Atomic Structure & Mass Spectrometry (OCR A Level Chemistry A) : Revision Note
Isotopes & Relative Atomic Mass
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons.
Isotopes can also be described as atoms of the same elements but with different mass numbers
Therefore, the mass of an element is given as relative atomic mass (Ar) by using the average mass of the isotopes
The relative atomic mass of an element can be calculated by using the relative abundance values by using the following equation:
The relative abundance of an isotope is either given or can be read off the mass spectrum
Worked Example
Calculating the relative atomic mass of oxygen
A sample of oxygen contains the following isotopes:
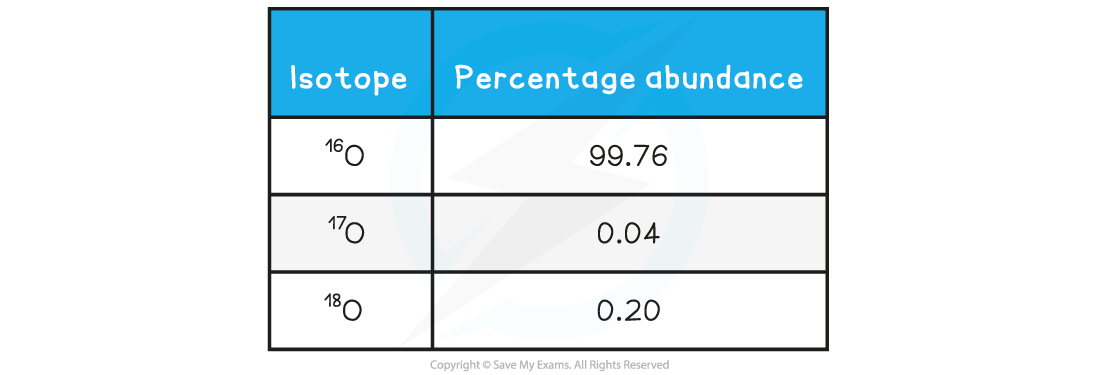
What is the relative atomic mass of oxygen in this sample, to 2 decimal places?
16.00
17.18
16.09
17.00
Answer The correct answer option is A
Ar =
Ar = 16.0044
Ar = 16.00
Mr from Mass Spectra
The percentage abundance of the isotopes in an element can be found by the use of a mass spectrometer
The basic processes of mass spectrometry are:
The sample is vapourised
The sample is ionised to form positive ions
The ions are accelerated
Heavy ions move slower / are less deflected
The ions are detected as a mass-to-charge ratio, written as
Each ion produces a signal, so the larger the signal, the greater the abundance
The mass spectra produced can be used to calculate the relative atomic mass of an element and its isotopes
Worked Example
Calculating the relative atomic mass of boron Calculate the relative atomic mass of boron using its mass spectrum, to 2dp:

Answer
Ar =
Ar = 10.801
Ar = 10.80
Relative molecular and formula mass
These are essentially the same ideas
Relative molecular mass is applied to chemicals that have a fixed formula in terms of the number of atoms involved, e.g. ethanol, C2H5OH, contains two carbon atoms, six hydrogen atoms and one oxygen
Relative formula mass is applied to chemicals that use an empirical formula to represent them, e.g. calcium chloride, CaCl2, is an ionic lattice containing a ratio of 1 calcium ion : 2 chloride ions throughout the structure
These terms are often mis-used, with relative molecular mass being applied to any compound regardless of its composition
The relative molecular and formula mass are both calculated by adding up the relative atomic masses of all the component atoms
Worked Example
Calculate:
The relative molecular mass of ethanol, C2H5OH
The relative formula mass of calcium chloride, CaCl2
(Ar values: C = 12.0, H = 1.0, O = 16.0, Ca = 40.1, Cl = 35.5)
Answers
Answer 1: (2 x C) + (5 x H) + O + H → (2 x 12.0) + (5 x 1.0) + 16.0 + 1.0 = 46.0
Answer 2: Ca + (2 x Cl) → 40.1 + (2 x 35.5) = 111.1

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
