HTML (OCR A Level Computer Science): Revision Note
Exam code: H446
HTML
What is HTML?
HTML, or Hypertext Markup Language, is the foundational language used to structure content on the web
HTML consists of a series of elements, often referred to as "tags," which can be used to structure and format a webpage
The
<html>tag is the root element of an HTML page. The tag includes all other HTML elements used on the pageMost tags are opened and closed e.g.
<html>and</html>whereas some tags are only opened e.g.<img>and<link>The content layer of a web page is made up of HTML elements such as headings (
<h1>, <h2>, etc.), paragraphs (<p>), links (<a>), images (<img>), and more
Examiner Tips and Tricks
An exam question which asks you to write HTML is asking you to write code which is specifically HTML. This means all spelling and syntax MUST be correct for you to get the marks
The head
The head section contains information about the web page that's not displayed on the page itself
The head section is enclosed by
<head>and</head>TagsSome of the content inside the head tag is shown in the browser tab
Page title
The
<title>element is used to set the page title that shows in the browser tabThe crown is placed inside the
<head>section of the HTML documentE.g.
<title>Sample Webpage</title>
External stylesheet
External stylesheets are linked in the
<head>section using the<link>elementThe
relthe attribute is set to "stylesheet", and thehrefthe attribute contains the relative file path to the CSS fileStylesheets are loaded in the order they are listed, so hierarchy is important
E.g.
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
The body
The body section contains the main content of the web page, such as text, images, videos, hyperlinks, tables etc.
The body section is enclosed by
<body>and</body>TagsThe content inside the body tag is displayed in the browser window
Headings
Headings help users understand how a page is organised and structured. They help guide the user's eye around the page and help them quickly find the information they're looking for
Headings are also important for users that use screen readers, such as visually-impaired users. Screen reader software uses headings to help the user navigate around the page (e.g. providing a list of all the headings on the page, and allowing the user to jump straight to a particular heading)
The tags used for headings are
<h1>, <h2>,<h3>etc.<h1>is the highest level heading, with<h2>and<h3>serving as subheadingsThe number in the tag denotes the level of the heading. Headings should be used hierarchically, with
<h1>the most prominent, and<h6>the least prominentHeadings are also important for Search Engine Optimisation (SEO), as they help search engines like Google understand the content and structure of the page
E.g.
<h1>Welcome to My Sample Webpage</h1>
<h2>About This Page</h2>
Images
The
<img>tag embeds an image into an HTML documentThe
imgtag includes thesrcattribute which specifies the URL of the image (the source of the attribute), and the alt attribute which provides alternative text for screen readers or in cases where the image cannot be displayed. The tag also helps search engines understand the content of the imageThe height and width attributes specify the dimensions of the image
E.g.
<img src="https://cdn.savemyexams.com/logo/sme-logo-small.svg" alt="Save My Exams Image" height="100" width="200">
Links
The
<a>tag, or anchor tag, is used to create hyperlinksThe tag includes the
hrefattribute which specifies the URL that the link points toThis can be included within another tag to specify the text which will be displayed
E.g.
<p>Visit the <a href="https://www.savemyexams.co.uk">Save My Exams site</a> for more information.</p>An image can also become a hyperlink
E.g.
<a href=”https://www.savemyexams.co.uk”><img src=”logo.png”></a>
Div
The
<div>tag is a generic container that can be used to group other HTML elements togetherThe div tag is often used in conjunction with CSS to style sections of a webpage
Form
The
<form>tag is used to create a form for user input
Input
The
<input>tag is used within a<form>tag to create interactive controls for web-based formsThe type attribute can be set to "
text" to create a textbox, or "submit" to create a submit buttonThe name attribute is used to identify the input
E.g.
<form action="/submit" method="post">
<label for="age">Age:</label>
<input type="number" id="age" name="age" min="0">
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email">
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
Paragraph
The
<p>tag is used for a paragraph of textE.g.
<p>This is a sample webpage created to demonstrate the usage of various HTML tags.</p>
Lists
The
<li>tag is used to define a list itemThe
<ol>and<ul>Tags are used to create ordered and unordered listsAn ordered list will look like numbered bullet points
An unordered list will look like normal bullet points
<li>tags are nested within these to show each item in the listE.g.
<ul>
<li>html</li>
<li>head</li>
<li>title</li>
<li>body</li>
<li>h1, h2, h3</li>
<li>p</li>
<li>a</li>
<li>img</li>
<li>div</li>
<li>form</li>
<li>input</li>
<li>script</li>
</ul>
JavaScript
The
<script>tag is used to embed or reference JavaScript code within an HTML documentE.g.
<script src="script.js"></script>
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It's important to note that the correct usage of relative paths/URLs depends on the file structure and organisation of your web project. Carefully consider the relative relationship between files and directories to ensure accurate referencing of resources
Classes & Identifiers in HTML
Classes and identifiers (IDs) can be used to specify an HTML element
A class can have many HTML elements
An ID specifies a unique ID for an HTML element
Only 1 element can have the ID
A class or an ID can have specific styling applied to it in the CSS
E.g.
<body>
<div id="header">
<h1>Study Guide</h1>
</div>
<div class="subject" id="maths">
<h2>Maths Revision</h2>
<p>Key topics to revise are algebra, trigonometry, and statistics.</p>
</div>
<div class="subject" id="english">
<h2>English Revision</h2>
<p>Focus on improving your grammar, vocabulary, and essay writing skills.</p>
</div>
<div class="subject" id="science">
<h2>Science Revision</h2>
<p>Remember to revise the core concepts in physics, chemistry, and biology.</p>
</div>
</body>
Styling is covered in more detail in CSS but here’s an example to illustrate the use of classes and IDs:
/* styles.css */
#header {
background-color: lightblue;
padding: 10px;
text-align: center;
}
.subject {
border: 1px solid black;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
}
#maths {
background-color: #FFDDDD;
}
#english {
background-color: #DDFFDD;
}
#science {
background-color: #DDDDFF;
}
Example Webpage in HTML
Here’s an example webpage and the HTML code written to create it:
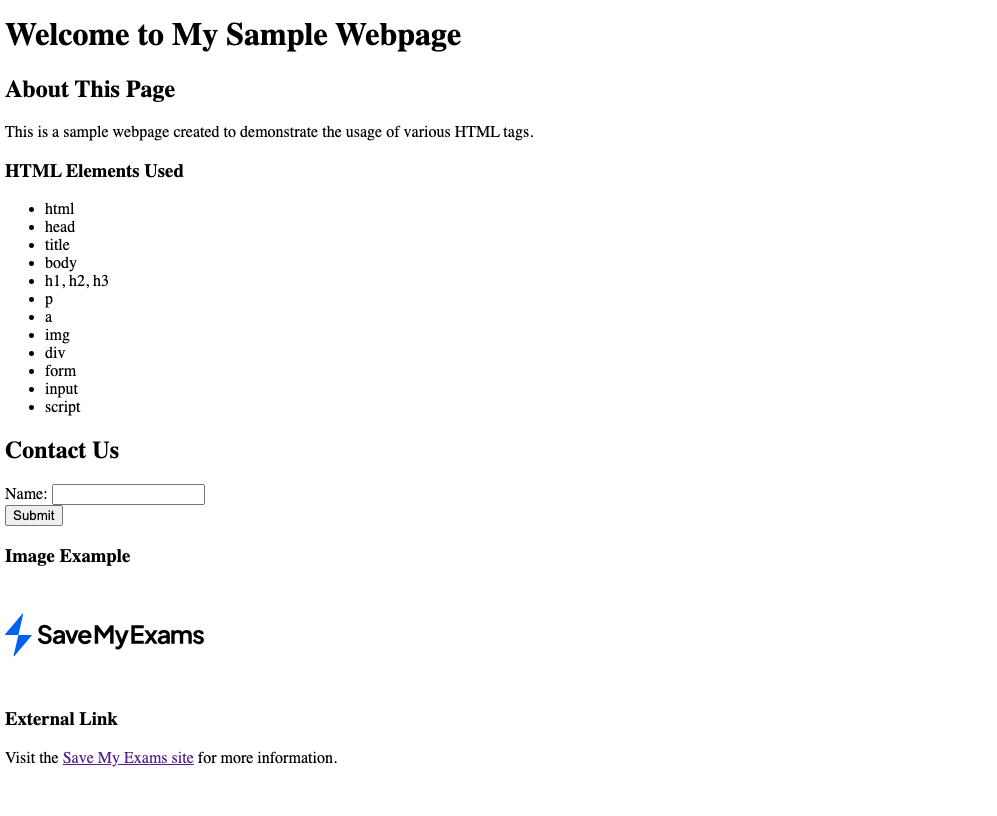
This is the code for this webpage:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Sample Webpage</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome to My Sample Webpage</h1>
<h2>About This Page</h2>
<p>This is a sample webpage created to demonstrate the usage of various HTML tags.</p>
<h3>HTML Elements Used</h3>
<ul>
<li>html</li>
<li>head</li>
<li>title</li>
<li>body</li>
<li>h1, h2, h3</li>
<li>p</li>
<li>a</li>
<li>img</li>
<li>div</li>
<li>form</li>
<li>input</li>
<li>script</li>
</ul>
<h2>Contact Us</h2>
<form action="/submit_form" method="post">
<div>
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name">
</div>
<div>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</div>
</form>
<h3>Image Example</h3>
<img src="https://cdn.savemyexams.com/logo/sme-logo-small.svg" alt="Save My Exams Image" height="100" width="200">
<h3>External Link</h3>
<p>Visit the <a href="https://www.savemyexams.co.uk">Save My Exams site</a> for more information.</p>
</body>
<script src="script.js"></script>
</html>
Worked Example
One page in the website contains a hyperlink on an image. When the image stored as “ticket.png” is clicked, the user is hyperlinked to the page stored as “booking.htm”.
Write the HTML code to implement this hyperlink.
3 marks
How to answer this question:
You can use the example code from above to write the link:
<a href=”https://www.savemyexams.co.uk”><img src=”logo.png”></a>
You’ll need to change the link to the one given in the question (booking.htm) and change the image name to the one given in the question too (ticket.png)
The marks are awarded for:
Correct
<a>with closing</a>hrefproperty to correct pagecorrect
<img>tag with src property to correct file
Answer:
Example answer:
<a href=”booking.htm”><img src=”ticket.png”></a>
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When you’re given a link or filename in the question, make sure you copy it exactly as it appears. Your case (capital letters) and spelling need to be spot on to make sure you don’t drop marks! E.g. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fQBfpaiYlWg is not the same as https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fqbfpaiyiwg

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?