Economic Influences (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
The effects on businesses of changing economic variables
Economic influences can present significant opportunities and threats to business activities
Businesses need to anticipate and respond to changing economic variables in order to maximise their chance of success
The following economic variables need to be considered
Inflation
Inflation is the general rise in prices in an economy over time
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) measures monthly changes in the prices of a range of goods and services and compares these changes to earlier periods, calculating the rate of inflation
In the UK government, monetary policy focuses on achieving a 2% inflation rate and tasks the Bank of England with taking steps to maintain this (e.g. raising the interest rate)
After several decades of relatively low levels of inflation, the UK has recently experienced rapidly increasing levels

Rapid inflation is causing problems for businesses and households in the UK
High or fluctuating levels of inflation can be problematic for businesses for several reasons
Problems caused by inflation
Increased costs
Workers often demand higher wages to compensate for the increase in the cost of living
Suppliers increase the costs of raw materials and components
Utilities, such as electricity, become more expensive
Higher repayments on loans
Interest rates usually rise as the Bank of England uses the base rate as a tool to control inflation, making new and variable-rate borrowing more expensive
Consumers change spending habits
Inflation deters consumers from making significant purchases, and they may reduce demand for their usual lower-priced wants too, e.g cinema tickets
Purchasing on credit becomes more expensive
International competitiveness
Where domestic inflation rates are higher than those in other countries:
UK businesses are less likely to be competitive and lose sales
Imports from overseas competitors are likely to be cheaper than domestic goods
Uncertainty
This occurs when businesses cannot predict prices even in the short term
Survival may need to become the key business objective until stability returns
Spending and contract decisions are likely to be delayed
Exchange rates
The exchange rate is the value of one currency expressed in terms of another
Exchange rates are an important economic influence for businesses that import raw materials and components and for businesses that export their products
Exchange rates fluctuate for a range of reasons, including:
Changing demand for a currency
Economic growth
Changes to interest rates
The impact on business of changes in currency values
Change to currency value | Impact on exporting businesses | Impact on importing businesses |
|---|---|---|
An increase in the value of the £ against other currencies (appreciation) |
|
|
A decrease in the value of the £ against other currencies (depreciation) |
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Many businesses are affected as both importers of raw materials and components and as exporters of goods and services overseas.
It would be unusual for UK-based exporters to wholeheartedly celebrate a weak pound or be entirely dismayed at a strong pound, as the global nature of business means that for many firms, both costs and revenues are affected by exchange rate movements.
For most businesses, exchange rate stability is more important in the medium to long term because volatility makes planning, forecasting and setting objectives very difficult.
Interest rates
The interest rate is a percentage reward offered for saving money, and the percentage charged for borrowing money
Lenders commonly charge interest on borrowing at a rate higher than the Bank of England base rate
They then offer a lower rate on savings and investments
If interest rates rise, businesses will have to pay more on new or variable-rate borrowing, which will increase their costs
Businesses may be less willing to make capital investments when their retained profit may be more profitably invested in savings schemes
Customers are less likely to purchase goods on credit when interest rates are high, leading to a fall in sales
Exporting businesses may see the demand for their products overseas fall, as higher interest rates usually strengthen the value of the domestic currency and make their products comparably more expensive abroad
Taxation and government spending
Governments impose direct and indirect taxes on businesses and households
Direct taxes are levied on income, e.g. income tax and corporation tax
Indirect taxes are levied on spending, e.g. value-added tax (VAT)
The impact of an increase in taxation
Impact | Explanation |
|---|---|
Revenue |
|
Costs |
|
Business decisions |
|
Increased government spending is usually funded by increases in taxes or increases in public sector borrowing
Increased investment spending (e.g. on roads or regeneration) can encourage businesses to invest and lead to economic growth
Increased public sector spending can lead to targeted improvements (e.g in public health or education levels) that can improve productivity
In recent years, the UK government has focused increasingly on the reduction of government spending
Infrastructure projects have been scaled back or cancelled
E.g. the scale of the planned HS2 (High Speed 2) rail line intended to connect London with cities in the North has been significantly reduced
Businesses in cities such as Leeds and Manchester are now unlikely to benefit from more efficient transport links, which affects access to markets and workers
Spending on key services such as health and education has been reduced
Public sector wage rises have been limited
Businesses have been affected by ongoing strike action across the public sector, which has increased employee absence levels and made it difficult to function effectively
The business cycle
The business cycle describes the upturns and downturns in the level of a country’s economic activity (gross domestic product or GDP) over time
A recession occurs when an economy experiences two consecutive quarters (six months) or more of negative economic growth
A boom is defined as a period of time in which an economy experiences increasing/high rates of economic growth
The business cycle over time
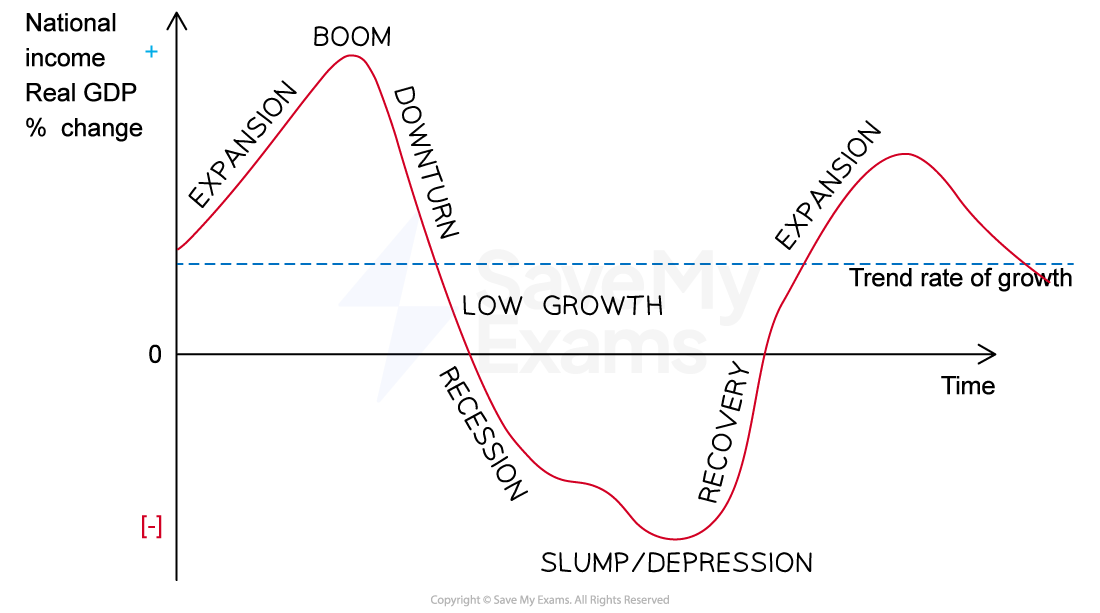
Stage of the business cycle | Characteristics | Impact on businesses |
|---|---|---|
Recession |
|
|
Boom |
|
|
The effects of economic uncertainty on the business environment
Economic uncertainty occurs when it is difficult to forecast the level of supply and demand in an economy
Businesses will find planning difficult and are likely to be reluctant to make significant decisions, especially with regard to capital expenditure
Economic uncertainty may occur as a result of:
A fluctuating exchange rate
Economic growth uncertainty
Turbulence in the price of key commodities, such as oil
Businesses must always be prepared for economic uncertainty by:
Building up cash reserves when times are good
Keeping informed about the economic climate
Being ready to take advantage of opportunities when they arise
Examiner Tips and Tricks
MOPS is a useful acronym that could be used in 20-mark questions as a tool to place the business context at the heart of evaluative answers. It is frequently highlighted in the examiners' report as an example of good evaluative practice.
MOPS stands for:
Market
Objectives
Product
Situation
When you consider the impact of any external influence on a business’s decision, try to explain why some of these factors are relevant, with specific reference to evidence from the case study. This will help you make a balanced decision.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?