Production, Productivity & Efficiency (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Methods of production
Production is the transformation of resources (e.g. raw materials, components and processes) into finished goods or services
Goods are physical products, such as bicycles and T-shirts
Services are non-physical items, such as hairdressing, tourism and manicures
Businesses can organise their production processes in a variety of ways
The main methods of production

The method of production used by a business will depend on a number of factors, including:
The level of output required to be produced
The nature of the product
Whether the product is standardised or customised
The level of automation used in production
Job production
Producing one item at a time, as ordered by the customer
Advantages
High-quality product
Motivated and highly skilled workers
Customised products can be produced
Disadvantages
Production is slow
Labour costs are high
Batch production
Groups of the same product are produced before moving on to a group of different products
Advantages
Workers can specialise
Production can take place as the previous batch starts running out
Disadvantages
Requires careful coordination to avoid shortages
Money is tied up in stock, as completed products need to be stored
Flow production
Continuous manufacturing of standardised products, usually on a production line
Advantages
Low unit costs due to economies of scale
Rapid production
Usually highly automated (capital-intensive)
Disadvantages
Customisation is difficult
Capital equipment can be expensive to purchase
Cell production
This involves workers being organised into multi-skilled teams, with each team responsible for a particular part of the production process
Advantages
Cell production is often more efficient than other methods, as workers share their skills and expertise
Motivation is usually high, as employees work as a team
Disadvantages
Requires extensive reorganisation of production processes
Teams' efficiency may be reduced by weaker workers
Worked Example
Blush Cosmetics uses batch production to make its range of soaps and bath bombs, with a variety of unique ingredients and scents. The business sells its products in its own high street store and online and has recently started supplying its products in small quantities to a chain of exclusive hotels.
Explain one likely reason why Blush Cosmetics chooses to use batch production. [4]
Step 1: Identify a reason for the business to use batch production
One reason for Blush Cosmetics to use batch production is that it allows groups of products with varied ingredients to be manufactured. [K]
Step 2: Include a reference to the business scenario
Blush Cosmetics sells a range of bath bombs and soaps that have different fragrances, colours and ingredients. [Ap]
Step 3: Develop the reason using a connective
Blush Cosmetics needs to produce significant levels of output to meet increasing demand and batch production, as well as to provide the opportunity to change ingredients between batches [An], which can allow quite large quantities to be produced for the company's high street and online stores [An].
Or:
Using batch production can allow Blush Cosmetics to produce smaller quantities of unique products for exclusive hotel customers [Ap], meeting their specific needs [An].
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Carefully consider the needs of the customers to whom a business sells when recommending a suitable method of production.
Where the selling price is a key driver of consumer demand, flow production (where unit costs are minimised) is likely to be very suitable.
Where demand is driven by quality or where customisation is required, job production or batch production is likely to be a better choice.
Calculating productivity
Productivity is the output per input (person or machine) per hour (e.g. an IKEA worker is able to produce two Poāng chairs per hour)
This is not production, which is the total amount of output produced in a time period (e.g. IKEA produced 300 Poāng chairs in February)
Labour productivity
The labour productivity of a business is a measure of the output per worker during a specified period of time
Labour productivity is calculated using the formula
Capital productivity
Capital productivity is a measure of the output of capital employed (e.g. machinery) during a specified period of time
Capital productivity is calculated using the formula
Worked Example
The table shows the number of pairs of luxury wool socks produced by Scotty Socks Ltd in 2021 and 2022.
Year | Units produced |
|---|---|
2021 | 46,000 |
2022 | 69,000 |
In 2021, Scotty Socks employed 50 staff. In 2022, the number of staff employed by the business increased by 20%.
Calculate the percentage change in labour productivity between 2021 and 2022.
[4]
Step 1: Calculate the labour productivity for 2021
[1]
Step 2: Calculate the labour productivity for 2022
[1]
Step 3: Calculate the percentage difference between the two years ([new−old] ÷ old)
[1]
Step 4: Identify whether the percentage difference is an increase or a decrease
25% increase [1]
Worked Example
Rolvo Ltd forecasts that by the end of the year, it will produce 250,800 units and that capital productivity will be 1,100 units per machine.
Calculate the number of machines Rolvo Ltd has in use.
Step 1: Divide the output by the capital productivity
Factors that influence productivity
The productivity within a business can often be improved
When productivity increases, business costs decrease
When business costs decrease, the firm can either pass on this decrease to consumers in the form of lower prices or maintain the selling prices and enjoy higher profit margins
Factors that influence productivity
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Employee motivation |
|
Skills, education and training staff |
|
Business organisation and working practices |
|
Investment in capital equipment |
|
The link between productivity and competitiveness
Competitiveness refers to the ability of a business to maintain or grow its sales and market share, given the presence and actions of rivals
Businesses that increase their level of productivity (e.g. of workers or capital equipment) are likely to be more competitive
Productivity and competitiveness
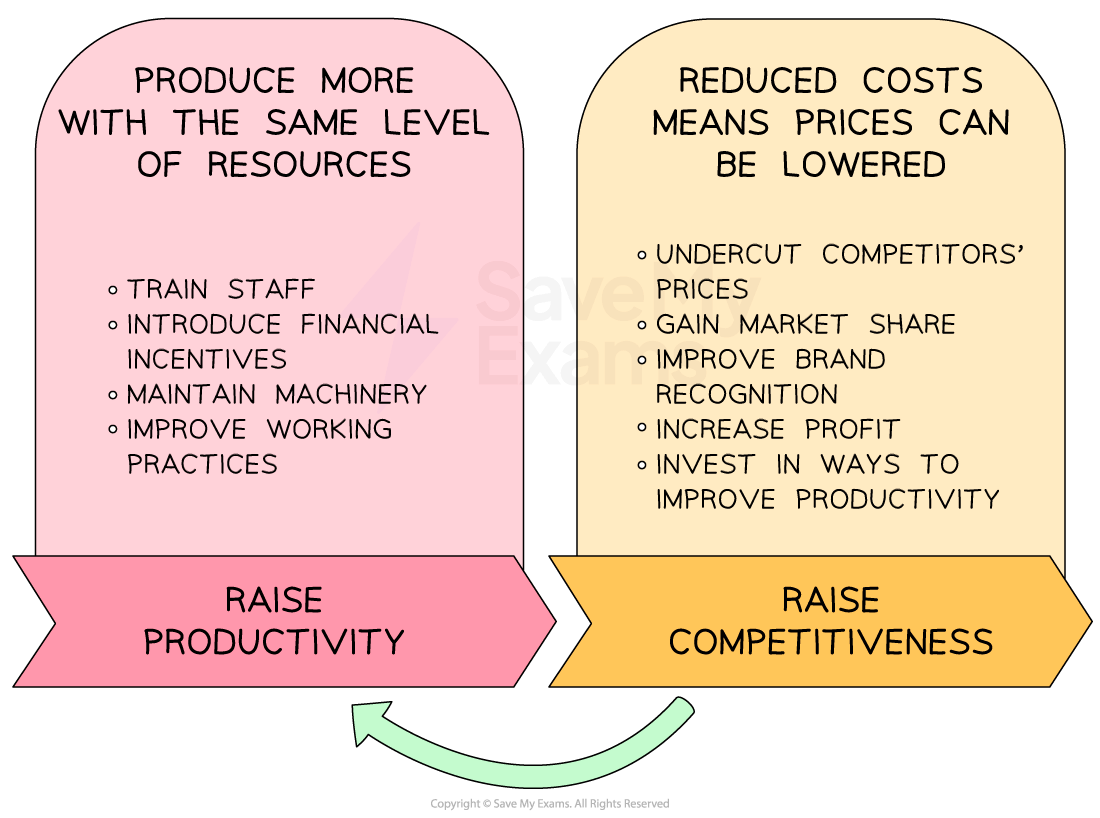
Businesses that are competitive are likely to have the financial resources required to continue investing in improvements to their productivity
Understanding efficiency
Efficiency refers to the ability of a business to use its production resources as cost-effectively as possible
Efficiency is often measured in terms of the average cost per unit
The average cost per unit is calculated using the formula
Maximum efficiency is achieved when the cost per unit is at its lowest
Diagram showing maximum efficiency
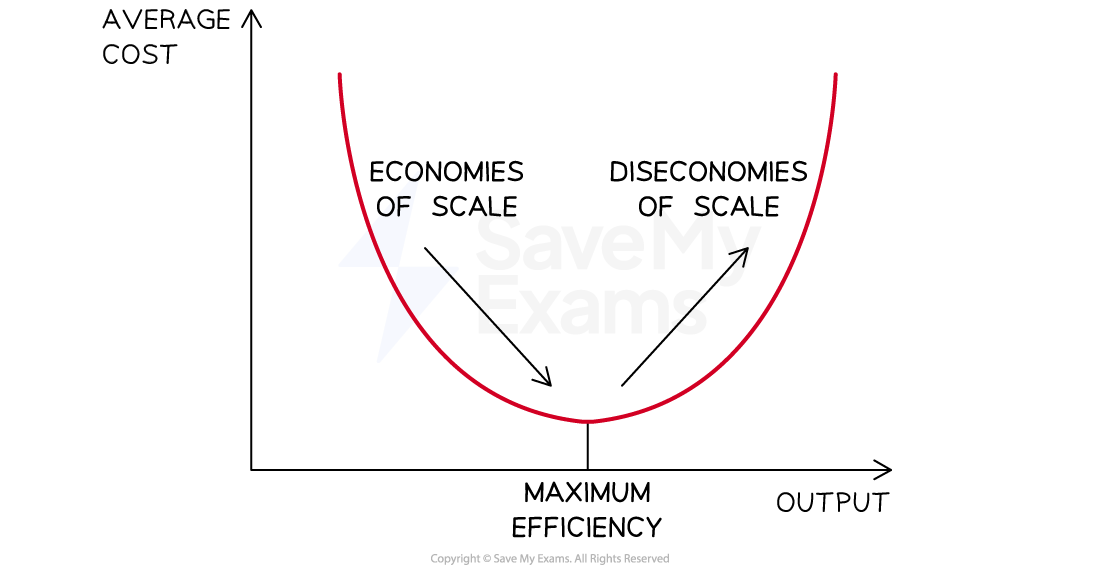
The average cost curve shows that the most efficient level of production is achieved when:
Economies of scale are maximised
Total costs are spread across an optimum level of output
Diseconomies of scale are minimised
Factors that influence efficiency
Factors that can influence business efficiency
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Standardisation of the production process |
|
Relocation or downsizing |
|
Investment in capital equipment |
|
Organisational restructuring |
|
Outsourcing |
|
Adoption of lean production techniques |
|
Capital-intensive and labour-intensive production
Labour-intensive production predominantly uses physical labour in the production of goods/services
The delivery of services is usually more labour-intensive than manufacturing
In countries where labour costs are low (e.g. Bangladesh), labour-intensive production is common
Small-scale production is likely to be labour-intensive
For example, UK schools are labour-intensive operations, as teachers plan and deliver lessons and provide pastoral support
Capital-intensive production predominantly uses machinery and technology in the production of goods and services
Large-scale production of standardised products is likely to be capital-intensive
Manufacturing in developed countries, where labour costs are relatively high, is likely to be capital-intensive
For example, automotive manufacturers such as Ford use robots and other production technology to manufacture vehicles, with supervisors overseeing the quality of output
Evaluation of labour-intensive and capital-intensive production
Type of production | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
Capital-intensive |
|
|
Labour-intensive |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?