Gibbs Free Energy (AQA A Level Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 7405
Gibbs Free Energy
Gibbs free energy
As we have seen in the previous sections, the feasibility of a reaction is determined by two factors, the enthalpy change and the entropy change
The two factors come together in a fundamental thermodynamic concept called the Gibbs free energy (G)
The Gibbs equation is:
ΔGꝋ = ΔHreactionꝋ - TΔSsystemꝋ
The units of ΔGꝋ are in kJ mol-1
The units of ΔHreactionꝋ are in kJ mol-1
The units of T are in K
The units of ΔSsystemꝋ are in J K-1 mol-1(and must therefore be converted to kJ K-1 mol-1 by dividing by 1000)
Calculating ΔGꝋ
There are two ways you can calculate the value of ΔGꝋ
From ΔHꝋ and ΔSꝋ values
From ΔGꝋ values of all the substances present
Worked Example
ΔGꝋ from ΔHꝋ and ΔSꝋ valuesCalculate the free energy change for the following reaction:
2NaHCO3 (s) → Na2CO3 (s) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
ΔHꝋ = +135 kJ mol-1 ΔSꝋ = +344 J K-1 mol-1
Answer
Step 1: Convert the entropy value in kilojoules
ΔSꝋ = +344 J K-1 mol-1 ÷ 1000 = +0.344 kJ K-1 mol-1
Step 2: Substitute the terms into the Gibbs Equation
ΔGꝋ = ΔHreactionꝋ - TΔSsystemꝋ
= +135 - (298 x 0.344)
= +32.49 kJ mol-1
The temperature is 298 K since standard values are quoted in the question
Worked Example
ΔGꝋ from other ΔGꝋ valuesWhat is the standard free energy change, ΔGꝋ, for the following reaction?
C2H5OH(l) + 3O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + 3H2O(g)
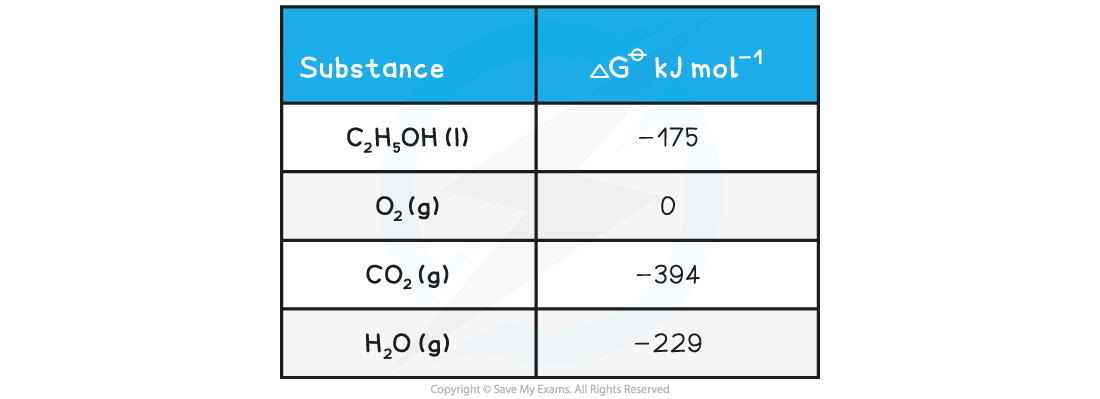
Answer
ΔGꝋ = ΣΔGproductsꝋ - ΣΔGreactantsꝋ
ΔGꝋ = [(2 x CO2 ) + (3 x H2O )] - [(C2H5OH) + (3 x O2)]
ΔGꝋ = [(2 x -394 ) + (3 x -229 )] - [-175 + 0]
ΔGꝋ = -1300 kJ mol-1
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The idea of free energy is what's 'leftover' to do useful work when you've carried out the reaction. The enthalpy change is the difference between the energy you put in to break the chemical bonds and the energy out when making new bonds; the entropy change is the 'cost' of carrying our the reaction, so free energy is what is you are left with!

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?