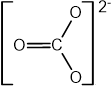
This question is about how electrons are arranged inside the atom.
State the maximum number of electrons that can be held in each of the first three shells of an atom.
From the second shell onwards, p-sub-shells exist.
i) State how many orbitals there are in a p-sub-shell.
[1]
ii) State how the electrons are arranged if a p-sub-shell is full.
[2]
State why the 2s orbitals are filled before the 2p orbitals.
Write the full electronic configuration of the Period 2 element, fluorine, Z = 9.
Did this page help you?