Budgets (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
The purpose of budgets
A budget is a financial plan that a business (or department in the business) sets for costs and revenue
The budget is usually closely aligned with the business objective
Reasons for using budgets
Reason | Explanation |
|---|---|
Planning and monitoring |
|
Control |
|
Coordination and communication |
|
Motivation and efficiency |
|
Types of budgets
Budgets are usually set annually and then monitored on a monthly basis
Businesses may set budgets to monitor the financial performance of any aspect of the business
Budgets are generally prepared using one of two methods:
Historical figure budgets
Zero-based budgeting
Historical figure budgets
Budgets are usually based on historical data (e.g. sales and costs data from previous years) and allow for factors such as inflation and other relevant economic indicators (e.g. exchange rate variations)
Zero-based budgeting
In some cases, businesses make the decision not to allocate budgets and use a zero-budgeting approach
This is particularly useful when a business needs to control costs closely (e.g. to improve profitability)
Zero budgeting requires all spending to be justified, which means that many unnecessary costs can be eliminated
It can be time-consuming, as evidence to support spending decisions needs to be collected and presented
Zero budgeting also requires skilled and confident employees to make a persuasive case to convince those who are making purchasing decisions
Variance analysis
A budget variance is the difference between the figure budgeted and the actual figure achieved by the end of the budgetary period (e.g. 12 months)
Variance analysis seeks to determine the reasons for the differences between the actual figures and the budgeted figures
Favourable variances
A favourable variance is when the actual figure achieved is better than the budgeted figure
A favourable variance in a revenue or profit budget is when the actual figure is higher than the budgeted figure
A favourable variance in a costs budget is when the actual figure is lower than the budgeted figure
Adverse variances
An adverse variance is when the actual figure achieved is worse than the budgeted figure
An adverse variance in a revenue or profit budget is when the actual figure is lower than the budgeted figure
An adverse variance in a costs budget is when the actual figure is higher than the budgeted figure
Worked Example
Selected financial information for Bunsen PLC in 2022
| £m |
Budgeted sales revenue | 12,460 |
Actual sales revenue | 13,718 |
Budgeted total costs | 8,420 |
Actual total costs | 10,627 |
Using the data, calculate the total profit variance for Bunsen PLC in 2022. You are advised to show your workings. [4]
Step 1: Calculate the budgeted profit for 2022
[1]
Step 2: Calculate the actual profit for 2022
[1]
Step 3: Subtract the budgeted profit from the actual profit for 2022
[1]
Step 4: Identify the nature of the variance
In this case, the variance is adverse because the actual profit for 2022 is lower than the budgeted profit for 2022
The correct answer is £949 in adverse variance [1]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Although the Bunsen PLC example shows an adverse profit variance, it is worth noting that the company’s actual sales revenue was higher than budgeted. There could be some sales executives in the business who deserve some sincere congratulations!
You may recommend that the business investigate the reasons for the adverse profit variance. The focus of the examination must be on the higher-than-budgeted costs rather than on this seemingly positive sales performance. You may recommend that Bunsen review its supply agreements or that it adopt a zero-budgeting approach.
Once variances have been identified, a business should carefully investigate the reasons why the variances have occurred and take appropriate action, such as:
Where adverse cost variances are identified, a business may seek alternative suppliers or investigate ways to improve efficiency
Where adverse sales variances are identified, a business may review its marketing activities to improve their effectiveness
Where favourable cost variances are identified, a business may review key quality indicators such as the volume of returns or waste levels to ensure that output standards are being met
Where favourable sales variances occur, a business may reward client-facing staff with performance-based incentives
Difficulties of budgeting
Budgeting requires significant expertise to be of genuine use to a business, and there are several difficulties associated with its construction
The main difficulties of budgeting
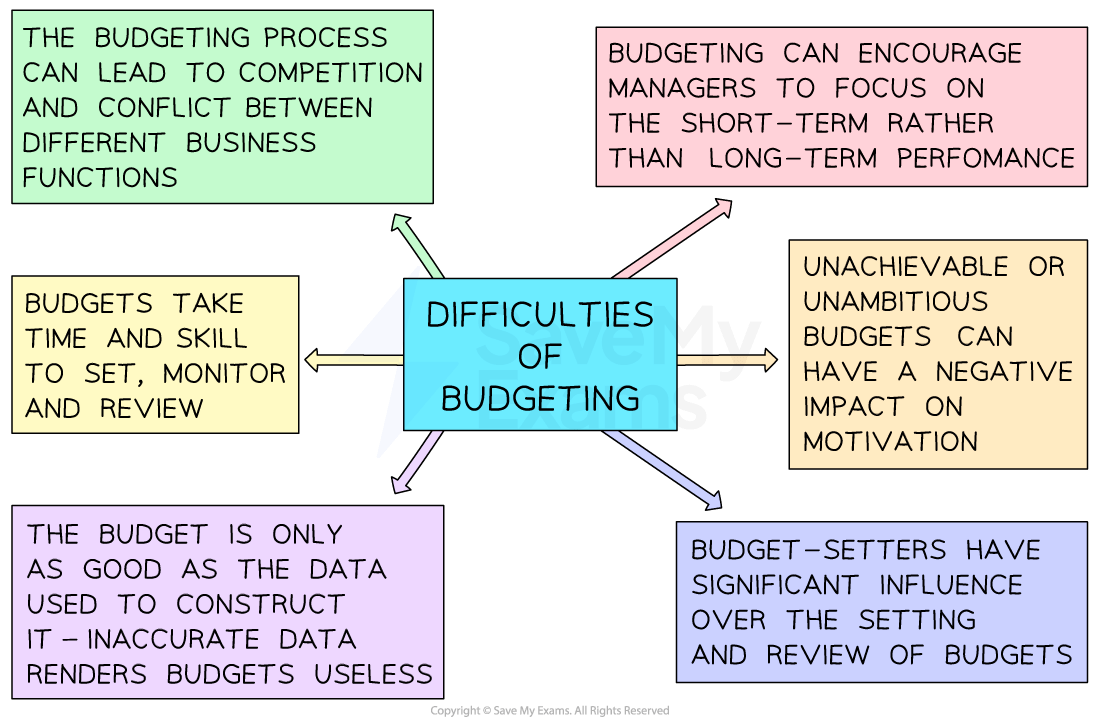
Data must be up-to-date, accurate and free of bias
Sources of data must be selected carefully and used with care to ensure the most appropriate assumptions are made
Those who are constructing budgets will require skills and relevant experience to do so effectively
This may involve training or the recruitment of specialist staff
Budgets can encourage managers to focus on the short-term rather than the long-term success of the business, as budgets are usually set year to year
Unrealistic budgets (over or under) can lead to a lack of motivation among those tasked to achieve the financial plan
Conflict between budget holders may arise, reducing the effectiveness of the business as a whole

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
