Reactions of Alkanes (OCR A Level Chemistry A) : Revision Note
Reactivity of Alkanes
The unreactive nature of alkanes can be explained by two factors
The high bond enthalpies of the C-C and C-H bonds
The very low polarity of the sigma (σ) bonds present
Bond enthalpy
The C-C bond has a bond enthalpy of 346 kJ mol-1 and the C-H bond has a bond enthalpy of 411 kJ mol-1
The C-H bond is stronger as the bond length is less than the C-C bond
This is because the hydrogen atom only consists of one shell, so the distance between the nuclei is shorter
Creating greater force of attraction to the nuclei and the pair of electrons between them
Polarity
The electronegativities of carbon and hydrogen are very similar, therefore the bonds will have very low polarity

Ethane is an example of an alkane that lacks polarity due to almost similar electronegativities of the carbon and hydrogen atoms
Complete & Incomplete Combustion
Alkanes are combusted (burnt) on a large scale for their use as fuels
Complete combustion
When alkanes are burnt in excess (plenty of) oxygen, complete combustion will take place and all carbon and hydrogen will be oxidised to carbon dioxide and water respectively
For example, the complete combustion of octane to carbon dioxide and water

The complete combustion of alkanes
Incomplete combustion
When alkanes are burnt in only a limited supply of oxygen, incomplete combustion will take place and not all the carbon is fully oxidised
Some carbon is only partially oxidised to form carbon monoxide
For example, the incomplete combustion of octane to form carbon monoxide

The incomplete combustion of alkanes
Incomplete combustion often takes place inside a car engine due to a limited amount of oxygen present
With a reduced supply of oxygen, carbon will be produced in the form of soot:

Car exhaust fumes include toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), oxides of nitrogen (NO/NO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
When released into the atmosphere, these pollutants have serious environmental consequences damaging nature and health
Carbon monoxide
CO is a toxic and odourless gas which can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness and eventually death
The CO binds well to haemoglobin which therefore cannot bind oxygen and carbon dioxide
Oxygen is transported to organs
Carbon dioxide is removed as waste material from organs
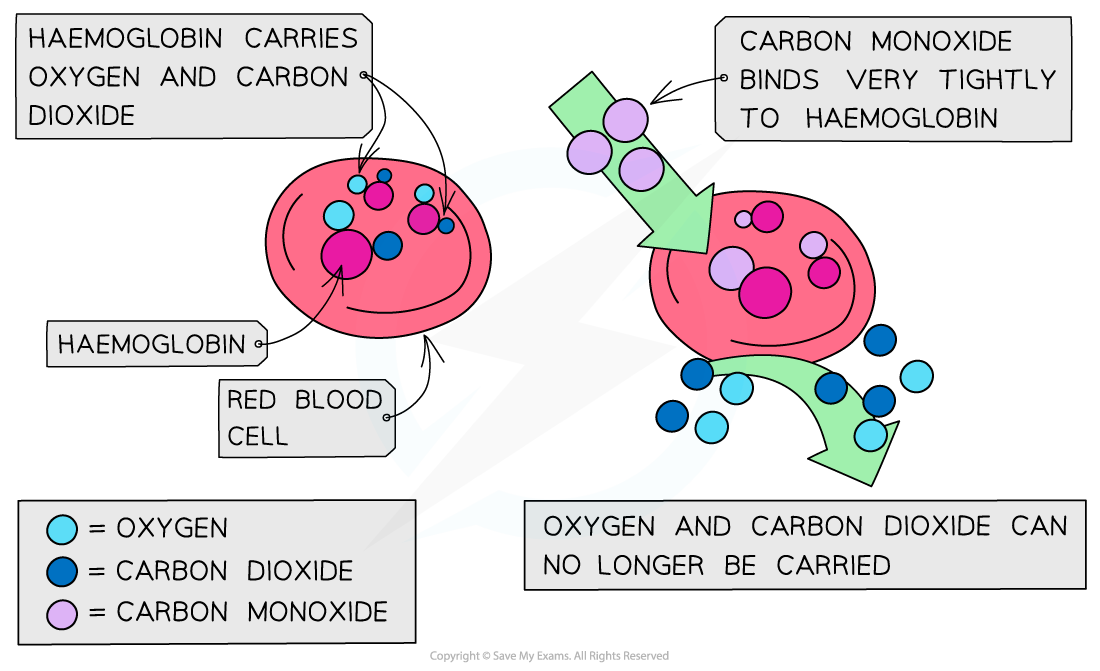
The high affinity of CO to haemoglobin prevents it from binding to O2 and CO2

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
