Human Resources (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
An introduction to human resources
In common with all resources, a business's employees — its human resources — need to be managed
Staff costs can make up a large proportion of a business's costs, so objective monitoring of employee performance is a key element of effective financial and operational control
Businesses commonly monitor the following human resources metrics:
Labour productivity
Labour turnover
Labour retention
Absenteeism
Labour productivity
Labour productivity is a measure of output per employee
It is calculated using the formula
Figures used in this formula are for a specific time period (e.g. a week, month or year)
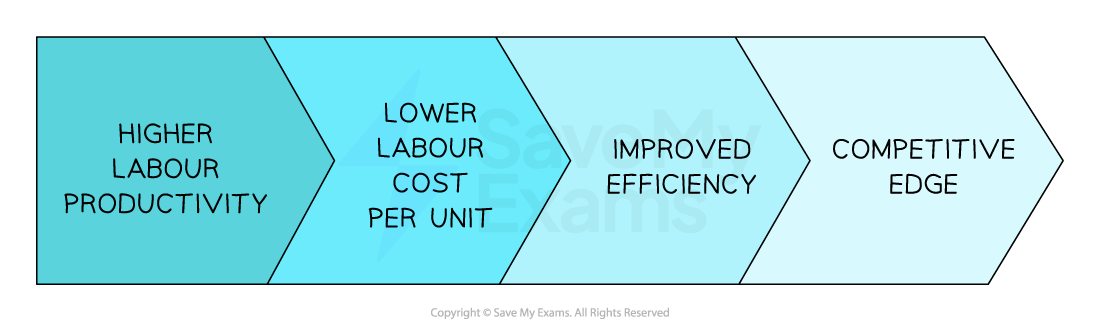
Businesses aim to increase the level of labour productivity to improve competitiveness
Labour productivity and competitiveness
Worked Example
Last year, Marinka Homewares made 424,000 lava lamps with a production workforce of 350 employees. This year, it forecasts that 480,000 lava lamps will be made with a production workforce of 365 employees.
Calculate the percentage increase in annual labour productivity per worker between last year and this year's forecast.
(4)
Step 1: Apply the labour productivity formula to calculate the labour productivity for both years
(2)
Step 2: Calculate the percentage increase between last year and this year
(2)
Labour turnover and retention
Labour turnover measures the proportion of employees leaving a business during a specific time period
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the formula
A rising rate of labour turnover can signal internal human resource management problems, such as:
Poor management, leading to workers losing commitment
A poor recruitment and selection approach, leading to staff leaving soon after starting their job
Low wage levels compared to those that could be earned elsewhere
External factors can also increase labour turnover in a business
A buoyant local economy in which workers are attracted to employment opportunities elsewhere
Improved transport links that provide an opportunity for workers to seek work across a wider geographical area
Consequences of high labour turnover
Problems | Opportunities |
|---|---|
|
|
Worked Example
In 2022, Domus Construction Ltd employed an average of 7,200 workers, six per cent of whom worked at the head office.
During 2022, fifty-four head office employees left the business.
Calculate the labour turnover of Domus Construction's head office in 2022.
(3)
Step 1: Calculate the number of head office workers
(1)
Step 2: Apply the labour turnover formula
(1)
Labour retention
Labour retention measures the proportion of employees remaining with a business during a specific time period
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the formula
A high level of labour retention means that few staff are leaving the business during a given period
Worked Example
In 2022, the University of West Surrey employed an average of 4,240 employees, 265 of whom left the university during the year.
Calculate the University of West Surrey's staff retention rate in 2022.
(2)
Step 1: Calculate the number of employees not leaving
(1)
Step 2: Calculate the retention rate using the formula
(1)
Absenteeism
The absenteeism rate is a measure of the proportion of staff who were absent from work during a specific period of time (e.g. a day, week or month)
It is expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the formula
High levels of absenteeism can cause several problems for a business, including:
Absence due to illness requires sick pay to be paid
Hiring temporary staff to cover for those absent increases costs
Output is likely to be temporarily reduced if staff are key to the production process
Other staff may become demotivated if they have to constantly cover for absent workers
A wider culture of absenteeism may develop
Worked Example
On January 16, twenty-two of Belling Stoneworks Ltd's 189 employees were absent.
Calculate Belling Stoneworks Ltd's absenteeism rate on January 16.
(2)
Step 1: Substitute the values into the formula
(2)
Human resources strategies to improve employee performance
Raising the labour productivity rate, as well as reducing staff turnover and absenteeism rates, are key human resource management objectives
Increased labour productivity will lower the labour cost per unit and contribute to improved competitiveness
More output will be produced, so there is more output to sell — potentially increasing revenue
Money is saved on recruitment, selection and training costs, and a positive group spirit may emerge
Strategies to improve employee performance
Strategy | Explanation |
|---|---|
Offering financial rewards |
|
Offering employees shares in the company |
|
Consultation |
|
Empowerment |
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?