Calculus involving Inverse Trig (Edexcel A Level Further Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 9FM0
Written by: Paul
Updated on
Differentiating inverse trig functions
What are the inverse trigonometric functions?
arcsin, arccos and arctan are functions defined as the inverse functions of sine, cosine and tangent respectively
which is equivalent to
which is equivalent to
What are the derivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions?
Unlike other derivatives these look completely unrelated at first
their derivation involves use of the identity
hence the squares and square roots!
All three are given in the formula booklet
Note with the derivative of
that
is the same as
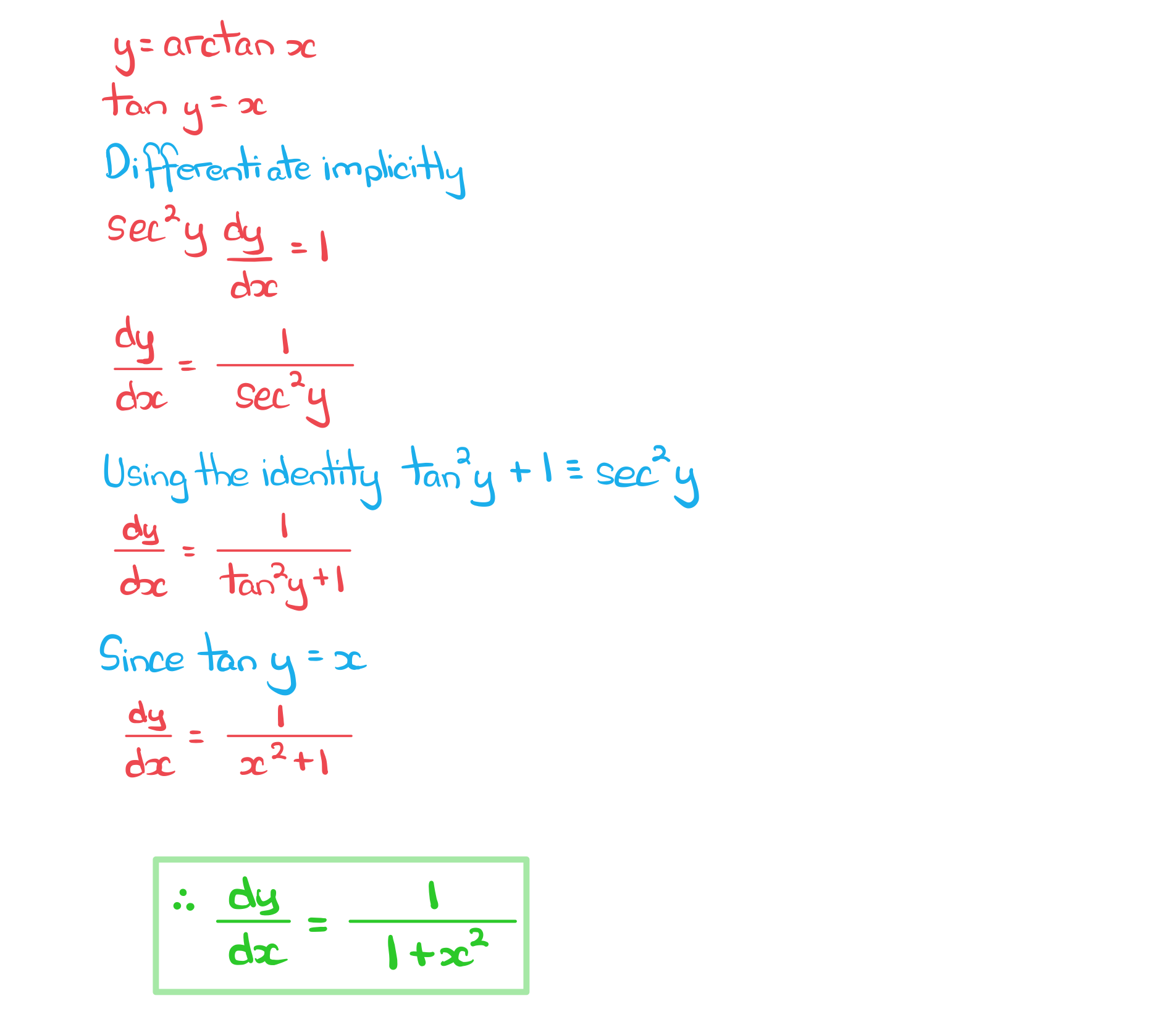
How do I show or prove the derivatives of the inverse trigonometric functions?
For
Rewrite,
Differentiate implicitly,
Rearrange,
Using the identity
rewrite,
Since,
,
Similarly, for
Notice how the derivative of
is positive but is negative for
This subtle but crucial difference can be seen in their graphs
has a positive gradient for all values of
in its domain
has a negative gradient for all values of
in its domain
Examiner Tips and Tricks
For
the terms on the denominator can be reversed (as they are being added rather than subtracted)
Don't be fooled by this, it sounds obvious but on awkward "show that" questions it can be off-putting!
Worked Example
a) Show that the derivative of is
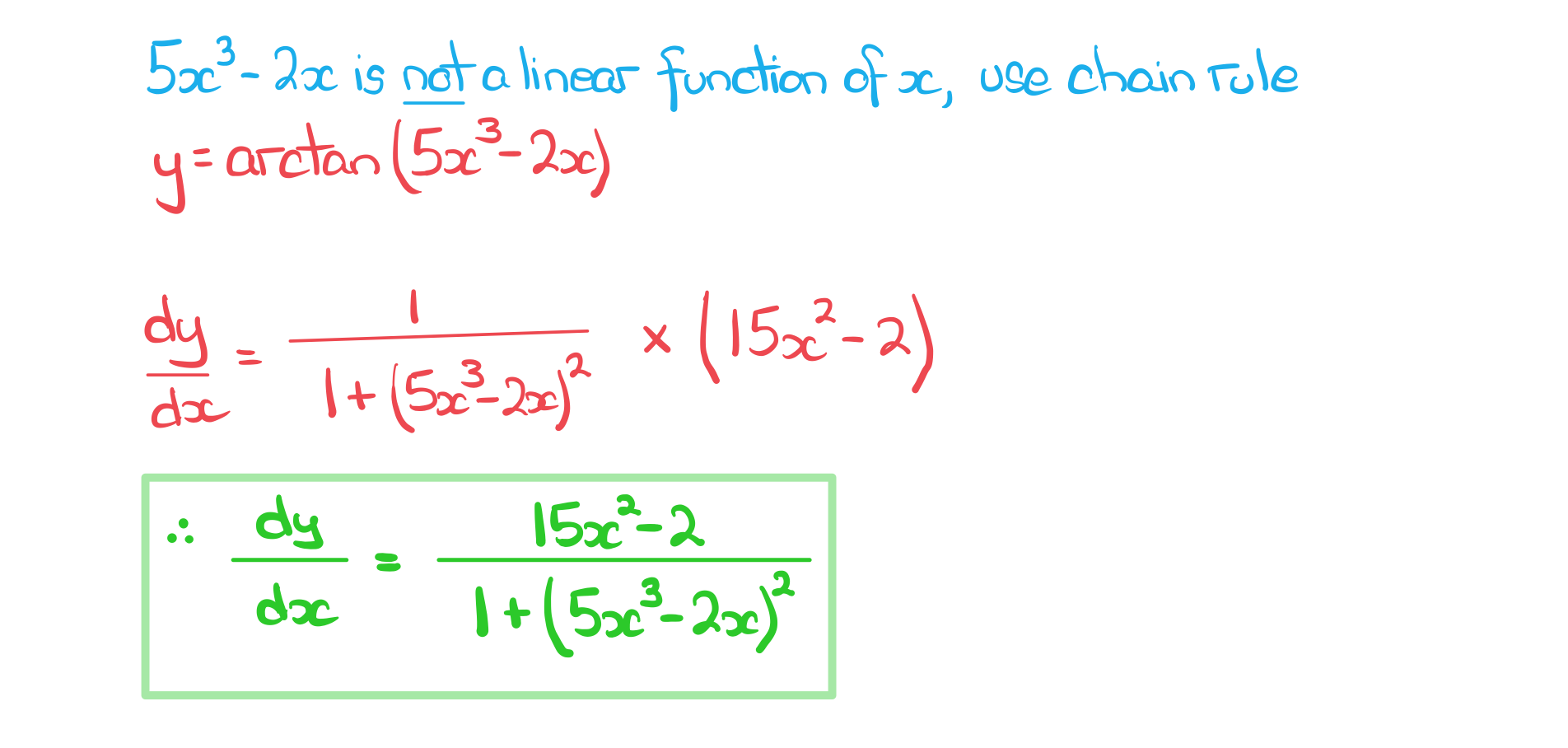
b) Find the derivative of .
Integrating inverse trig functions
How do I integrate inverse trig functions?
Use integration by parts in the same way you would integrate
These can be integrated using parts however
rewrite as the product ‘
’ and choose
and
1 is easy to integrate and the inverse trig functions have standard derivatives listed in the formula booklet
The expression
integrates to
The expression
integrates to

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
