Polymer Repeat Units (OCR A Level Chemistry A): Revision Note
Exam code: H432
Polymer Repeat Units
Repeat units for addition polymers
A repeat unit is the smallest group of atoms that when connected one after the other make up the polymer chain
It is represented by square brackets in the displayed and general formula
In poly(alkenes) (such as poly(ethene)) and substituted poly(alkenes) (such as PVC) made of one type of monomer the repeating unit is the same as the monomer except that the C=C double bond is changed to a C-C single bond

The repeating units of poly(ethene) and poly(chloroethene) are similar to their monomer except that the C=C bond has changed into a C-C bond
Worked Example
Identify the monomers present in the given sections of addition polymer molecules:
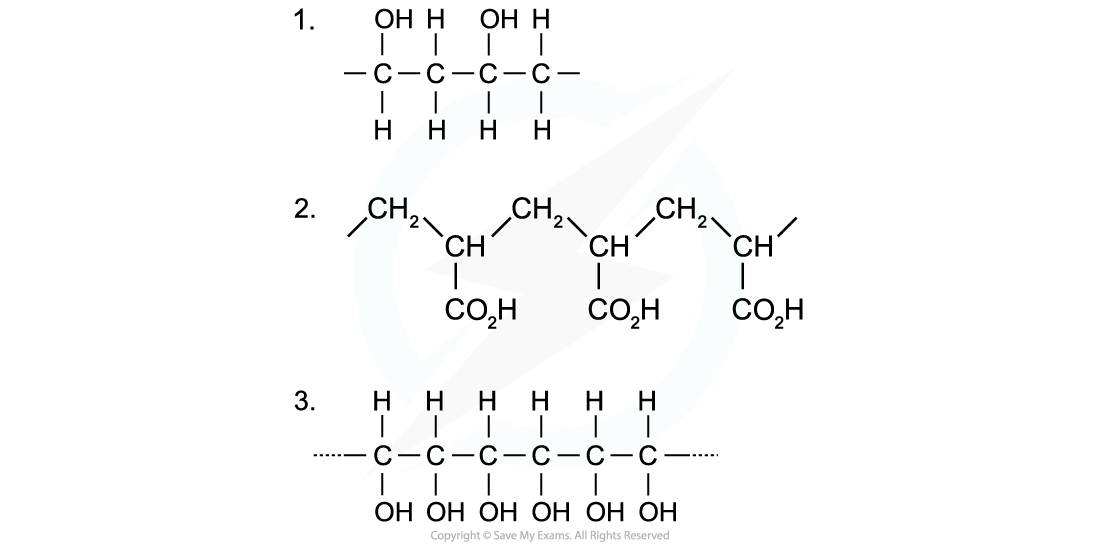
Answers:
Answer 1:
When ethenol (CH(OH)=CH2) is polymerised, the C-C double bond opens to produce a repeating unit of CH(OH)-CH2. This gives the polymer poly(ethenol)

Answer 2:
To find the monomer, first the repeating unit should be deduced. Repeating units have only 2 carbons in the polymer main chain

Since the repeating unit is now found, it can be concluded that the monomer is prop-2-enoic acid

Answer 3:
Again, the repeating unit only has 2 carbons in the polymer chain which in this case are two carbon atoms that each contain one OH group
Thus, when ethene-1,2-diol (CH(OH)=CH(OH)) is polymerised, the C=C double bond opens to produce a repeating unit of CH(OH)-CH(OH) which gives the polymer poly(ethene-1,2-diol)

Repeat units for condensation polymers
Remember we can tell the type of polymerisation by identifying the linking between the monomers
If a chan of carbon atoms is present, the polymer is an addition polymer
If there is an ester link, the polymer is a polyester (formed by condensation polymerisation)
If there is an amide link, the polymer is a polyamide (formed by condensation polymerisation)

This polymer structure shows an ester functional group linking monomers together

An amide link - also known as a peptide link - is the key functional group in a polyamide
Worked Example
Draw the repeating unit and identify the monomers used to make the following polymers

Answer:


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
