Second Law (N2L) used with vectors?
- The resultant force (F) and acceleration (a) are vectors
- For forces and motion in two dimensions, F N and a m s-2 will be made up of two components – a horizontal (x-) component and a vertical (y -) component
- Displacement , velocity and weight are also vector quantities
- Time and mass are scalar quantities
- Vectors appear in bold (non-italic) font in textbooks, on exam papers, etc (i.e. F, a) but in handwriting should be underlined (i.e. F , a )
What notation is used for forces as vectors?
- All vectors are written either as column vectors or in i-j format
- As a column vector
would look like
- In i-j notation
would look like
When do I use F = ma (N2L) in vector/2D form?
- If vectors/2D are being used this will be clear from the information given in the question – any vector quantities will be given as a column vector or written in i-j notation
- Remember
is used when motion is involved – equations may come from ‘suvat’ (if the acceleration is constant), or using N2L directly; look for (resultant) force, mass and acceleration being involved
- Use
(N2L in 1D) or an appropriate ‘
’ (in 1D) equation to set up and solve separate equations for both the horizontal (
-) and vertical (
-) components.
How is Newton’s Second Law (N2L) used with problems involving weight?
- Weight is a force, so it is a vector quantity
where
is the acceleration due to gravity
- Weight always acts vertically downwards so it only acts in the j-direction
- Treating the two dimensions separately means weight only needs to be considered when looking at the vertical (
-) direction
- Most 2D/vector problems are based on a bird’s-eye view – the two dimensions being left/right and forwards/backwards, so the up/down (third) dimension where weight would apply, is often not involved
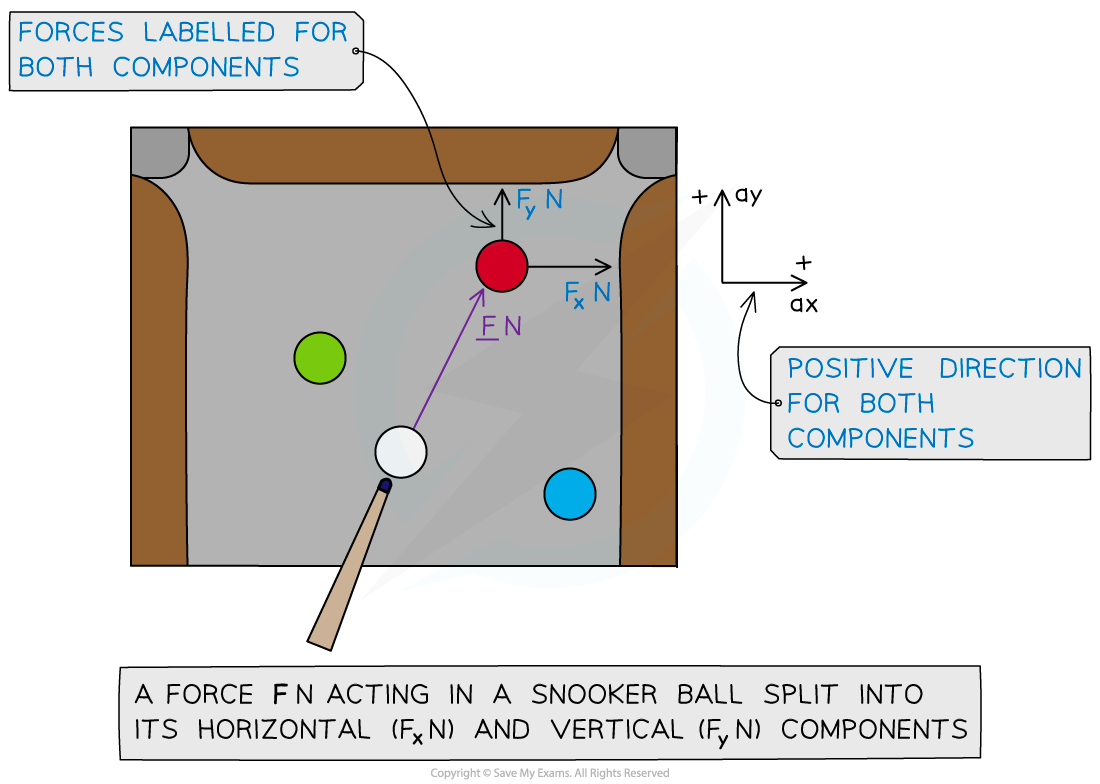
How do we apply Newton’s Second Law (F = ma) in problems involving vectors?
- Step 1. If necessary, draw a diagram and label all forces acting on the particle(s)
- label the i and j directions and any other useful information.
- If a diagram is given, add any missing information to it.
- Step 2. Taking each dimension/component at a time use F = ma
- If there is more than one particle involved you may have to do this for each
- Step 3. Solve the equations for each component and put the final answers back into vector notation
- In some harder problems simultaneous equations may arise
Worked example


Examiner Tip
- If not given in the question, draw a diagram; label all forces and the positive direction for both components.
- Add to a diagram if given one, do not assume it is complete.
- Write a list of the quantities that are given in a question and another list of those you are asked to find. This will help you decide which equation(s) to use.
- A third list of the quantities you are not concerned with can help as these may be used to find intermediate results.
- Unless told otherwise, use g = 9.8 m s-2 and round your final answer to two significant figures.
- Some questions may direct you to use g = 10 m s-2 in which case round your final answer to one significant figure.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
