Uses of the Scalar Product (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9709
Did this video help you?
Uses of the scalar product
This revision note covers several applications of the scalar product for vectors – namely, how you can use the scalar product to:
find the angle between vectors or lines
test whether vectors or lines are perpendicular
find the closest distance from a point to a line
How do I find the angle between two vectors?
Recall that a formula for the scalar (or ‘dot’) between vectors
and
is
where
is the angle between the vectors when they are placed ‘base to base’
that is, when the vectors are positioned so that they start at the same point
We arrange this formula to make
the subject:
To find the angle between two vectors
Calculate the scalar product between them
Calculate the magnitude of each vector
Use the formula to find
Use inverse trig to find
How do I find the angle between two lines in 3D?
To find the angle between two lines, find the angle between their direction vectors
For example, if the lines have equations
and
, then the angle
between the lines is given by
How do I know if vectors or lines are perpendicular?
Two (non-zero) vectors
and
are perpendicular if, and only if,
If the a and b are perpendicular then:
If
then:
a and b are perpendicular
For example, the vectors
and
are perpendicular since
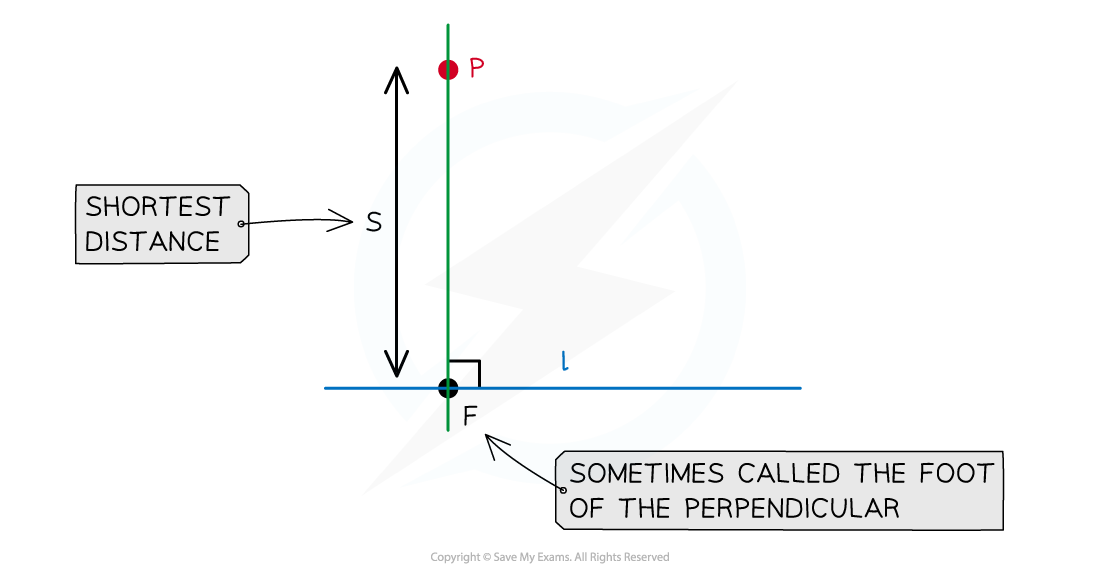
How do I find the shortest distance from a point to a line?
Suppose that we have a line
with equation
and a point
not on
Let
be the point on
which is closest to
(sometimes called the foot of the perpendicular)
Then the line between
and
will be perpendicular to the line
To find the closest point
Call
and
Since
lies on
, we have
, for a unique real number
Find the vector
using
is perpendicular to
so form an equation using
Solve this equation to find the value of
Use the value of
to find
The shortest distance between the point and the line is the length
Note that the shortest distance between the point and the line is sometimes referred to as the length of the perpendicular
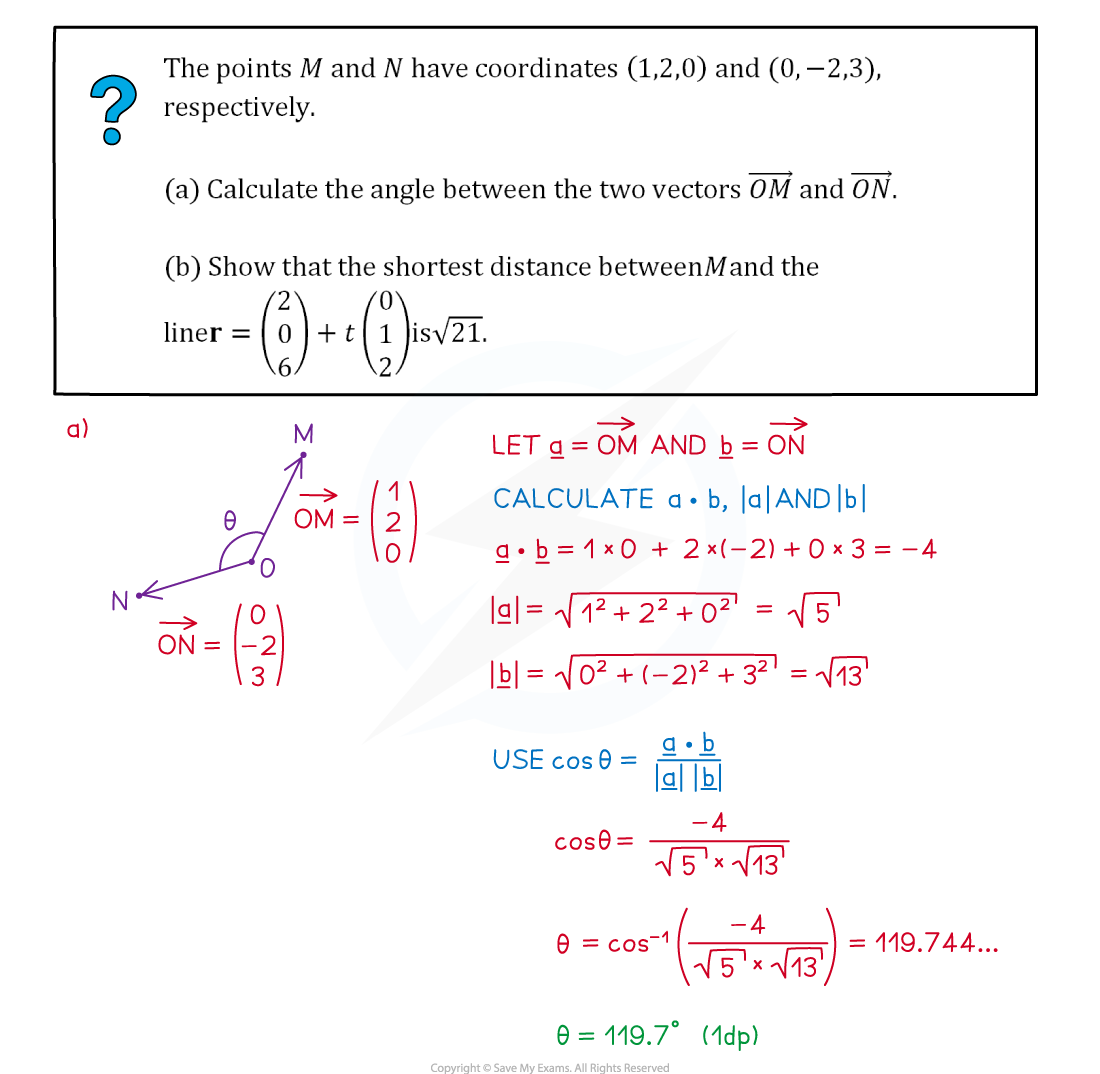
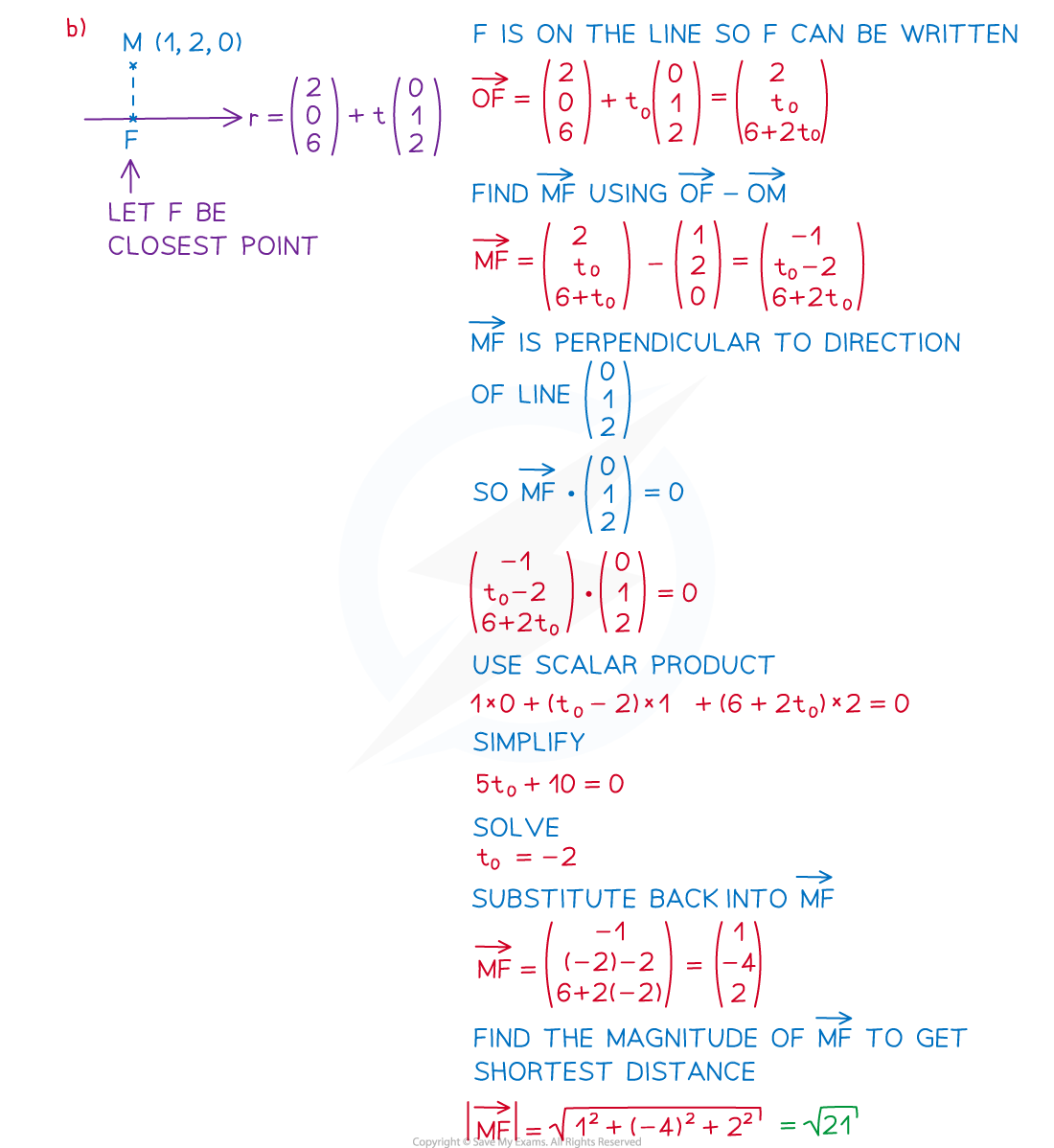
Worked Example
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It can be easier and clearer to work with column vectors when dealing with scalar products.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?