Hess' Law (AQA A Level Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 7405
Using Hess's Law
Calculating ΔHr from ΔHf using Hess’s Law energy cycles
The products can be directly formed from the elements = ΔH2
OR
The products can be indirectly formed from the elements = ΔH1 + ΔHr

The enthalpy change from elements to products (direct route) is equal to the enthalpy change of elements forming reactants and then products (indirect route)
Equation
ΔH2 = ΔH1 + ΔHr
Therefore,
ΔHr = ΔH2 – ΔH1
Worked Example
Calculating the enthalpy change of reaction
Calculate the ΔHr for the following reaction:
2NaHCO3 (s) → Na2CO3 (s) + CO2 (g) + H2O (I)
The table below shows the standard enthalpy of formations (ΔHfꝋ) relevant to this reaction:

Answer
Step 1: Write the balanced equation at the top

Step 2: Draw the cycle with the elements at the bottom
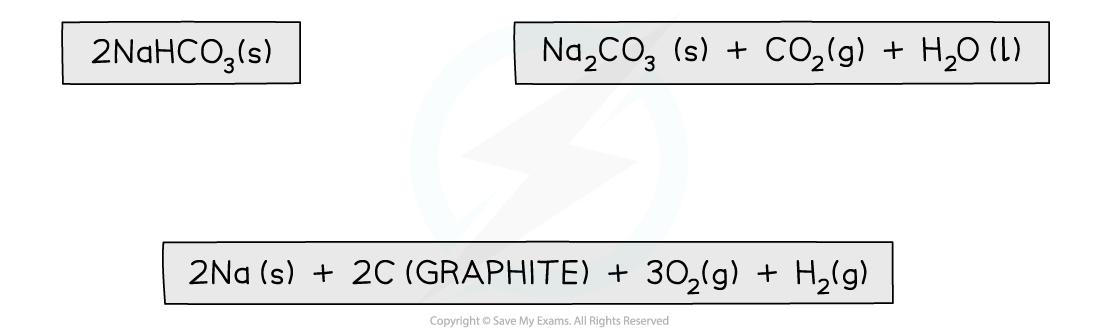
Step 3: Draw in all arrows, making sure they go in the correct directions. Write the standard enthalpy of formations
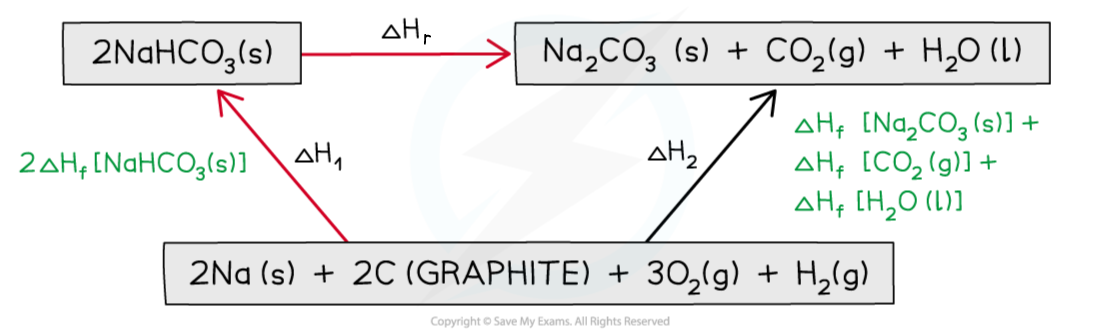
Step 4: Apply Hess’s Law

Calculating average bond energies using Hess's cycles
Bond energies cannot be found directly so enthalpy cycles are used to find the average bond energy
This can be done using enthalpy changes of atomisation and combustion or formation
The enthalpy change of atomisation (ΔHatꝋ ) is the enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from its elements under standard conditions.
Eg. ΔHatꝋ [H2] relates to the equation:
½ H2(g) → H(g)

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?