Quality Management (Edexcel A Level Business) : Revision Note
Quality management methods
Quality considers the characteristics and features of a product that satisfy the needs of customers
Businesses need to maintain a level of quality that continues to attract and retain customers
There are a number of approaches to managing quality in the production process
Methods of quality management
Method | Explanation |
|---|---|
Quality control |
|
Quality assurance |
|
Quality circles |
|
Total quality management (TQM) |
|
Continuous improvement (Kaizen)
Kaizen involves a business taking continuous steps to improve productivity through the elimination of all types of waste in the production process
Changes are small and ongoing rather than significant one-off’s and are constantly reviewed to ensure that the desired positive impact on productivity is achieved
Comparison of kaizen and one-off improvements
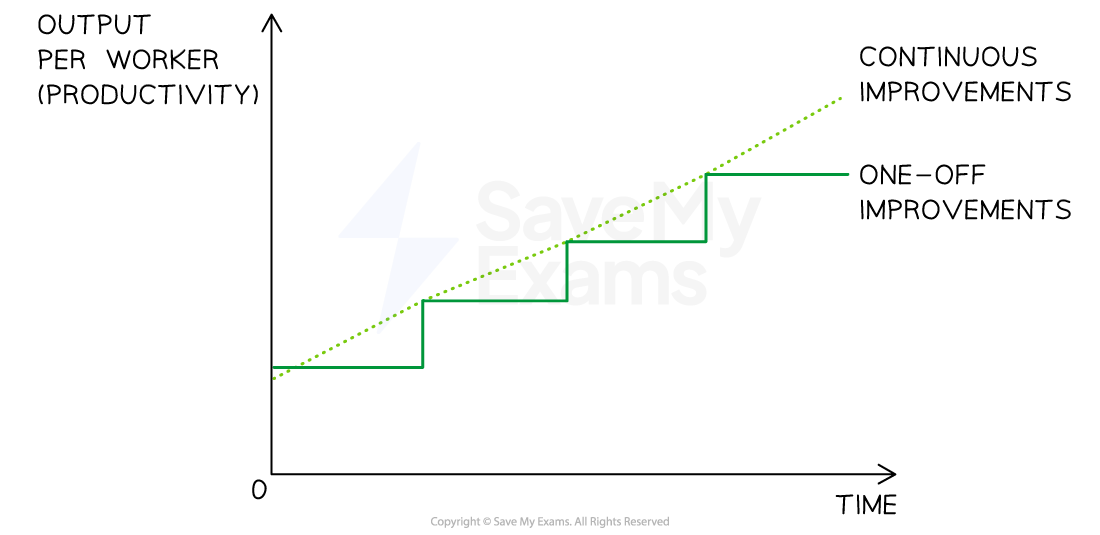
Elements of Kaizen commonly include
Total Quality Management
Just in Time stock management
Teamwork and quality circles
Zero defects in manufacturing
High levels of automation
High levels of cooperation between workers and management
Kaizen requires a long-term management commitment to change
Competitive advantage from quality management
The quality of a businesses products can provide a competitive advantage
Unit costs are likely to be low if a business takes a preventative approach through the use of quality assurance or TQM
Low costs may allow a business to reduce its selling price to better compete with or undercut its rivals
Increased finance may be available to fund marketing activity to improve brand recognition and attract new customers
High levels of quality can be used in promotional activity and provide a unique selling point for businesses in competitive markets
Successfully developing a USP for quality can ease expansion into new markets as a result of the positive reputation it creates

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?

