Solubility Product (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Chemistry) : Revision Note
The Solubility Product, Ksp
Solubility is defined as the number of grams or moles of compound needed to saturate 100 g of water, or it can also be defined in terms of 1 kg of water, at a given temperature
For example, sodium chloride (NaCl) is considered to be a soluble salt as a saturated solution contains 36 g of NaCl per 100 g of water
Lead chloride (PbCl2) on the other hand is an insoluble salt as a saturated solution only contains 0.99 g of PbCl2 per 100 g of water
Solubility product
The solubility product (Ksp) is:
The product of the concentrations of each ion in a saturated solution of a relatively soluble salt
At 298 K
Raised to the power of their relative concentrations
C (s) ⇌ aAx+ (aq) + bBy- (aq)
Ksp = [Ax+ (aq)]a [By- (aq)]b
When an undissolved ionic compound is in contact with a saturated solution of its ions, an equilibrium is established
The ions move from the solid to the saturated solution at the same rate as they move from the solution to the solid
For example, the undissolved magnesium chloride (MgCl2) is in equilibrium with a saturated solution of its ions
MgCl2 (s) ⇌ Mg2+ (aq) + 2Cl- (aq)
Ions in a saturated solution
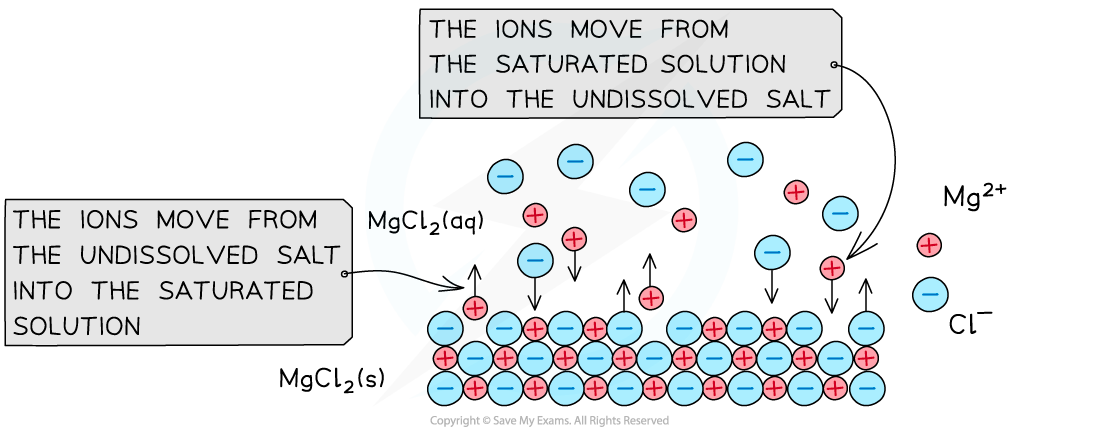
When the undissolved MgCl2 salt comes in contact with its ions in a saturated solution, an equilibrium between the salt and ions is established
The solubility product for this equilibrium is:
Ksp = [Mg2+ (aq)] [Cl- (aq)]2
The Ksp is only useful for sparingly soluble salts
The smaller the value of Ksp, the lower the solubility of the salt
Ksp Expressions
The general equilibrium expression for the solubility product (Ksp) is:
C (s) ⇌ aAx+ (aq) + bBy- (aq)
Ksp = [Ax+ (aq)]a [By- (aq)]b
Worked Example
Expressing Ksp of ionic compounds
Give the equilibrium expressions, including units, for the solubility products of the following ionic compounds:
Ca(OH)2
Fe2O3
SnCO3
Answer 1 - Ca(OH)2:
Step 1 - Write the balanced chemical equation:
Ca(OH)2 (s)
Ca2+ (aq) + 2OH– (aq)
Step 2 - Write the Ksp expression:
Ksp = [Ca2+ (aq)] [OH– (aq)]2
Step 3 - Deduce the units:
Ksp = [mol dm-3] x [mol dm-3]2
Ksp = [mol dm-3]3
Ksp = mol3 dm-9
Answer 2 - Fe2O3:
Step 1 - Write the balanced chemical equation:
Fe2O3 (s)
2Fe3+ (aq) + 3O2– (aq)
Step 2 - Write the Ksp expression:
Ksp = [Fe3+ (aq)]2 [O2– (aq)]3
Step 3 - Deduce the units:
Ksp = [mol dm-3]2 x [mol dm-3]3
Ksp = [mol dm-3]5
Ksp = mol5 dm-15
Answer 3 - SnCO3:
Step 1 - Write the balanced chemical equation:
SnCO3 (s)
Sn2+ (aq) + CO32– (aq)
Step 2 - Write the Ksp expression:
Ksp = [Sn2+ (aq)] [CO32– (aq)]
Step 3 - Deduce the units:
Ksp = [mol dm-3] x [mol dm-3]
Ksp = [mol dm-3]2
Ksp = mol2 dm-6

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
