The Common Ion Effect (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Chemistry) : Revision Note
The Solubility Product & the Common Ion Effect
A saturated solution is a solution that contains the maximum amount of dissolved salt
If a second compound, which has an ion in common with the dissolved salt, is added to the saturated solution, the solubility of the salt reduces and a solid precipitate will be formed
This is also known as the common ion effect
For example, if a solution of potassium chloride (KCl) is added to a saturated solution of silver chloride (AgCl) a precipitate of silver chloride will be formed
The chloride ion is the common ion
The solubility product can be used to predict whether a precipitate will form or not
A precipitate will form if the product of the ion concentrations is greater than the solubility product (Ksp)
Common ion effect in silver chloride
When a KCl solution is added to a saturated solution of AgCl, an AgCl precipitate forms
In a saturated AgCl solution, the silver chloride is in equilibrium with its ions
AgCl (s) ⇌ Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq)
When a solution of potassium chloride is added:
Both KCl and AgCl have the common Cl- ion
There is an increased Cl- concentration so the equilibrium position shifts to the left
The increase in Cl- concentration also means that [Ag+ (aq)] [Cl-(aq)] is greater than the Ksp for AgCl
As a result, the AgCl is precipitated
The common ion effect with KCl (aq) and AgCl (aq)
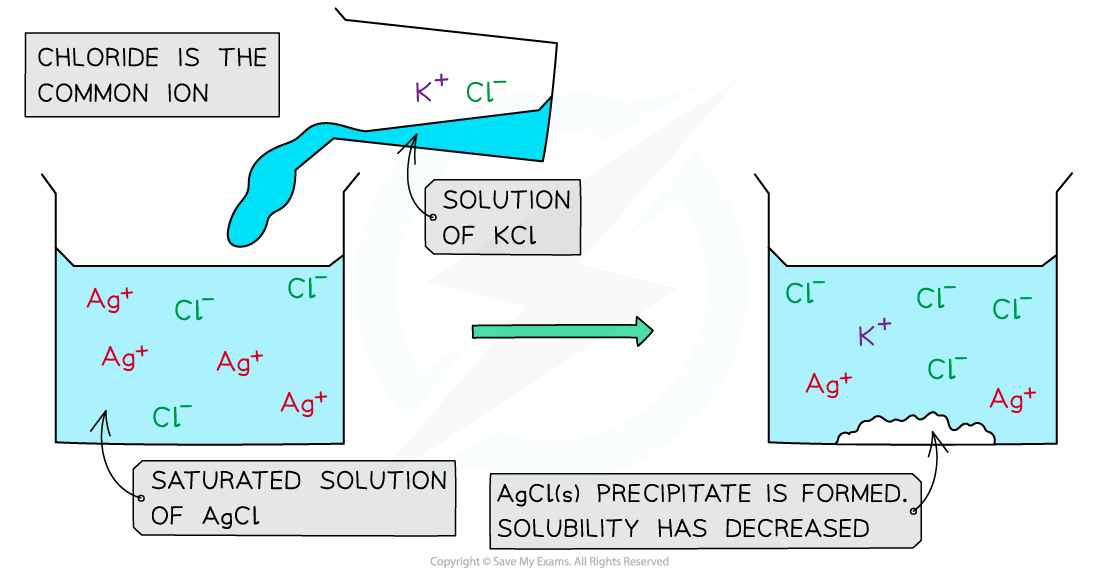
The addition of potassium chloride to a saturated solution of silver chloride results in the precipitate of silver chloride
Worked Example
Calculations using the Ksp values and the concentration of the common ion
Predict whether a precipitate of CaSO4 will form if a saturated solution of 1.0 x 10-3 mol dm-3 CaSO4 is mixed with an equal volume of 1.0 x 10-3 mol dm-3 Na2SO4.
Ksp CaSO4 = 2.0 x 10-5 mol2 dm-6.
Answer
Step 1: Determine the equilibrium reaction of CaSO4:
CaSO4 (s) ⇌ Ca2+ (aq) + SO42- (aq)
Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression for Ksp:
Ksp = [Ca2+ (aq)] [SO42- (aq)]
Step 3: Determine the concentrations of the ions:
There are equal volumes of each solution
This means that the total solution was diluted by a factor of 2
The new concentration of the Ca2+ ion is halved:
[Ca2+] =
[Ca2+] = 5.0 x 10-4 mol dm-3
The sulfate ion concentration remains the same as it is a common ion and its concentration is the same in both solutions
Step 4: Substitute the values into the expression:
Product of the ion concentrations = [Ca2+ (aq)] x [SO42- (aq)]
Product of the ion concentrations = (5.0 x 10-4) x (1.0 x 10-3)
Product of the ion concentrations = 5.0 x 10-7 mol2 dm-6
Step 5: Determine if a precipitate will form:
As the product of the ion concentration (5.0 x 10-7 mol dm-3 ) is smaller than the Ksp value (2.0 x 10-5 mol2 dm-6), the CaSO4 precipitate will not be formed

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
