pKₐ (AQA A Level Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 7405
pKₐ
The range of values of Ka is very large and for weak acids, the values themselves are very small numbers
Table of Ka values
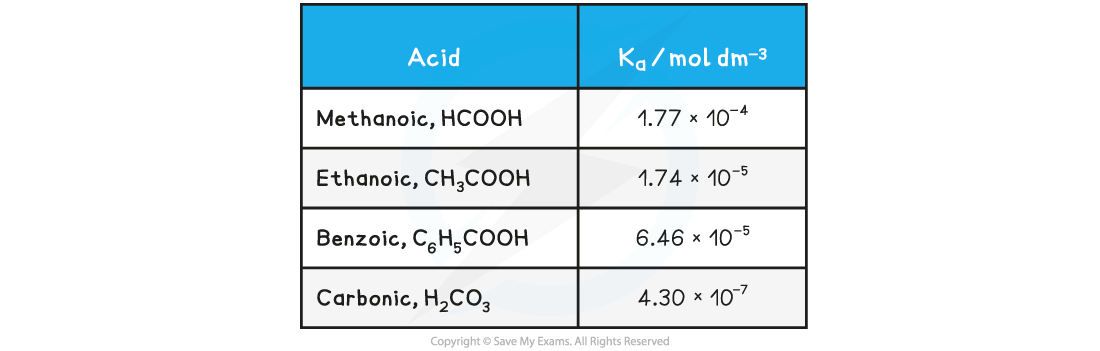
For this reason it is easier to work with another term called pKa
The pKa is the negative log of the Ka value, so the concept is analogous to converting [H+] into pH values
pKa = -logKa
Looking at the pKa values for the same acids:
Table of pKa values
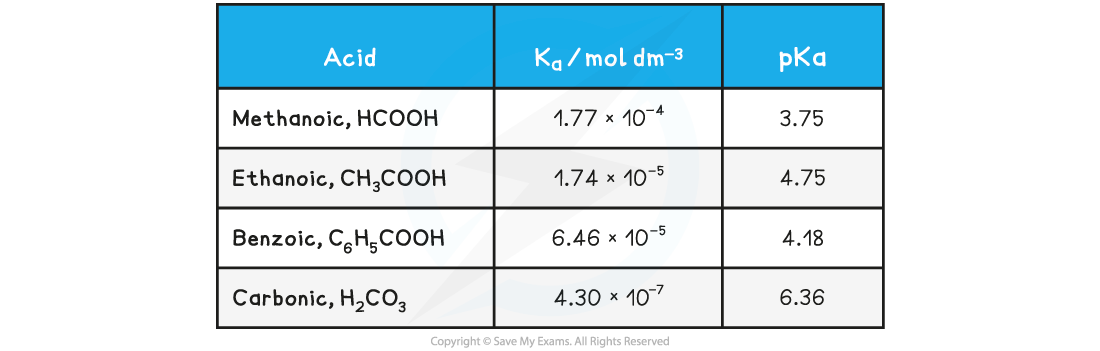
The range of pKa values for most weak acids lies between 3 and 7
Worked Example
Finding Ka and pKa
At 298 K, a solution of 0.100 mol dm-3 ethanoic acid has a hydrogen ion concentration of 1.32 x 10-3 mol dm-3. Calculate the Ka & pKa of the acid.
Answer
Step 1: Write down the equation for the partial dissociation of ethanoic acid
CH3COOH (aq) ⇌ H+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq)
Step 2: Write down the equilibrium expression to find Ka
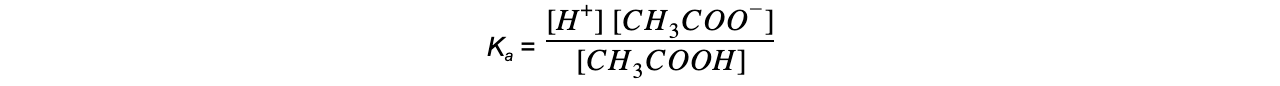
Step 3: Simplify the expression
The ratio of H+ to CH3COO- is 1:1
The concentration of H+ and CH3COO- is, therefore, the same
The equilibrium expression can be simplified to:
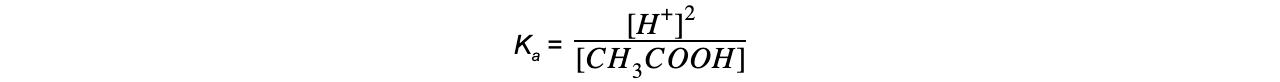
Step 4: Substitute the values into the expression to find Ka
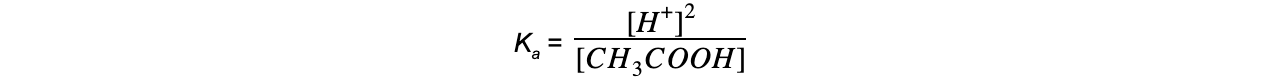
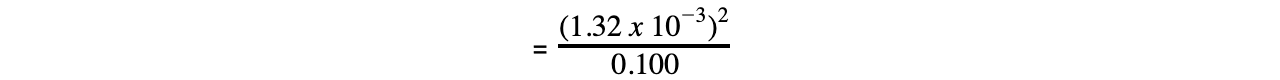
= 1.74 x 10-5
Step 5: Determine the units of Ka
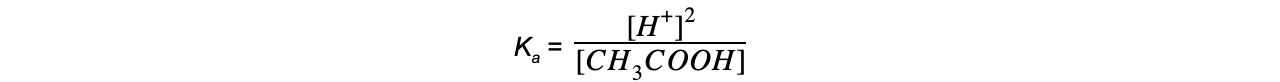
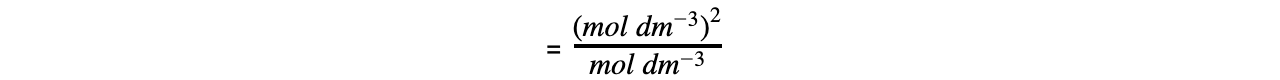
= mol dm-3
The value of Ka is therefore 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3
Step 6: Find pKa
pKa = - log10Ka
= - log10 (1.74 x 10-5)
= 4.76
Kₐ from pH
How are Ka values found?
If we neutralise a weak acid with a strong base such sodium hydroxide the equation for the reaction is:
HA (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaA (aq) + H2O (l)
HA (aq) + OH- (aq) → A- (aq) + H2O (l)
When half of the acid has been neutralised the concentration of [HA] is equal to the concentration of [A-]
Since the acid is poorly dissociated it is assumed all the A- comes from the product rather than HA dissociating
This simplifies the expression to

In practice, to find Ka the pH of a weak acid is measured as it is neutralised by a strong base and a graph is plotted for pH versus volume of base added
This type of graph is known as a pH titration curve
A vertical tie-line is drawn to the curve at half the volume of base needed for neutralisation
At this point pKa = pH, so by reading off the pH value from the y-axis, you find the Ka of the acid
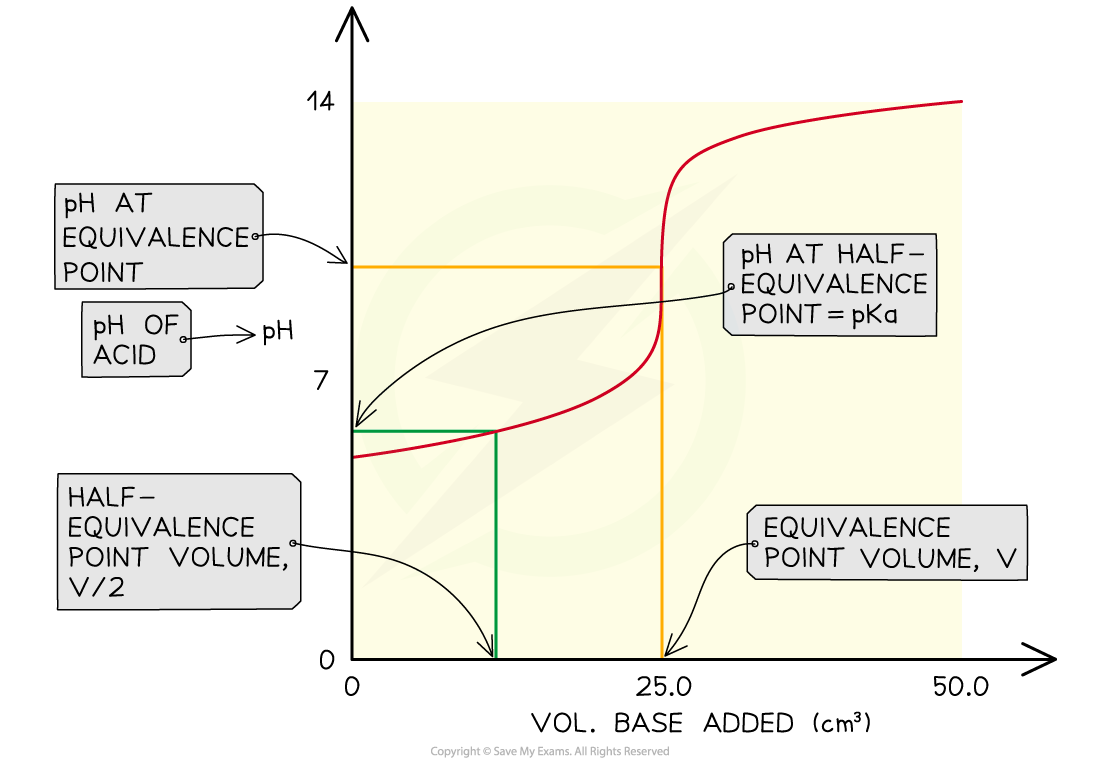
Finding the Ka of a weak acid from a pH titration curve
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can regard the symbol p as meaning -log10 of a value. You don't need to include the 10 as 'log' means log base 10. If a natural logarithm (base e) is required it is given the symbol ln. Other uses of p include pOH and pKw . The latter gives a useful shortcut in problem-solving:
Kw = [H+][OH-] = 1.00 x 10-14 mol2 dm-6 at 298 K
-logKw = -log[H+] + (-log[OH-]) = -log(1.00 x 10-14)
pKw = pH + pOH = 14.00

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?