Conditions that Prompt Trade (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Push factors
Push factors are factors that push a business to expand outside of its own country
When faced with saturated markets or intense competition, businesses may consider engaging in international trade as a way to access new markets, diversify their customer base and gain a competitive advantage
There may be adverse conditions within a domestic market, which may cause a business to look at opportunities in countries abroad
E.g. due to the UK leaving the European Union, some businesses have decided to move their operations outside the country
Sony has moved its headquarters from the UK to the Netherlands
Honda closed a production plant in Wales in 2021
HSBC chose to move its London base to France
Saturated markets
Saturated markets occur when the demand for goods and services has reached a peak, so it becomes challenging for businesses to grow and expand within the local market
This often prompts businesses to explore opportunities in global markets, which can help sustain their growth and profitability
Intense competition
In a competitive market, businesses need to find ways to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive advantage
One way to achieve this is by exploring new markets and expanding their customer base
By exporting goods and services to new markets, businesses can reduce their reliance on a single market and diversify their revenue streams, thereby reducing their exposure to market volatility and competition
Pull factors
Pull factors encourage businesses to operate within markets abroad that present significant growth opportunities
Two pull factors that can prompt trade are economies of scale and risk spreading
Benefiting from economies of scale
Economies of scale usually occur when a business expands its production into new markets abroad
Businesses may also be able to purchase raw materials and labour at lower prices than within their domestic markets
E.g. Ikea expanded into China as there was opportunity for growth with families demanding more furniture due to the removal of the one-child policy
Producing furniture in China helped to reduce transportation and distribution costs
Spreading risk
By accessing multiple markets, businesses can diversify their customer base and reduce their exposure to risks associated with operating in a single market
This can include economic, political and other types of risks that could impact their operations and profitability
E.g. Aston Martin produces motor cars in the UK, but it exports them to multiple markets to reduce exposure to risks associated with operating in a single market
There may be a recession in the UK but not in the USA
Offshoring and outsourcing
Businesses use offshoring and outsourcing to develop their international trade
Offshoring
Offshoring is when a company moves part of the production process, or all of it, to another country
Reasons for offshoring include:
Lower labour costs
Access to raw materials
Access to skilled labour
Advantages and disadvantages of offshoring
Advantages of offshoring | Disadvantages of offshoring |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outsourcing
Outsourcing occurs when a business hires an external organisation to complete certain tasks or business functions
E.g. Apple outsources the production of the iPhone to Foxconn in China
The key reasons for a business choosing to outsource include:
Reduced costs
Allows businesses to focus on core competencies
Easier to comply with rules and regulations in other countries, as they are often less demanding for a local business
The main difference between offshoring and outsourcing is that offshoring is still carried out under the same business, whereas outsourcing is done by a completely different business
Advantages and Disadvantages of Outsourcing
Advantages of outsourcing | Disadvantages of outsourcing |
|---|---|
|
|
Product life cycle extension
The product life cycle represents the value of sales from the time a product is introduced into the market until it is no longer sold
A typical product life cycle
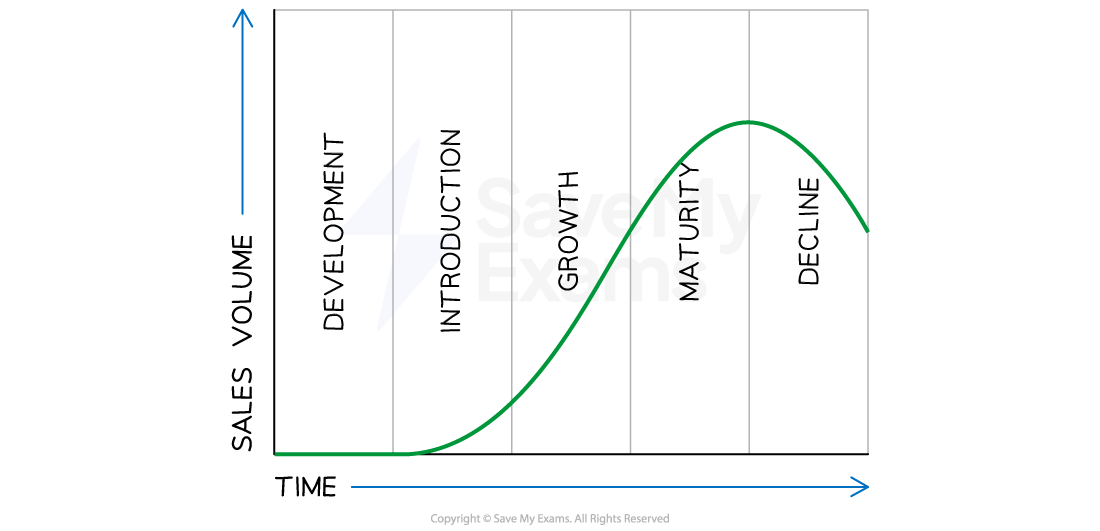
The stages of the product life cycle include introduction, growth, maturity and decline
An extension strategy is a method used by a business to lengthen the life cycle of a product or service
E.g. a business could sell its product in new international markets
A product could reach maturity in one market but could then be introduced into another market
This allows the business to generate more revenue

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?