E(X) & Var(X) of Discrete Random Variables (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
E(X) of DRVs
What does E(X) mean and how do I calculate E(X)?
means the expected value or the mean of a random variable
The expected value does not need to be an obtainable value of
For example: the expected value number of times a coin will land on tails when flipped 5 times is 2.5
For a discrete random variable, it is calculated by:
Multiplying each value of
with its corresponding probability
Adding all these terms together
Look out for symmetrical distributions (where the values of
are symmetrical and their probabilities are symmetrical)
The mean of these is the same as the median
For example: if
can take the values 1, 5, 9 with probabilities 0.3, 0.4, 0.3 respectively then by symmetry the mean is 5
Worked Example
Daphne pays $15 to play a game where she wins a prize of $1, $5, $10 or $100. The random variable represents the amount she wins and has the probability distribution shown in the following table:
1 | 5 | 10 | 100 | |
0.35 | 0.5 | 0.05 | 0.1 |
Calculate the expected value of Daphne's prize.

Var(X) of DRVs
How do I calculate E(X2)?
means the expected value or the mean of the random variable
It is calculated by:
Squaring each value of
to get the values of
Multiplying each value of
by its corresponding probability
Adding all these terms together
It's formula is
Is E(X²) equal to (E(X))²?
No!
is the mean of the squares of
is the square of the mean of
For example, if
= 1 or
= -1, both with probabilities of 0.5 then
the mean is 0 so
= 02 = 0
but the squares of
are 1 and 1, so
What is Var(X) and how do I calculate Var(X)?
means the variance of a random variable
How spread out
values are from their mean
High
means more spread out
How consistent
values are around their mean
High
means more variability so less consistent
For any random variable this can be calculated using the formula
This is the mean of the squares of
minus the square of the mean of
is always positive
The standard deviation of a random variable
is
An alternative formula is
The expected value of the squares of the distances from the mean
This is its formal definition, but less useful in practice
How do I find E(X2) if Var(X) and E(X) are known?
Rearrange the formula
Then substitute in the values for
and
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Check if your answer makes sense:
The mean should fit within the range of the values of X.
The variance must be positive.
Worked Example
The discrete random variable has the probability distribution shown in the following table:
2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | |
0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
(a) Find the value of .

(b) Find the value of .
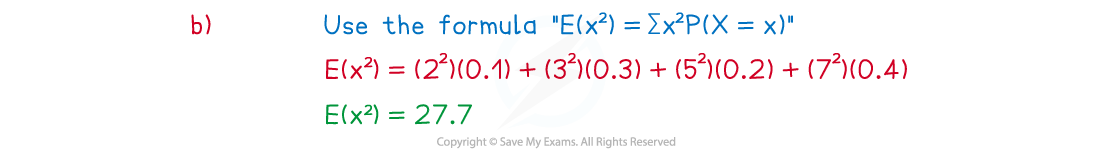
(c) Find the value of .

E(g(X)) of DRVs
How do I calculate E(g(X))?
means
The expected value (mean) of
is a function of
Let
be any function of
Then
Multiply values of
by their corresponding probabilities
does not mean substitute the value of
into

Worked Example
The random variable has the following probability distribution.
1 | 8 | 27 | |
0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
Determine which out of or
is greater.


Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?