Marketing Strategy (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
The product life cycle
The product life cycle describes the different stages a product goes through from its conception to its eventual decline in sales
There are typically five stages in the product life cycle: development, introduction, growth, maturity and decline
A typical product life cycle
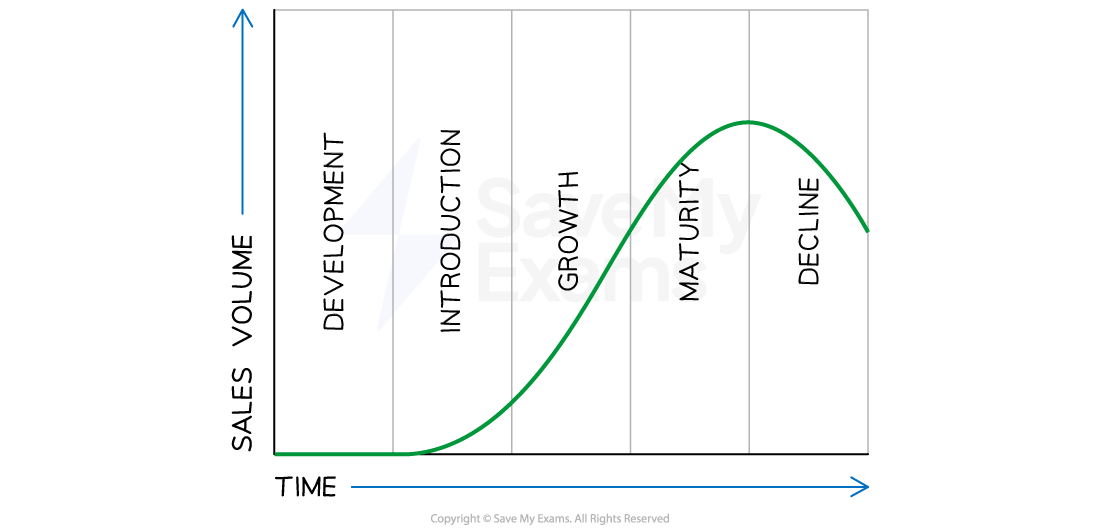
The implications for cash flow and marketing vary at each stage of the product life cycle
Companies should tailor their marketing strategies and manage their cash flow to ensure long-term profitability and success
The product life cycle, cash flow and marketing strategy
Stage | Explanation | Implication |
|---|---|---|
Development |
|
|
Introduction |
|
|
Growth |
|
|
Maturity |
|
|
Decline |
|
|
Extension strategies to the product life cycle
Extension strategies refer to the techniques used by businesses to extend the life of a product beyond its natural life cycle
These strategies are designed to boost sales and maintain profitability for a product that has reached the decline stage of its life cycle
There are two types of extension strategies:
Product-related extension strategies
Promotion-related extension strategies
By making product- and promotion-related changes, businesses can continue to appeal to customers and extend the life of their products
Product-related extension strategies
Involves changing or modifying the product to make it more appealing to customers and extend its life cycle, which can be achieved in one of three ways:
Product improvements (e.g. Samsung releases new versions of its Galaxy Smartphone every year with upgraded features and improvements to the previous model)
Line extensions (e.g. Coca-Cola introduced Diet Coke and Coke Zero as line extensions of its original Coca-Cola)
Repositioning (e.g. when IBM's personal computer division started losing market share to other brands, it repositioned its products as high-end business machines and focused on the enterprise market)
Promotion-related extension strategies
Involves changing the marketing and promotion of the product to extend its life cycle and could include one or more of the following changes:
Changes to advertising (e.g. Kellogg's continues to recreate adverts for its Corn Flakes cereal, which has been around since 1906)
Price promotions (e.g. Cyber Monday occurs on the first Monday after Thanksgiving in the US, and electronics firms discount prices significantly to boost sales of their products)
Sales promotions (e.g. many coffee shops offer a loyalty program in which customers can earn a free drink for every six consumed)
Boston Matrix and the product portfolio
The Boston Matrix is a tool used by businesses to analyse their product portfolio and make strategic decisions about each product
The matrix classifies products into four categories based on their market share and the market growth rate:
Cash cow
Problem child/question mark
Star
Dog
The Boston Matrix

By categorising products into these categories, businesses can allocate resources more effectively, optimising their cash flow and developing marketing strategies that align with the product's potential
Product classification in the Boston Matrix, cash flow and marketing strategy
Product type | Explanation | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Cash cow |
|
|
Problem child / question mark |
|
|
Star |
|
|
Dog |
|
|
Marketing strategies for different types of markets
Marketing strategies vary depending on the type of market being targeted:
Mass markets, niche markets, business-to-business (B2B) markets and business-to-consumer (B2C) markets
Mass markets
Mass markets are characterised by large numbers of customers who have similar needs and wants (e.g. retail clothing)
Mass markets focus on building brand awareness and appealing to a broad audience
Advertising campaigns are usually designed to reach as many people as possible and use mass media such as TV, radio and print ads
The messages are often simple, and the goal is to create a strong brand identity that resonates with a large segment of the population
Niche markets
Niche markets are characterised by smaller groups of customers with specific needs and wants (e.g. organic food stores, luxury car dealerships)
Marketing strategies focus on targeting a specific segment of the population and building relationships with them
Advertising campaigns are usually more targeted and may use social media to reach potential customers
The messages are often more detailed and include technical information that is relevant to the specific needs of the target market
Business-to-business
B2B marketing focuses on selling products to other businesses (e.g. software companies selling to other businesses, manufacturers selling parts to other manufacturers)
In B2B marketing, the emphasis is on building relationships with other businesses and demonstrating how your product can help them be more successful
Advertising campaigns may include case studies that demonstrate the value of your product/service
The messages are often more technical and may focus on features and benefits that are relevant to other businesses
Business-to-consumer
B2C marketing focuses on selling products/services directly to consumers (e.g. clothing retailers)
In B2C marketing, the emphasis is on building brand loyalty and creating a positive customer experience
Advertising campaigns may include social media ads or influencer marketing campaigns that appeal to the emotions of consumers
The messages are often more emotional and may focus on the lifestyle benefits of using the product/service
Developing customer loyalty
Developing customer loyalty helps businesses to grow and be successful in the long term
Customer loyalty drives repeat purchases, which helps the firm to reduce marketing costs when launching new products
Three commonly used methods of building customer loyalty include providing excellent customer service, offering loyalty cards and offering saver schemes
Ways to develop customer loyalty
Method | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
Customer service |
|
|
Loyalty cards |
|
|
Saver schemes |
|
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?