Carboxylic Acids (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Chemistry) : Revision Note
Production of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are compounds with a -COOH functional group
They can be prepared by a series of different reactions
Oxidation of primary alcohols & aldehydes
Carboxylic acids can be formed from the oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes by either acidified K2Cr2O7 or acidified KMnO4 and reflux
The oxidising agents themselves get reduced causing the solutions to change colour
In K2Cr2O7 the orange dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) are reduced to green Cr3+ ions
In KMnO4 the purple manganate ions (MnO4-) are reduced to colourless Mn2+ ions
Oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes
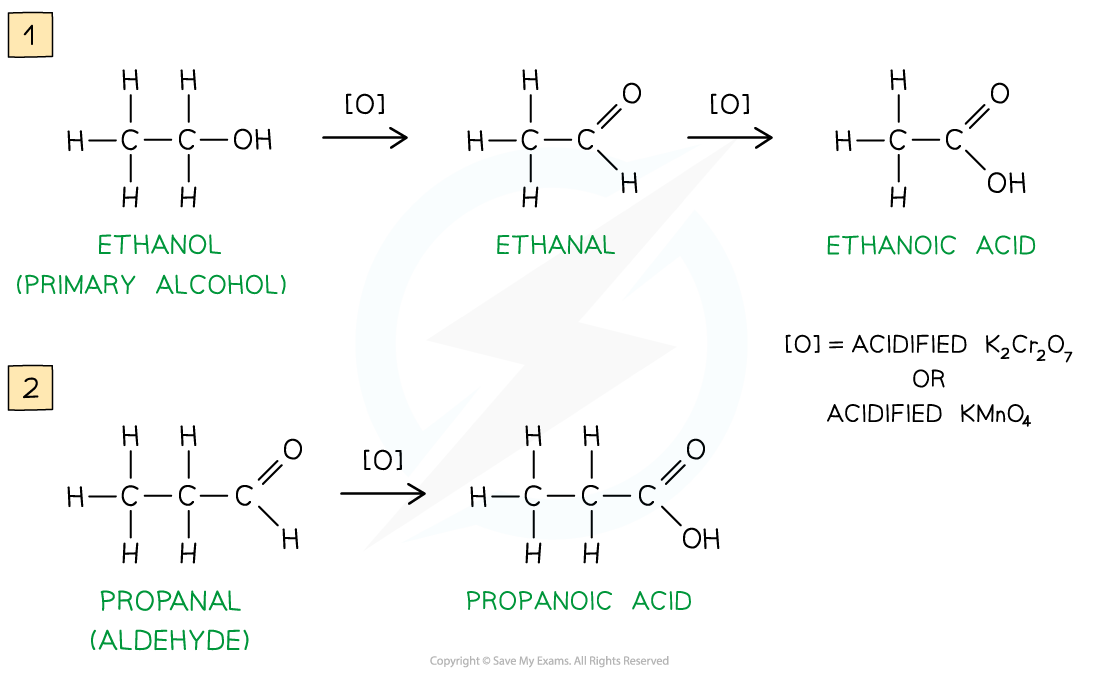
Oxidation of primary alcohols (1) and aldehydes (2) gives carboxylic acids
Hydrolysis of nitriles
Carboxylic acids can also be prepared from the hydrolysis of nitriles using either dilute acid or dilute alkali followed by acidification
Hydrolysis by dilute acid results in the formation of a carboxylic acid and ammonium salt
Hydrolysis by dilute alkali results in the formation of a sodium carboxylate salt and ammonia; Acidification is required to change the carboxylate ion into a carboxylic acid
The -CN group at the end of the hydrocarbon chain is converted to a -COOH group
Hydrolysis of nitriles

Hydrolysis of nitriles by either dilute acid (1) or dilute alkali and acidification (2) will form a carboxylic acid
Hydrolysis of esters
Esters are formed from the condensation reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid
Hydrolysis of esters by dilute acid or dilute alkali and heat followed by acidification will reform the alcohol and the carboxylic acid
Hydrolysis by dilute acid is a reversible reaction where an equilibrium is established
Hydrolysis by dilute alkali is an irreversible reaction as all the ester is broken down to form a sodium carboxylate salt and an alcohol; acidification is required to change the carboxylate ion into a carboxylic acid
Hydrolysis of esters

Hydrolysis of esters by either dilute acid (1) or dilute alkali and heat followed acidification (2) will form a carboxylic acid
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids
Carboxylic acids are weak acids as they do not completely dissociate in water
This means that the position of the equilibrium lies to the left and that the concentration of H+ is much smaller than the concentration of the carboxylic acid
The solution has a pH value of less than 7
Example dissociation of a carboxylic acid

Carboxylic acids are weak acids that do not fully dissociate in water, the position of the equilibrium lies to the left
Carboxylic acids are reactive compounds which can undergo many types of reactions including:
Redox reactions with reactive metals
Neutralisation reactions with alkali
Acid-base reactions with carbonates
Esterification with alcohols
Reduction by LiAlH4
DIfferent reactions of carboxylic acids

Carboxylic acids undergo a wide variety of reactions

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
