Profit (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Profit calculations
Profit is the money left over after all costs have been accounted for
There are several different types of profit
Types of profit
Type of profit | What does it show? | How is it calculated? |
|---|---|---|
Gross profit (GP) |
| GP = revenue − cost of sales |
Operating profit (OP) |
| OP = gross profit − operating expenses |
Net profit (NP) |
| NP = operating profit − (net interest + exceptional costs) |
Worked Example
An e-scooter manufacturer sells its products to retailers for £180 per unit. Variable costs are ⅖ of the selling price, with monthly fixed costs being £82,000. It sells 2,200 scooters a month.
The business pays £240 interest on a mortgage each month. This year, it purchased the patent for a new type of rechargeable battery for £17,000.
Calculate the business's net profit for the year.
[5]
Step 1: Calculate the variable cost per unit
Step 2: Calculate the gross profit per unit (selling price − variable cost per unit)
[1]
Step 3: Calculate the gross profit per month (gross profit per unit × units sold)
Step 4: Calculate the gross profit per year (gross profit per month × 12)
[1]
Step 5: Multiply monthly fixed costs by 12 (months)
Step 6: Subtract the annual fixed costs from the annual gross profit
[1]
Step 7: Multiply the monthly interest by 12 (months)
[1]
Step 8: Add the one-off purchase to the annual interest
Step 9: Subtract the interest and one-off costs from the operating profit
[1]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may not be asked to complete all of these calculations in one question.
The question may, for example, provide the gross profit and some other information and then ask you to calculate the net profit.
Look at the data carefully to ensure you are doing the correct calculation.
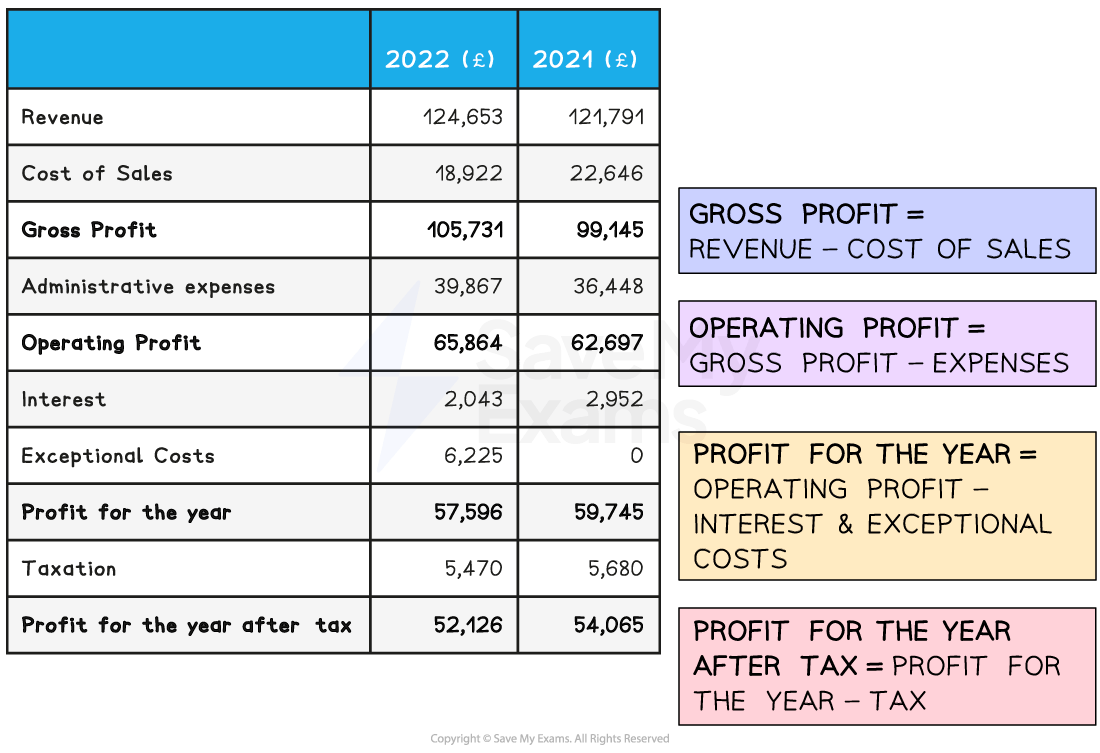
Statement of comprehensive income (profit and loss account)
The statement of comprehensive income is an end-of-year financial statement that shows all of a business's income and expenses over the previous 12 months
Each type of profit is calculated within the statement of comprehensive income
The previous year’s figures are also shown for comparison purposes
Example statement of comprehensive income for Head to Toe Wellbeing Ltd
Profit margins
A profit margin is the amount by which the sales revenue exceeds the costs
Profit margins can be calculated for each type of profit (gross, operating and net profit)
Profit margins can be compared to previous years to better understand business performance
Higher and increasing profit margins are preferable, as it means that more revenue is being converted to profit
Gross profit margin
This shows the proportion of revenue that is turned into gross profit and is expressed as a percentage
It is calculated using the formula
Worked Example
Head to Toe Wellbeing Ltd's revenue in 2022 was £124,653. Its gross profit was £105,731.
Calculate Head to Toe Wellbeing’s gross profit margin in 2022.
[2]
Step 1: Substitute the values into the formula
[1]
Step 2: Multiply the outcome by 100 to find the percentage
[1]
Operating profit margin
The operating profit margin shows the proportion of revenue that is turned into operating profit and is expressed as a percentage
It is calculated using the formula
Worked Example
Head to Toe Wellbeing Ltd’s revenue in 2022 was £124,653. Its operating profit was £65,864.
Calculate Head to Toe Wellbeing’s operating profit margin in 2022.
[2]
Step 1: Substitute the values into the formula
[1]
Step 2: Multiply the outcome by 100 to find the percentage
[1]
Net profit margin
The net profit margin (also known as the profit for the year margin) shows the proportion of revenue that is turned into net profit before tax and is expressed as a percentage
It is calculated using the formula
Worked Example
Head to Toe Wellbeing Ltd’s revenue in 2022 was £124,653. Its profit for the year was £57,596.
Calculate Head to Toe Wellbeing’s profit for the year margin (net profit) in 2022.
[2]
Step 1: Substitute the values into the formula
[1]
Step 2: Multiply the outcome by 100 to find the percentage
[1]
Ways to improve profitability
There are several steps a business can take to improve profitability
Main ways to improve profitability
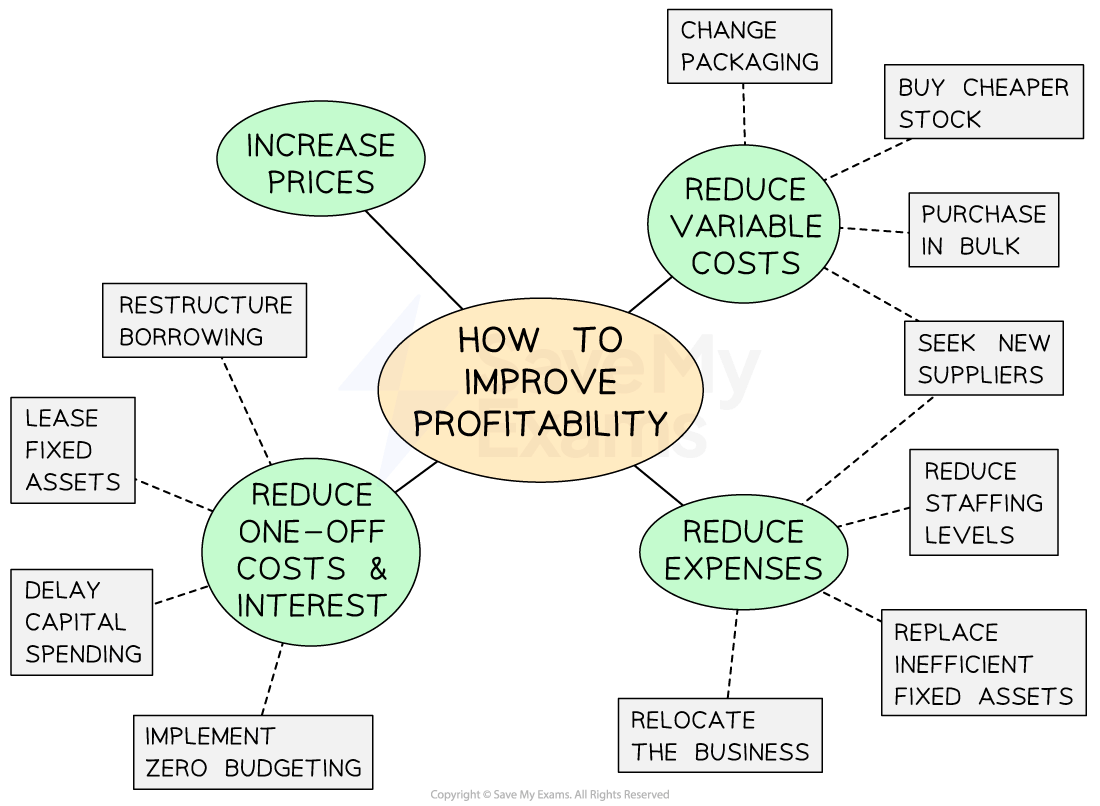
Raising prices
If costs remain the same, raising prices will improve profitability, as the difference between the selling price and the cost is now greater
Raising prices is likely to have an impact on demand, so a business must understand the price elasticity of demand for its products
Where demand for products is price elastic, increasing prices will result in lower revenue — in this case, profitability will be reduced
Where demand for products is price inelastic, increasing prices will increase revenue — in this case, profitability will rise
Reducing variable costs
This may involve purchasing cheaper/alternative resources, negotiating with suppliers or purchasing in bulk
Businesses must ensure that reducing variable costs will not have an adverse effect on the quality or desirability of products
Buying stock in greater quantities may require investment in increased storage space, which will reduce the impact of the cost savings made
Businesses may also be able to reduce the waste of raw materials and components
Reducing other expenses
Reducing staffing levels, relocating to cheaper premises or changing utility companies can reduce expenses
Reducing staffing levels may affect staff morale and negatively affect productivity
Relocation costs can outweigh some of the benefits of moving to a cheaper location
Replacing inefficient or outdated equipment may require staff training
Reducing one-off costs and interest charges
Delaying the purchase of fixed assets, entering leasing arrangements or restructuring borrowing can reduce costs
Delaying purchases of new fixed assets (e.g. machinery or vehicles) may negatively impact capacity utilisation as a result of increased breakdowns and maintenance of the old equipment
The leasing of equipment (e.g. photocopiers) can reduce one-off purchase costs, but the business never owns these assets, which weakens the balance sheet
Restructuring borrowing can result in lower monthly payments but requires lenders to agree to new terms, which they may not be willing to do
The distinction between profit and cash
Profit and cash are different financial terminologies
Profit is simply the difference between revenue generated and business costs
Cash is measured by taking into account the full range of money flowing in and out of a business
A new business may have to pay cash on purchase for all its supplies until a good business relationship has built up a level of trust with its suppliers
A supplier may then give the business trade credit of 30 or 60 days
This means that the business can receive its stock now and only pay for it in 30 or 60 days, so the cash outflow is delayed
As the business sells its products, it receives money generated from the business revenue, and this represents a cash inflow
At the end of 60 days, the business will pay its supplier (cash outflow), but the firm may still have stock available for sale
A profitable business is likely to fail if it does not have sufficient cash
Cash-poor businesses will struggle to pay their suppliers
E.g. lifestyle retailer Joules announced plans to liquidate in December 2022 as a result of cash flow difficulties despite making a profit of £2.6 million during the previous year

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?