Modelling with Volumes of Revolution (Edexcel A Level Further Maths) : Revision Note
Adding and Subtracting Volumes
Why might I need to add or subtract volumes of revolution?
As with the area between a curve and a line or the area between 2 curves, a required volume may be created by two functions
In this note we focus on volumes created by rotation around the x-axis but the same principles apply to rotation around the y-axis
Make sure you are familiar with the methods in Volumes of Revolution
The volumes created here can be created from areas that do not have the x-axis as one its boundaries
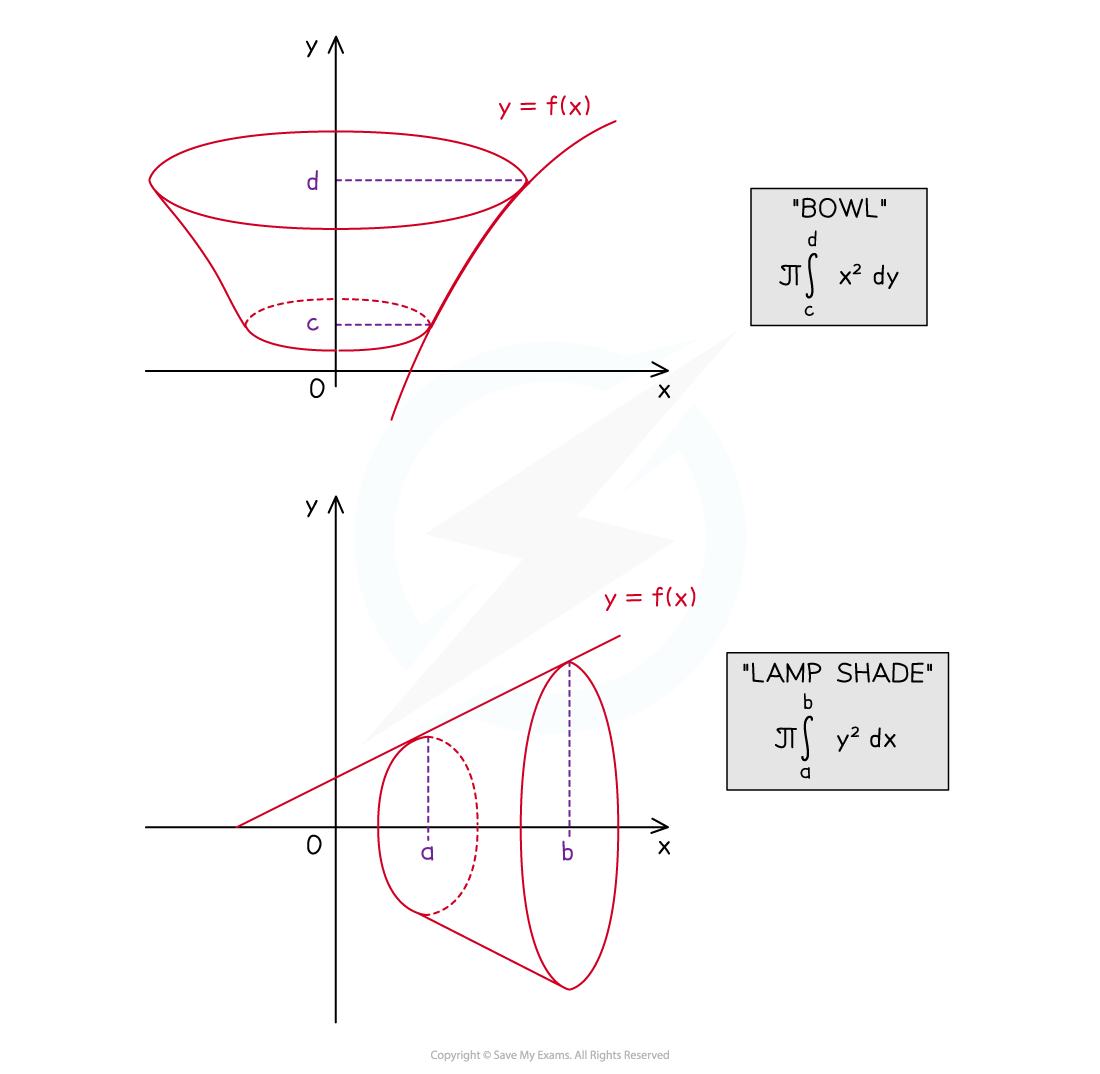
A cylinder is created by rotating a rectangle that borders the x-axis around the x-axis by 360°
An annular prism (a cylinder with a whole through it – like a toilet roll) is created by rotating a rectangle that does not have a boundary with the x‑axis around the x-axis by 360°
A rectangle would be defined by two vertical and two horizontal lines

Where a, b, c & d are all positive and a < b and c < d
The volume of revolution of this rectangle would be
How do I know whether to add or subtract volumes of revolution?
When the area to be rotated around an axis has more than one function (and an axis) defining its boundary it can be trickier to tell whether to add or subtract volumes of revolution
It will depend on
The nature of the functions and their points of intersection
Whether rotation is around the x-axis or the y-axis
Consider the region R, bounded by a curve, a line and the -axis, in the diagram below

If R is rotated around the
-axis the solid of revolution formed will have a ‘hole’ in its centre

Think in 2D and area
“region under the curve”
SUBTRACT
“region under the line”
If R is rotated around the
-axis the solid of revolution formed will look a little like a spinning top – with a ‘dome top half’ and a ‘cone bottom half’

Think in 2D and area
“top ‘half’ is the area ‘below’ the curve to the horizontal where the curve and line intersect” ADD
“bottom ‘half’ is area ‘below’ the line to the horizontal where the curve and line interest”
How do I solve problems involving adding or subtracting volumes of revolution?
Visualising the solid created becomes increasingly useful (but also trickier) for shapes generated by separate volumes of revolution
Continue trying to sketch the functions and their solids of revolution to help
STEP 1: Identify the axis that the area will be rotated around
Identify the functions
involved in generating the volume
Determine whether these will need to be added or subtracted
STEP 2: If rotating around the x-axis, square y for all functions
If rotating around the y-axis, rearrange all the y functions into the form
and square
In either case do this first without worrying about π or the integration and limits
STEP 3: Identify the limits for each volume involved and form the integrals required
The limits could come from a graph
STEP 4: Evaluate the integral for each function and add or subtract as necessary
The answer may be required in exact form
If not, round to three significant figures (unless told otherwise)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is possible, in subtraction questions, to combine the separate integrals into one
This is possible when the limits for each function are often the same in subtraction questions
This doesn’t really apply to addition questions as if the limits are the same, you would be adding some of the same volume twice
If in any doubt avoid this approach as accuracy is far more important
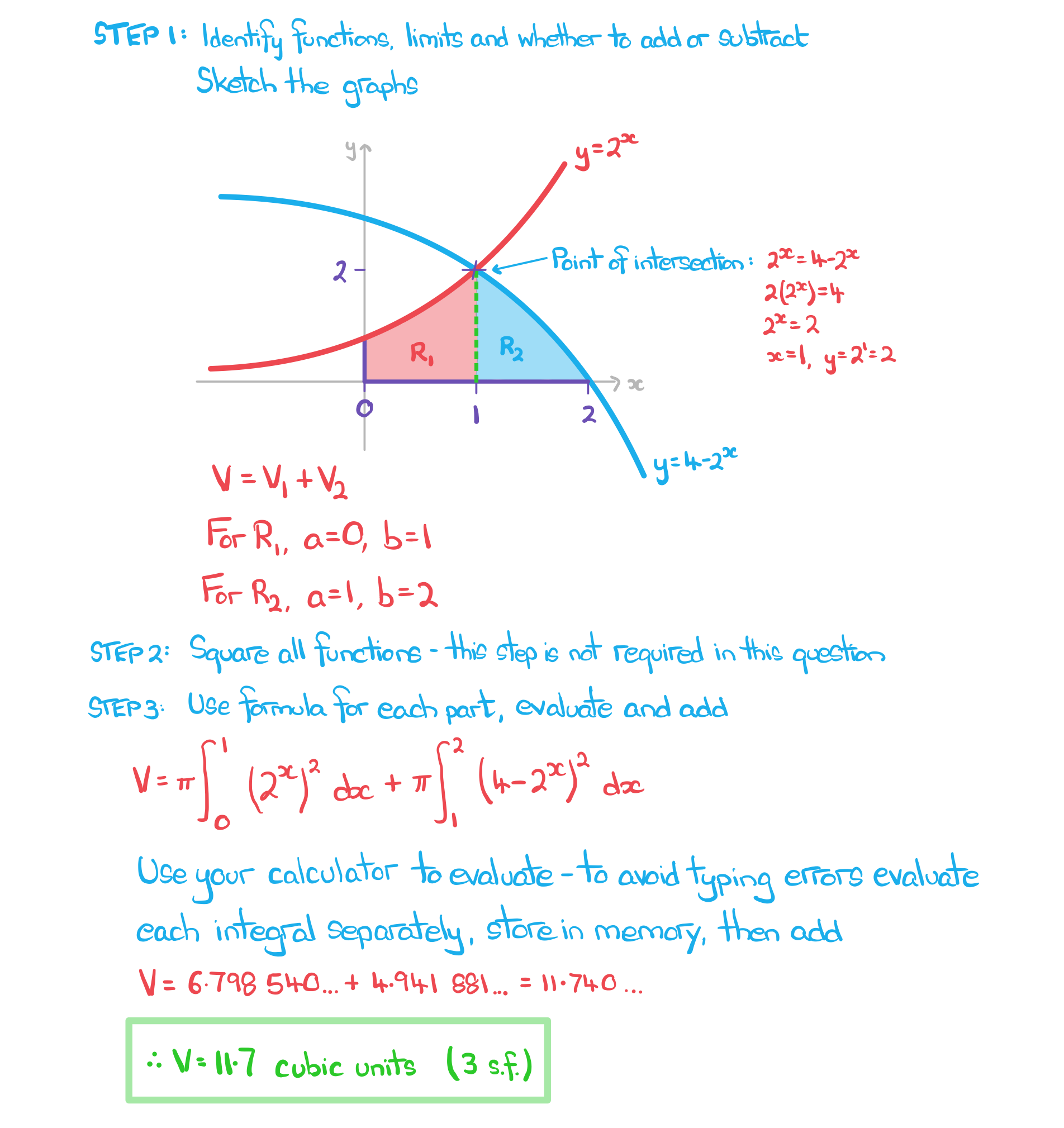
Worked Example
Find the volume of revolution of the solid formed by rotating the region enclosed by the positive coordinate axes and the graphs of and
by
radians around the
-axis. Give your answer to three significant figures.
Modelling with Volumes of Revolution
What is meant by modelling with volumes of revolution?
Many every day objects such as buckets, beakers, vases and lamp shades can be modelled as a solid of revolution
This can then be used to find the volume of the solid (volume of revolution) and/or other information about the solid that could be useful before an object is manufactured
Modelling with volumes of revolution could involve rotation around the x-axis or y-axis so ensure you are familiar with both
What modelling assumptions are there with volumes of revolution?
The solids formed are usually the main shape of the body of the object
For example, the handles on a vase would not be included
The lip on the top edge of a bucket would not be considered
A common question or assumption concerns the thickness of a container
The thickness is generally ignored as it is relatively small compared to the size of the object
thickness will depend on the purpose of the object and the material it is made from
Some questions may refer to the solid formed being the ‘inside’ of an object or refer to the ‘internal’ dimensions
If the thickness of the material is significant it would involve two related solids of revolution (Adding & Subtracting Volumes)
How do I solve modelling problems with volumes of revolution?
Visualising and sketching the solid formed can help with starting problems
Familiarity with applying the volume of revolution formulae for rotations around both the x and y axes
x-axis
y-axis
The volume of a solid may involve adding or subtracting different volumes of revolution
Subtraction would need to be used for solids formed from areas that do not have a boundary with the axis of rotation
Questions may go on to ask related questions in context so do take notice of the context
A question about a bucket being formed may ask about its capacity
This would be measured in litres so there may also be a mix of units that will need conversion (e.g. 1000cm3 = 1 litre)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Consider the context of the question to gauge whether your final answer is realistic
Look at the Worked Example below
a vase holding just 0.126 litres of water will not hold many flowers, but the question did state it was a miniature vase
For rotation around the y -axis remember to rearrange
into the form
Worked Example
The diagram below shows the region R, which is bounded by the function , the lines
and
, and the
-axis.
Dimensions are in centimetres.
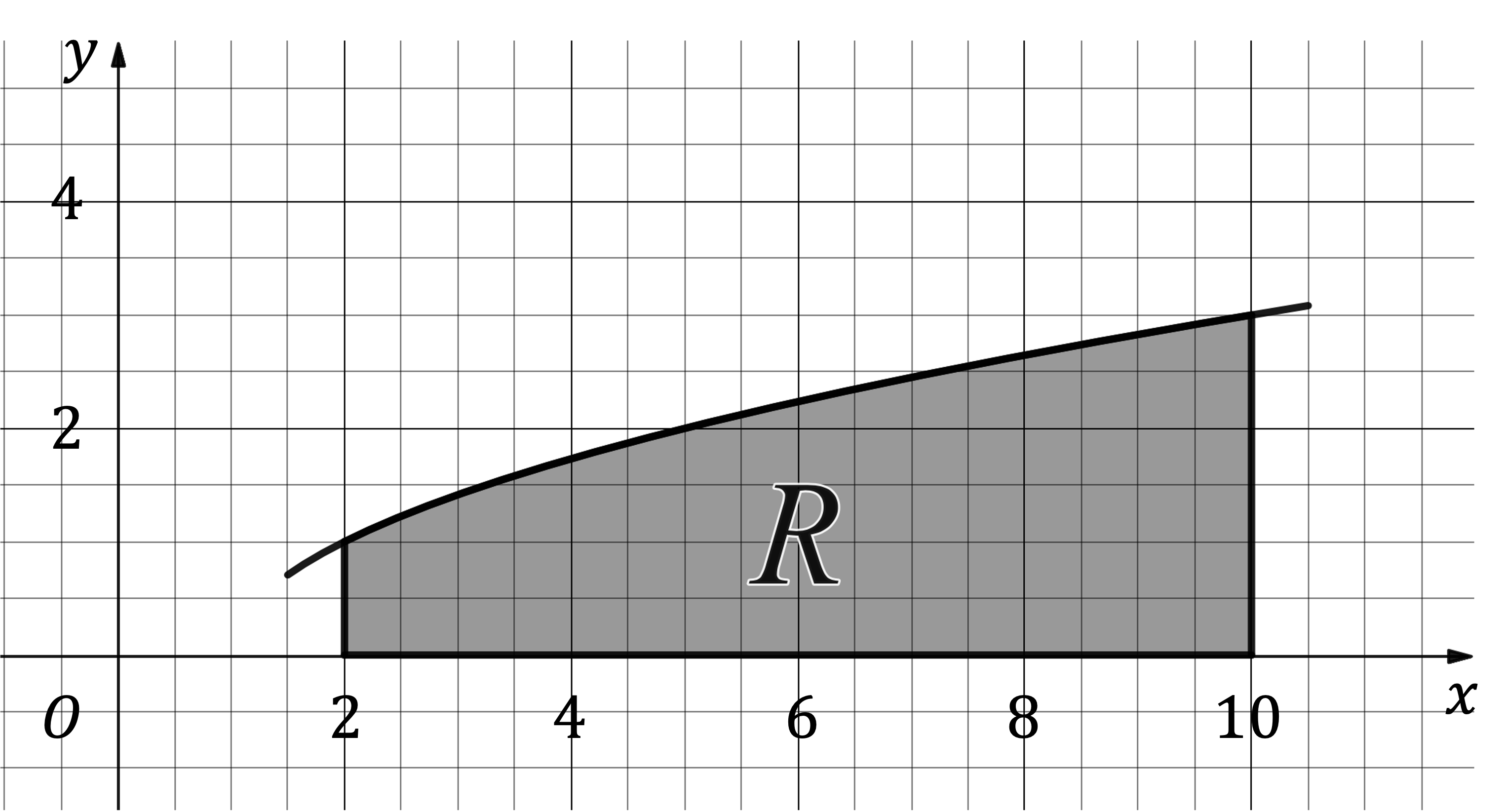
A mathematical model for a miniature vase is produced by rotating the region R through 2π radians around the x-axis.
Find the volume of the miniature vase, giving your answer in litres to three significant figures.


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
