Equilibrium Constants, Kc & Kp (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Chemistry) : Revision Note
Equilibrium Constant: Concentrations
Equilibrium expression & constant
The equilibrium expression is an expression that links the equilibrium constant, Kc, to the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium taking the stoichiometry of the equation into account
So, for a given reaction:
aA + bB ⇌ cC + dD
Kc is defined as:
Where:
[A] and [B] are the equilibrium concentrations of A and B, in mol dm-3
[C] and [D] are the equilibrium concentrations of C and D, in mol dm-3
a, b, c and d are the respective number of moles of each reactant and product
Solids are ignored in equilibrium expressions
The Kc of a reaction is specific and only changes if the temperature of the reaction changes
Worked Example
Deduce the equilibrium expression for the following reactions:
Ag+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq)
Ag (s) + Fe3+ (aq)
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
2NH3 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Answer
1. Ag+ (aq) + Fe2+ (aq) Ag (s) + Fe3+ (aq)
Kc =
2. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
Kc =
3. 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g)
Kc =
Mole Fraction & Partial Pressure
Partial pressure
For reactions involving mixtures of gases, the equilibrium constant Kp is used as it is easier to measure the pressure than the concentration for gases
The partial pressure of a gas is the pressure that the gas would have if it was in the container all by itself
The total pressure is the sum of the partial pressure:
Ptotal = PA + PB + PC + .......
Ptotal = total pressure
PA, PB, PC = partial pressures
How partial pressures contribute to total pressure
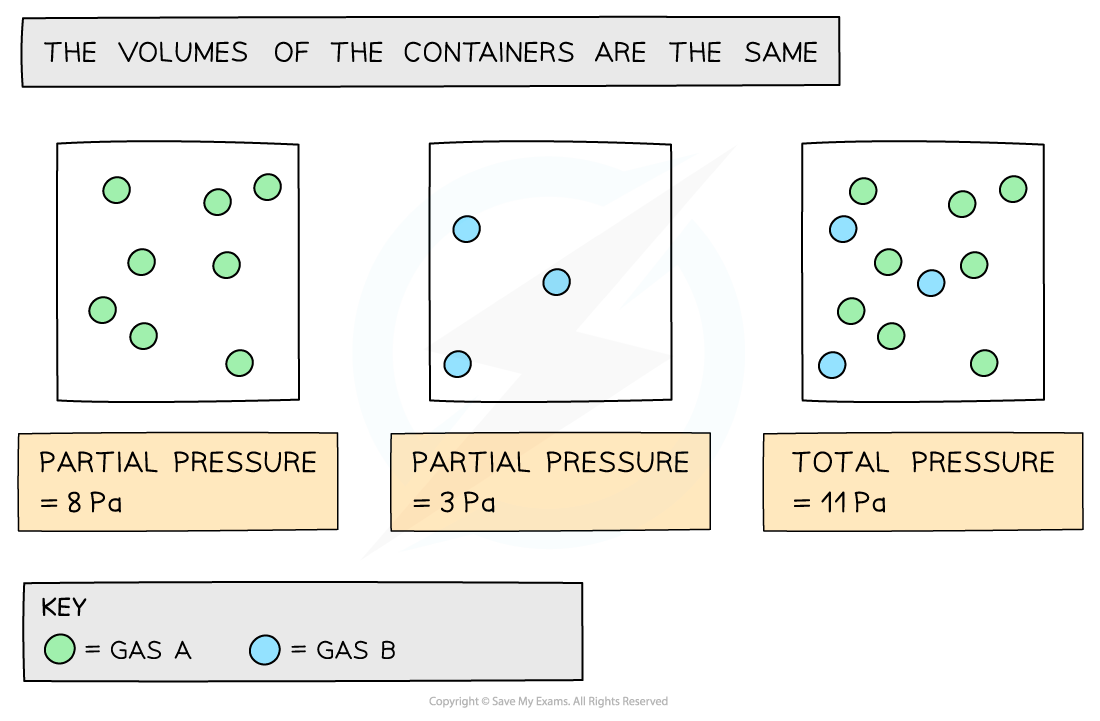
Partial pressures can be added together to calculate the total pressure
Mole fraction
The mole fraction of a gas is the ratio of moles of a particular gas to the total number of moles of gas present
To calculate the partial pressures of each gas the following relationship can be used:
The sum of the mole fractions should add up to 1.00, while the sum of the partial pressures should add up to the total pressure
Equilibrium Constant: Partial Pressures
Equilibrium expressions involving partial pressures
Equilibrium expressions in terms of partial pressures are written similarly to those involving concentrations with a few differences:
Comparing Kp and Kc expressions
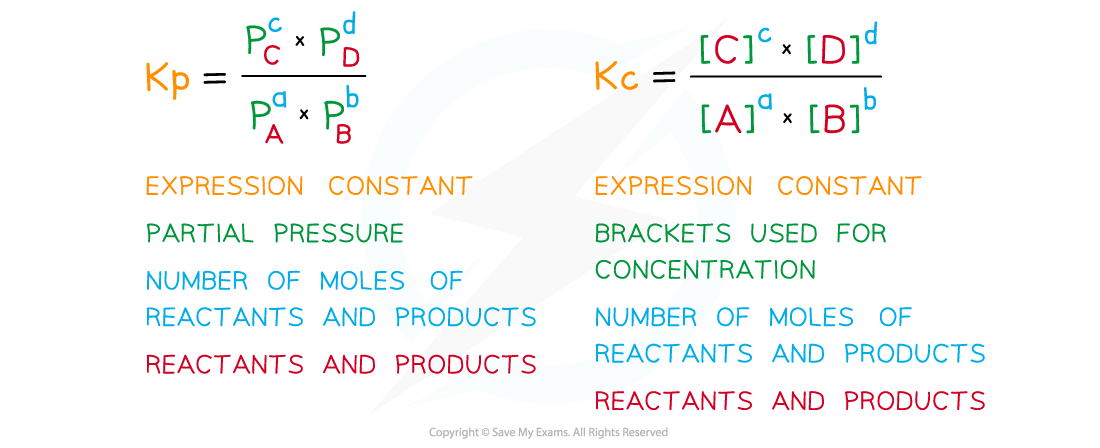
The process of writing the expressions is similar, but there is a different presentation and different information required
Worked Example
Deducing equilibrium expressions of gaseous reactions
Deduce the equilibrium expression for the following reactions:
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g)
2NH3 (g)
N2O4 (g)
2NO2 (g)
2SO2 (g) + O2 (g)
2SO3 (g)
Answer
1. N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
Kp =
2. N2O4 (g) 2NO2 (g)
Kp =
3. 2SO2 (g) + O2 (g) 2SO3 (g)
Kp =

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
