Liability (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
Limited and unlimited liability
The most common forms of business ownership are sole traders, partnerships, private limited companies, public limited companies and franchises (see subtopic 1.5)
When an entrepreneur starts a business, they need to consider what kind of legal structure they want for their business
Sole traders and partnerships offer no legal protection to the owners, in that the business assets and the owner's personal assets are viewed as being the same (unlimited liability)
The other forms of business ownership offer limited liability, in which the assets of the owners are considered to be separate from those of the business
Comparison of unlimited and limited liability
Liability | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Unlimited liability |
|
|
Limited liability |
|
|
Appropriate finance for limited and unlimited liability businesses
Methods of finance for limited liability businesses
There are numerous factors that decide which is the most appropriate form of finance for limited and unlimited liability businesses
More often than not, there will be a range or blend of sources of finance that a firm can use
Main methods of finance for limited liability businesses
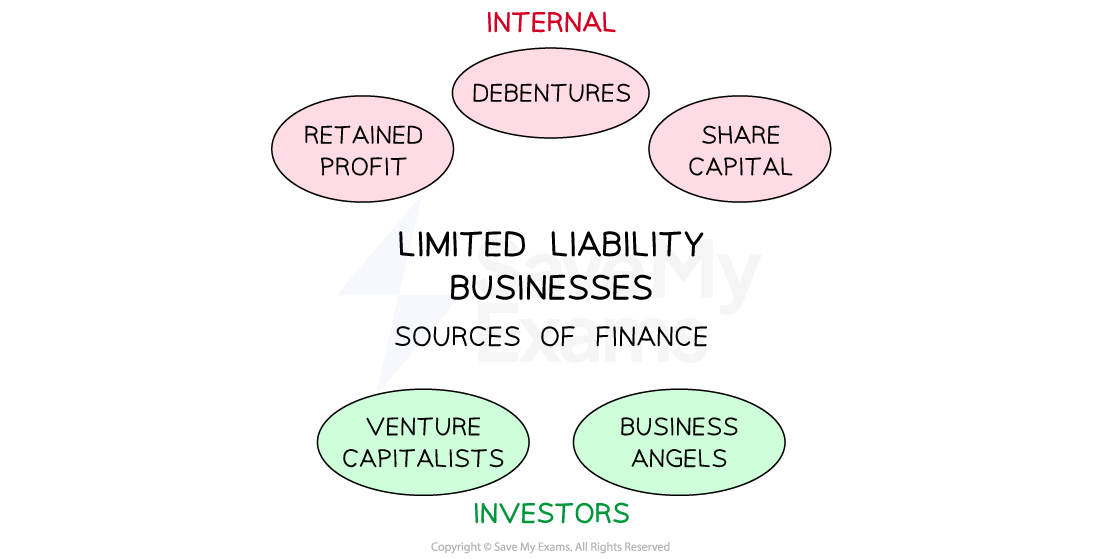
Unlimited liability businesses usually access different sources of funding than limited liability businesses
Some sources of funding are suitable for both types of businesses, e.g. an unsecured bank loan
Main methods of finance for unlimited liability businesses
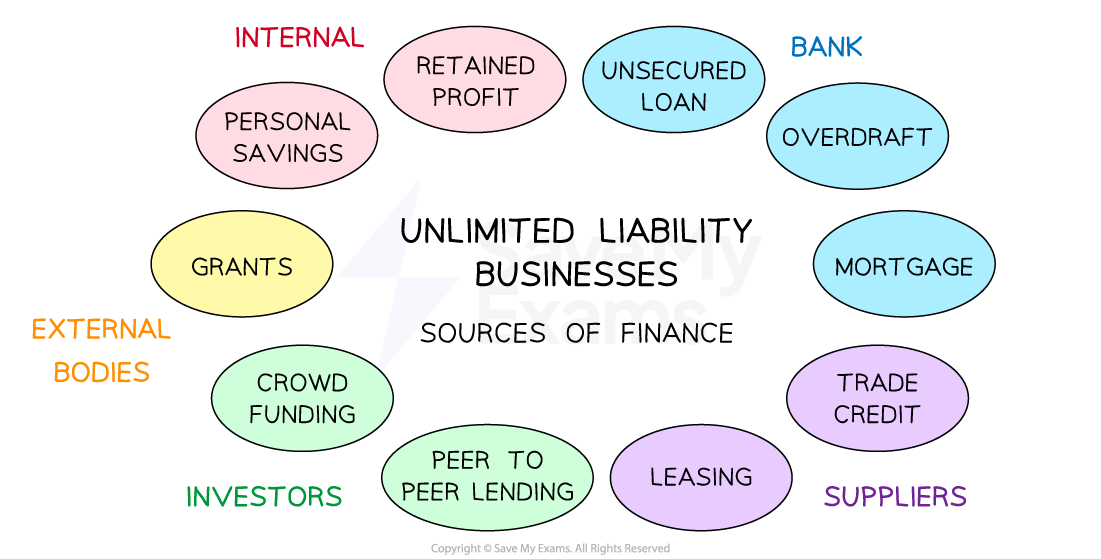
Businesses need to consider a range of factors before selecting the most appropriate method(s) of finance
Factors affecting the choice of finance
Factor | Explanation |
|---|---|
Why is the finance needed? |
|
For how long and how quickly is the finance needed? |
|
Who will lend to the business? |
|
How much will it cost, and how easy is it to access the finance? |
|
What is the legal status of the business? |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are sometimes required to recommend a suitable source of finance to meet the needs of the business presented in a case study.
Whilst candidates are often able to effectively analyse the benefits and drawbacks of each of the available methods and make a judgement, the very best responses consider the specific circumstances of the business. The table above provides some structure for that discussion.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?