Mass spectrometry (AQA A Level Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 7405
Interpreting a Mass Spectrum
Mass spectroscopy is an analytical technique used to identify unknown compounds
The molecules in the small sample are bombarded with high energy electrons which can cause the molecule to lose an electron
This results in the formation of a positively charged molecular ion with one unpaired electron
One of the electrons in the pair has been removed by the beam of electrons

The molecular ion can further fragment to form new ions, molecules, and radicals

Fragmentation of a molecule in mass spectroscopy
These fragmented ions are accelerated by an electric field
Based on their mass (m) to charge (z) ratio, the ion fragments are then separated by deflecting them into the detector
Most ions will only gain a charge of 1+ and therefore a ion with mass 12 and charge 1+ will have an m/z value of 12
It is, however, possible for a greater charge to occur. For example, an ion with mass 16 and charge 2+ will have a m/z value of 8
The smaller and more positively charged fragment ions will be detected first as they will get deflected the most and are more attracted to the negative pole of the magnet
Each fragment corresponds to a specific peak with a particular m/z value in the mass spectrum
The base peak is the peak corresponding to the most abundant ion
The m/z is sometimes referred to as the m/e ratio and it is almost always 1:1
Isotopes
Isotopes are different atoms of the same element that contain the same number of protons and electrons but a different number of neutrons.
These are atoms of the same elements but with different mass number
For example, Cl-35 and Cl-37 are isotopes as they are both atoms of the same element (chlorine, Cl) but have a different mass number (35 and 37 respectively)
Mass spectroscopy can be used to find the relative abundance of the isotopes experimentally
The relative abundance of an isotope is the proportion of one particular isotope in a mixture of isotopes found in nature
For example, the relative abundance of Cl-35 and Cl-37 is 75% and 25% respectively
This means that in nature, 75% of the chlorine atoms is the Cl-35 isotope and 25% is the Cl-37 isotope
The heights of the peaks in mass spectroscopy show the proportion of each isotope present

The peak heights show the relative abundance of the boron isotopes: boron-10 has a relative abundance of 19.9% and boron-11 has a relative abundance of 80.1%
Worked Example
Calculating m/z ratio
In a sample of iron, the ions 54Fe2+ and 56Fe3+ are detected. Calculate their m/z ratio and determine which ion is deflected more inside the spectrometer.
Answer

56Fe3+ has a smaller m/z ratio and will therefore be deflected more.
It also has the largest positive charge and will be more attracted to the negative pole of the magnet within the mass spectrometer.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A small m/z value corresponds to fragments that are either small or have a high positive charge or a combination of both.
Deducing Molecular Formula
Each peak in the mass spectrum corresponds to a certain fragment with a particular m/z value
The peak with the highest m/z value is the molecular ion (M+) peak which gives information about the molecular mass of the compound
The molecular ion is the entire molecule that has lost one electron when bombarded with a beam of electrons

The [M+1] peak is a smaller peak which is due to the natural abundance of the isotope carbon-13
The amount of naturally occurring C-13 is a little over 1%, so the [M+1] peak is very small
The height of the [M+1] peak for a particular ion depends on how many carbon atoms are present in that molecule; the more carbon atoms, the larger the [M+1] peak is
For example, the height of the [M+1] peak for an hexane (containing six carbon atoms) ion will be greater than the height of the [M+1] peak of an ethane (containing two carbon atoms) ion
Worked Example
Analysing mass spectra
Determine whether the following mass spectrum corresponds to but-1-ene or pent-1-ene:
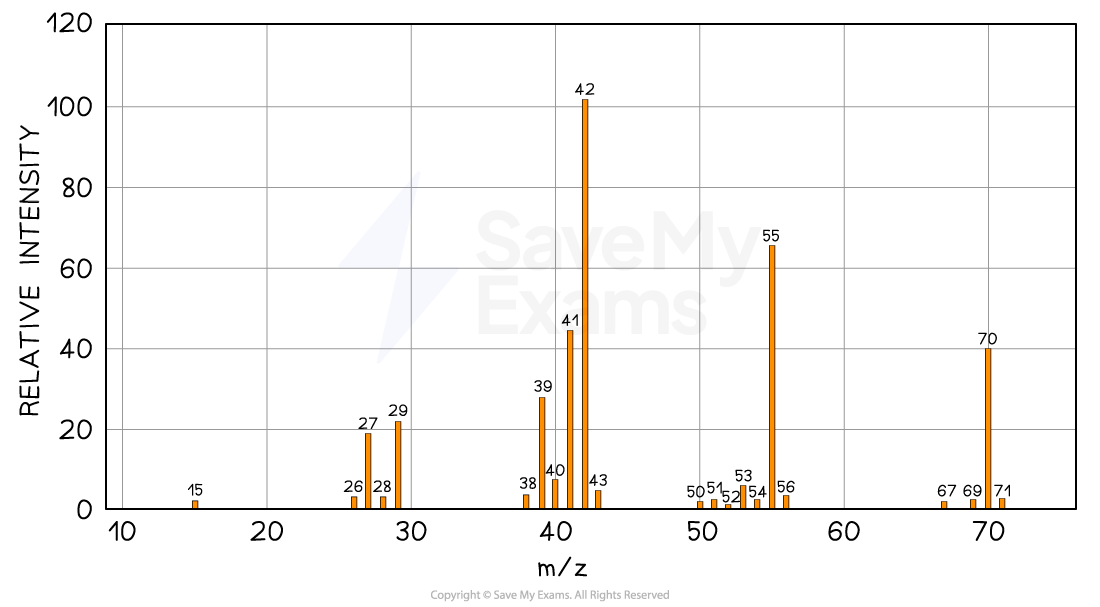
Answer
The mass spectrum corresponds to pent-1-ene as the molecular ion peak is at m/z = 70
The small peak at m/z = 71 is a C-13 peak, which does not count as the molecular ion peak
But-1-ene arises from the C4H8+ ion which has a molecular mass of 56
Pent-1-ene arises from the C5H10+ ion which has a molecular mass of 70
Fragmentation
The molecular ion peak can be used to identify the molecular mass of a compound
However, different compounds may have the same molecular mass
To further determine the structure of the unknown compound, fragmentation is used
Fragments may appear due to the formation of characteristic fragments or the loss of small molecules
For example, a peak at 29 is due to the characteristic fragment C2H5+
Loss of small molecules give rise to peaks at 18 (H2O), 28 (CO), and 44 (CO2)
Alkanes
Simple alkanes are fragmented in mass spectroscopy by breaking the C-C bonds
M/e values of some of the common alkane fragments are given in the table below
m/e Values of Fragments Table


Mass spectrum showing the fragmentation of C10H22
Halogenoalkanes
Halogenoalkanes often have multiple peaks around the molecular ion peak
This is caused by the fact that there are different isotopes of the halogens

Mass spectrum showing different isotopes of bromine in the molecular ion
Alcohols
Alcohols often tend to lose a water molecule giving rise to a peak at 18 below the molecular ion
Another common peak is found at m/e value 31 which corresponds to the CH2OH+ fragment
For example, the mass spectrum of propan-1-ol shows that the compound has fragmented in four different ways:
Loss of H• to form a C3H7O+ fragment with m/e = 59
Loss of a water molecule to form a C3H6+ fragment with m/e = 42
Loss of a •C2H5 to form a CH2OH+ fragment with m/e = 31
And the loss of •CH2OH to form a C2H5+ fragment with m/e = 29

Mass spectrum showing the fragmentation patterns in propan-1-ol (alcohol)
Worked Example
Ion fragmentation
Which of the following statements about the mass spectrum of CH3Br is correct?
A. There is one peak for the molecular ion with an m/e value of 44
B. There is one peak for the molecular ion with an m/e value of 95
C. The last two peaks have abundances in the ratio 3:1 and occur at m/e values of 94 and 96
D. The last two peaks are of equal size and occur at m/e values of 94 and 96
Answer
The correct answer is option D
Bromomethane (CH3Br) can produce 3 peaks
CH381Br → [CH381Br]+ + e− at m/e 96
CH379Br → [CH379Br]+ + e− at m/e 94
CH3Br → [CH3]+ + •Br at m/e 15
The last two peaks (which correspond to the molecular ion peak) therefore are equal in size and occur at m/e values of 94 and 96

Worked Example
Alcohol fragmentation
Which alcohol is not likely to have a fragment ion at m/e at 43 in its mass spectrum?
A. (CH3)2CHCH2OH
B. CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3
C. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH
D. CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3
Answer
The correct answer is option D
Because a line at m/e = 43 corresponds to an ion with a mass of 43 for example:
[CH3CH2CH2]+
[(CH3)2CH]+
2-butanol is not likely to have a fragment at m/e = 43 as it does not have either of these fragments in its structure.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?