Programming Classes, Objects, Methods & Attributes (OCR A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: H446
Programming Classes
To program classes, you should already have a solid understanding of what classes in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
How do you Define a Class?
In this example we will:
Define a class for a car sales program where the following is required:
Name of Manufacturer
Model of Car
Price
Mileage
Whether the car is preowned
Instantiate two objects for the car sales program ensuring that they have appropriate identifiers
List two methods that would be useful for a car object
Pseudocode

Pseudocode for creating classes, a constructor, and functions
Java
//creating a class called cars
public class Cars {
//creating class attributes for a car
private String Manufacturer;
private String Model;
private int Price;
private int Mileage;
private boolean PreOwned;
//Constructor - This is used to create the objects. More on this in the object chapter)
public Cars(String manufacturer, String model, int price, int mileage, boolean preOwned) {
this.Manufacturer = manufacturer;
this.Model = model;
this.Price = price;
this.Mileage = mileage;
this.PreOwned = preOwned;
}
//method to make the car go faster.
public void Accelerate(){
//code to be executed which will make the car go faster
}
//Method to honk horn
public void honkHorn(){
// code to be executed which will honk the car horn
}
}
Python
#creating a class called cars
class Cars:
# constructor - This is used to create the objects. More on this in the object chapter)
def __init__(self, manufacturer, model, price, mileage, preOwned):
self.Manufacturer = manufacturer
self.Model = model
self.Price = price
self.Mileage = mileage
self.PreOwned = preOwned
#method to make the car go faster.
def Accelerate(self):
# code to be executed which will make the car go faster
# method to honk horn
def honkHorn(self):
# code to be executed which will honk the car horn
Programming Objects
To program objects, you should already have a solid understanding of what objects in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
Defining an Object
Pseudocode
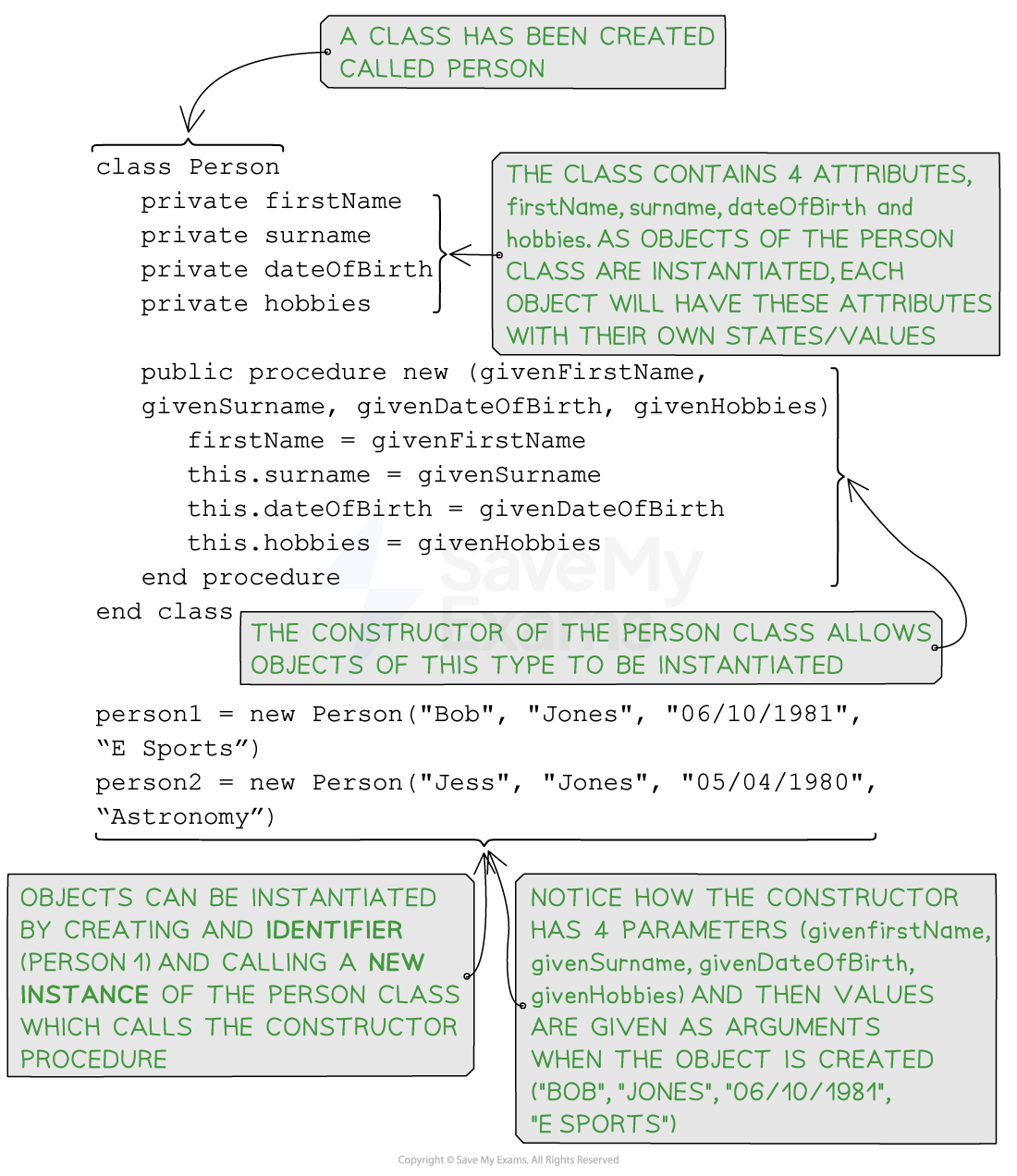
Pseudocode for the class 'person' and instantiating two objects
Java
//creating the person class
public class Person {
// creating 4 attributes for the person class
private String firstName;
private String surname;
private String dateOfBirth;
private String hobbies;
// Constructor -This creates objects of the person class
public Person(String firstName, String surname, String dateOfBirth, String hobbies) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.surname = surname;
this.dateOfBirth = dateOfBirth;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
//Creating Objects (Instances) of the person class
Person person1 = new Person("Bob", "Jones", "06/10/1981", “E Sports”);
Person person2 = new Person("Jess", "Jones", "05/04/1980", “Astronomy”);
Python
#creating the person class
class Person:
#Constructor -This creates objects of the person class
def __init__(self, firstName, surname, dateOfBirth, hobbies):
self.firstName = firstName
self.surname = surname
self.dateOfBirth = dateOfBirth
self.hobbies = hobbies
#Creating Objects (Instances) of the person class
person1 = Person("Bob", "Jones", "06/10/1981", "E Sports")
person2 = Person("Jess", "Jones", "05/04/1980", "Astronomy")
Programming Methods
To program methods, you should already have a solid understanding of what methods in Object Oriented Programming (OOP) are.
Defining Methods
Pseudocode
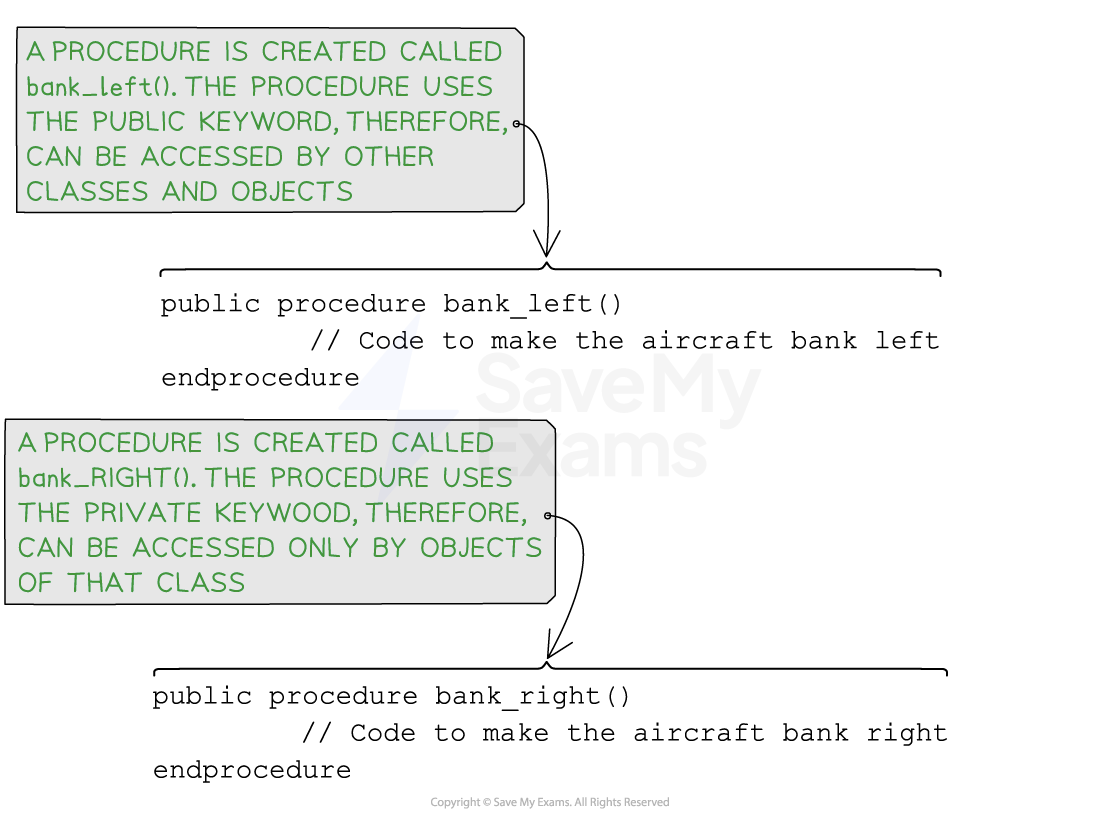
Pseudocode for creating methods
Java
//Creating a public method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}
//Creating a private Method called BankLeft
public void bankLeft() {
// Code to make the aircraft bank left
}
Python
#Creating a public method called BankLeft
def bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank left
#Creating a private method called BankLeft
In Python, there is no explicit access modifier for methods like "private" in Java.
By convention, methods with a single leading underscore _ are considered private and should not be accessed directly from outside the class.
_def _bank_left(self):
# Code to make the aircraft bank left
It's important to note that even though the method is marked as private, it can still be accessed and invoked from outside the class. However, as a rule, other developers should treat it as private and avoid accessing it directly.
Programming Attributes
Pseudocode
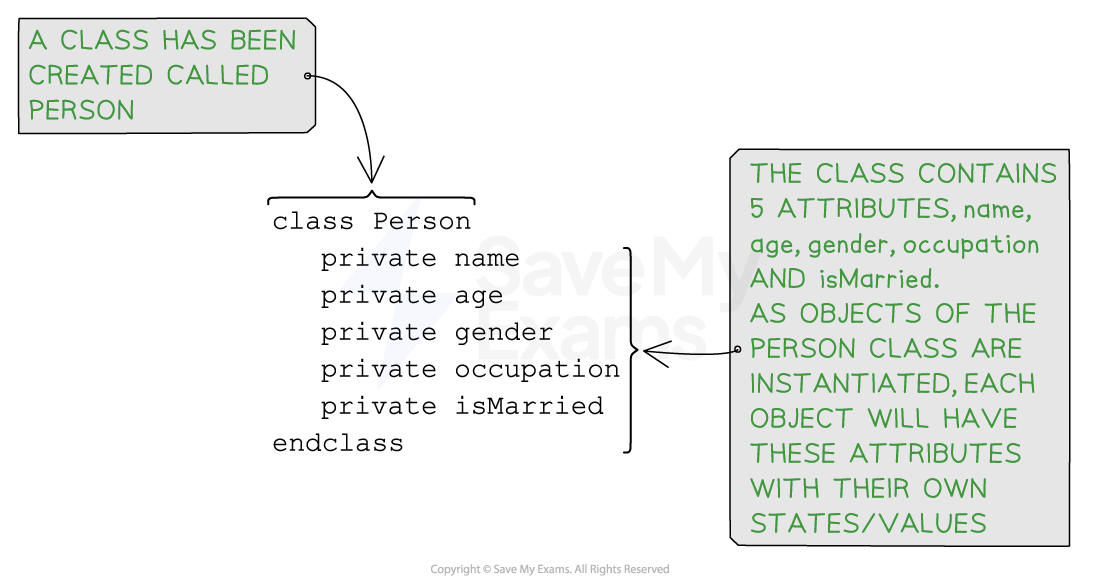
Example of a created class, "Person", containing several attributes
Java
public class Person {
// Attributes for the person class
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
private String occupation;
private boolean isMarried;
}
Python
In Python attributes are defined using the self keyword followed by the attribute name and its initial value.
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, attribute1, attribute2):
# Define attributes
self.attribute1 = attribute1
self.attribute2 = attribute2
Worked Example
Below is a sample of code for the class "Lizard".
class Lizard private speed private mass private size public procedure new(givenSpeed, givenMass, givenSize) speed=givenSpeed mass=givenMass size=givenSize endprocedure public function breakBlock(brick) if speed*mass>=brick.getStrength() then speed=((speed*mass)-brick.getStrength())/mass; return true else return false endif endfunction
.........endclass
Identify an attribute in the Lizard class.
1 marks
How to answer this question to get full marks:
There are 3 attributes in the Lizard class which are speed, mass and size
Answer:
Speed

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?