Producing Aldehydes & Ketones (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 9701
Production of Aldehydes & Ketones
Aldehydes and ketones are carbonyl compounds containing a C=O group
They can be prepared from the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols respectively
Oxidising agents
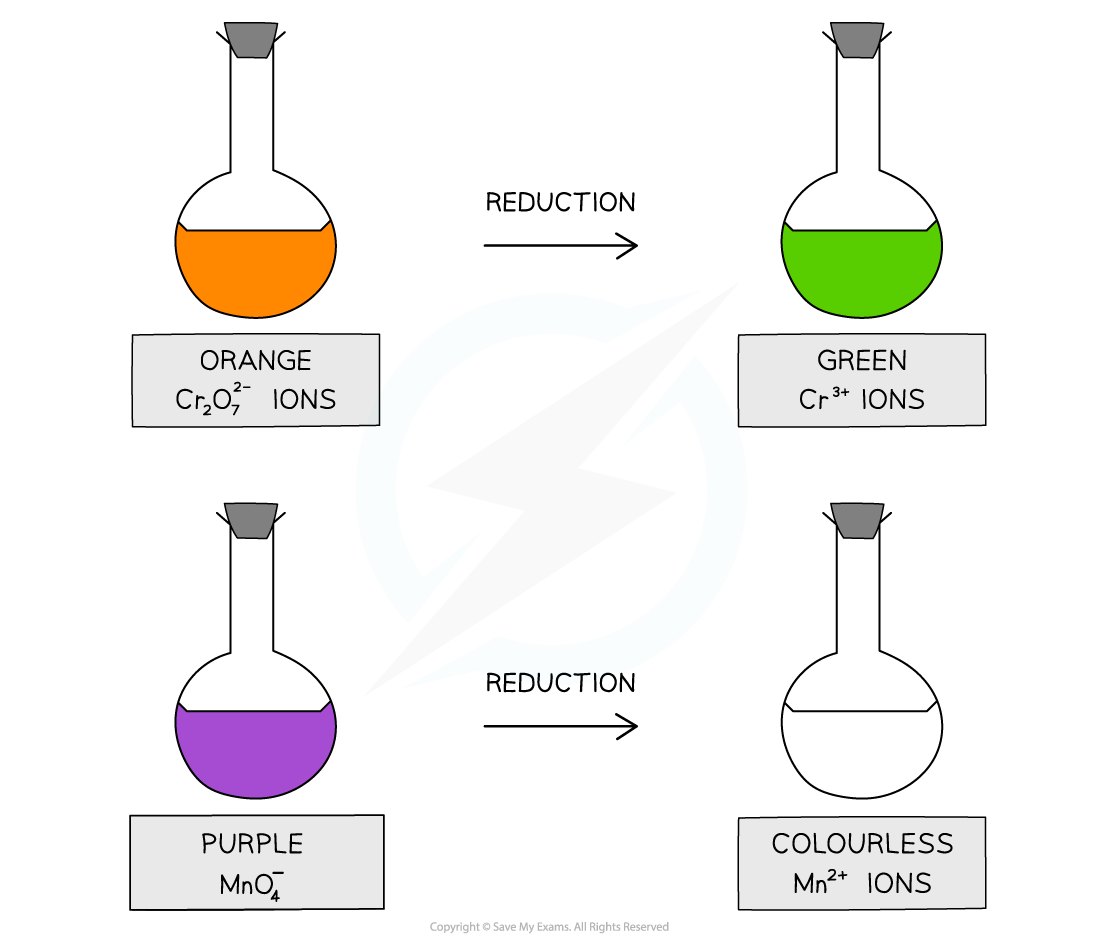
The oxidising agents used to prepare aldehydes and ketones from alcohols include acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) and acidified potassium manganate (KMnO4)
Acidified with dilute sulfuric acid, potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, is an orange oxidising agent
When the alcohols are oxidised the orange dichromate ions (Cr2O72-) are reduced to green Cr3+ ions
Acidified with dilute sulfuric acid, potassium manganate(VII), KMnO4 is a purple oxidising agent
When the alcohols are oxidised the purple manganate ions (MnO4-) are reduced to colourless Mn2+ ions
The colour change in common oxidising agents
Synthesis of aldehydes
To make an aldehyde, warm primary alcohol is slowly added to the oxidising agent
The formed aldehyde has a lower boiling point than the alcohol and can therefore be distilled off as soon as it forms
The aldehyde is then condensed into a liquid and collected
Using distillation to oxidise a primary alcohol to an aldehyde

Synthesis of ketones
To make a ketone, warm secondary alcohol is slowly added to the oxidising agent
Since the formed ketone cannot be further oxidised it does not need to be distilled off straightaway after it has been formed
Oxidation of propan-2-ol

Examiner Tips and Tricks
If the aldehyde formed is not distilled off, further refluxing with excess oxidising agent will oxidise the aldehyde to a carboxylic acid

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?