Hess' Law (OCR A Level Chemistry A): Revision Note
Exam code: H432
Hess’ Law & Enthalpy Cycles
Hess’s Law states that:
"The total enthalpy change in a chemical reaction is independent of the route by which the chemical reaction takes place as long as the initial and final conditions are the same."
This means that whether the reaction takes place in one or two steps, the total enthalpy change of the reaction will still be the same
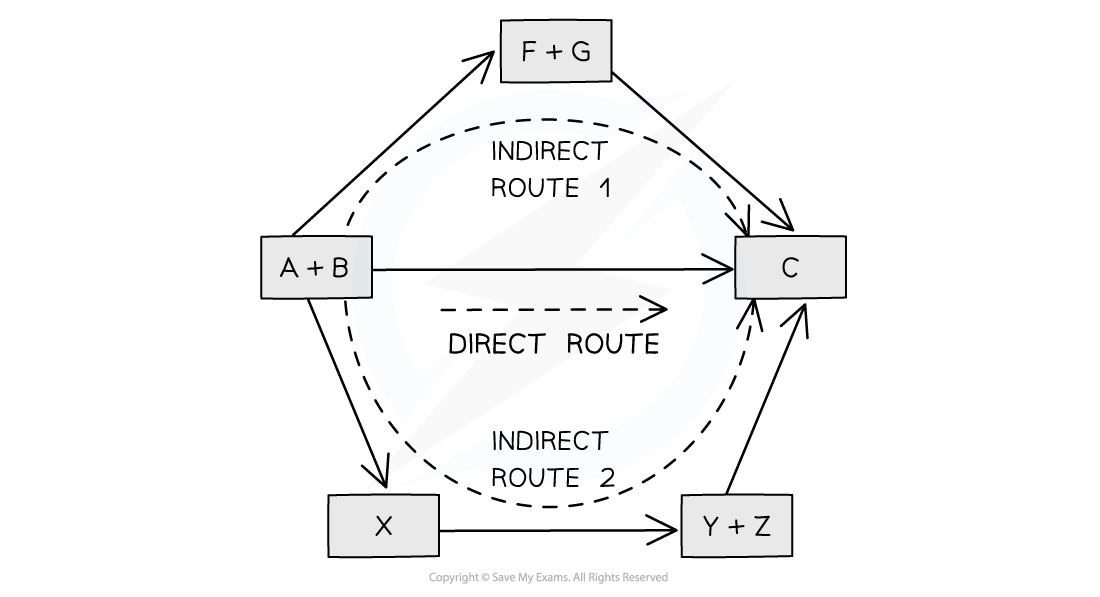
According to Hess’ Law, the enthalpy change of the direct route, going from reactants (A+B) to product (C), is equal to the enthalpy change of the indirect routes
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You do not need to learn Hess's Law word for word as it is not a syllabus requirement, but you do need to understand the principle as it provides the foundation for all the problem solving in Chemical Energetics
Hess’ Law is used to calculate enthalpy changes which can’t be found experimentally using calorimetry, e.g.:
3C (s) + 4H2 (g) → C3H8(g)
ΔfH (propane) can’t be found experimentally as hydrogen and carbon don’t react under standard conditions
Calculating ΔHr from ΔHf using Hess’s Law energy cycles
You can see the relationships on the following diagram:

The enthalpy change from elements to products (direct route) is equal to the enthalpy change of elements forming reactants and then products (indirect route)
The products can be formed:
Directly from the elements = ΔH2
OR
Indirectly from the elements = ΔH1 + ΔHr
Equation
ΔH2 = ΔH1 + ΔHr
Therefore for energy to be conserved,
ΔHr = ΔH2 – ΔH1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There are two rules that you can use to help with your calculations using enthalpy changes of formation and combustion
Using enthalpy changes of formation, ΔHf
ΔrH = ∑ΔHf(products) - ∑ΔHf(reactants)
Using enthalpy changes of combustion, ΔHc
ΔrH = ∑ΔHc(reactants) - ∑ΔHc(products)
Calculating ΔHr from ΔHf using Hess’s Law energy cycles
Knowing the enthalpy change of formation, ΔHf, allows us to determine the overall enthalpy change of a reaction, ΔHr
To do this, we follow these steps:
Write the equation for the reaction
Write the elements with the correct number of moles and state symbols underneath
Draw upwards pointing arrows to each compound
Write the appropriate values on the arrows and multiply by the number of moles
In a cycle, go from the reactants to the products, changing the sign of the value if the arrow points in the opposite direction
Worked Example
Calculating the enthalpy change of reaction
Use the information in the table to calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction:
NH4NO3 (s) + ½C (s) → N2 (g) + 2H2O (g) + ½CO2 (g)
Substance | C (s) | N2 (g) | H2O(g) | CO2 (g) | NH4NO3 (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
∆Hfө / kJ mol–1 | 0 | 0 | –242 | –394 | –365 |
Answer:
Step 1: Write the balanced equation

Step 2: Write the elements with the correct number of moles and state symbols underneath

Step 3: Draw upwards pointing arrows to each compound

Step 4: Write the appropriate values on the arrows and multiply by the number of moles

Step 5: In a cycle, go from the reactants to the products, changing the sign of the value if the arrow points in the opposite direction

ΔHrө = +365 - 484 - 197 = -316 kJ mol-1
The sign on -365 needs reversing as the cycle goes in the opposite direction to the arrow pointing upwards
There is no need to draw arrows from the elements to carbon and nitrogen as ΔHfө is 0 for elements
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Keep your enthalpy values inside their own brackets so that you don't accidentally lose a minus sign
Calculating ΔHf from ΔHc using Hess’s Law energy cycles
It can be difficult to find the enthalpy change of formation of compounds experimentally
However, many enthalpy changes of combustion can be measured experimentally so these can be used to find the enthalpy of formation
To do this, we follow these steps:
Write the equation for the formation of the compound
Write the combustion products below the equation
Draw downward pointing arrows from each substance to its combustion products
Write values on the arrows and multiply by the number of moles
In a cycle, go from the reactants to the products, changing the sign of the value if the arrow points in the opposite direction
Worked Example
Calculating the enthalpy change of formation
Using the data provided, calculate the standard enthalpy change of formation, ΔHf, of propanone.
3C (s) + 3H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → CH3COCH3 (l)
Substance | C (s) | H2 (g) | CH3COCH3 (l) |
|---|---|---|---|
∆HCө / kJ mol–1 | -394 | -286 | -1821 |
Answer:
Step 1: Write the balanced equation

Step 2:Write the combustion products below the equation

Step 3: Draw downward pointing arrows from each substance to its combustion product

Step 4: Write the appropriate values on the arrows and multiply by the number of moles

Step 5: In a cycle, go from the reactants to the products, changing the sign of the value if the arrow points in the opposite direction

ΔHfө = -1182 - 858 + 1821 = -219 kJ mol-1
The sign on -1821 needs reversing as the cycle goes in the opposite direction to the arrow pointing to the combustion products
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don't forget to make sure the number of atoms for each element is balanced when drawing your cycle.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?