The Market (Edexcel A Level Business): Revision Note
Exam code: 9BS0
An introduction to marketing
A market is any place where buyers and sellers can meet, e.g. amazon.co.uk or a shopping mall
Different markets have varying characteristics and are affected differently by changes
The aim of marketing is to help identify, anticipate and satisfy consumer needs and wants profitably
Needs are considered essential, e.g. shelter or food
Wants are desires that are non-essential, even if consumers consider them to be essential, e.g. Nike trainers
Market research is essential in helping businesses identify products and services they can develop in response to the needs and wants of their customers
Market research is the process of systematically gathering data from consumers that can be used to influence business decisions
Mass markets and niche markets
The characteristics of markets
In mass markets, products are aimed at broad market segments; e.g. Kellogg's Corn Flakes is an example of a breakfast cereal aimed at the mass market
Market segments are groups of consumers who share similar characteristics, e.g. age, lifestyle
Mass marketing occurs when businesses sell their products to most of the available market
Production usually happens on a large scale
In niche markets, products are aimed at a subset of the larger market, e.g. gluten-free products
Niche marketing occurs when businesses identify and satisfy the demands of a small group of consumers within the wider market
Production usually happens on a small scale
Characteristics of Mass Markets and Niche Markets
Mass Markets | Niche Markets |
|---|---|
|
|
Market size and market share
The size of a market can be measured through sales volume or sales value
Sales volume is the number of products sold, i.e. the physical number of units sold
Sales revenue = price × quantity sold, i.e. the financial value of the units sold
The market share that a business enjoys is the proportion of the total sales of a product/service compared to the market as a whole; e.g. Tesco has 26% of the UK grocery market
Market share can be calculated as follows:
Worked Example
In 2022, the UK coffee shop market was worth £4.6bn. Sales of Starbucks Coffee totalled £328m in 2022.
Using the data, calculate, to two decimal places, the market share of Starbucks Coffee in the coffee shop / café market. You are advised to show your workings.
[4]
Step 1: Identify the annual sales of Starbucks Coffee
Step 2: Identify the total market sales in the coffee shop market
[1]
Step 3: Substitute the figures into the formula
[1]
[1]
Step 4: Present the answer rounded to two decimal places
[1]
Examiner Tips and Tricks
By providing the formula and showing your working out, even if you do not get the right answer, you will still be able to gain some marks.
Brands
A brand is a name, image or logo that helps a product or service stand out from its competitors
Branding is one of the key ways businesses achieve product differentiation

Brands are unique and protected by law
Brands add value, often making the product or service more desirable to consumers
Adding value is the process by which firms increase the price that the consumer is willing to pay
Brands influence the position of the business within its market
Businesses operating in mass markets use branding to stand out from the competition
Businesses operating in niche markets use branding to communicate their offering to a small, well-defined group of consumers
Strong brands are more likely to be able to charge higher prices for their products than weaker brands
The perceived quality of a strong brand's products is better than that of weaker brands
Dynamic markets
A dynamic market is a market that is subject to rapid or continuous changes
Many markets are becoming more competitive, making change inevitable
Those businesses that do not adapt are less likely to survive in the long run
The mobile phone market is a good example of a dynamic market
Businesses with monopoly power (e.g. Amazon) might not face the same dynamic pressures as businesses in more competitive markets
Many markets are dynamic, but others change very slowly; e.g. the market for eggs and milk has been relatively stable for years

There are four areas to consider when examining dynamic markets
Online retailing
How markets change
Innovation and market growth
Adapting to change
1. Online retailing
Online retailing involves selling products via the internet
The advantages and disadvantages of online retailing for firms and consumers
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
|
|
2. How markets change
Changing market conditions offer new opportunities for firms but also pose threats
The following changes cause markets to be dynamic:
Changing consumer tastes and preferences, e.g. consumers desiring electric vehicles in place of traditional petrol/diesel cars
Changing demographics; e.g. many developed countries have an increasingly older population who have different wants and needs compared to previous markets
The amount of competition; e.g. international trade means larger market sizes but also more competition between an increasing number of firms
Competition can be direct, i.e. the sale of similar products, or indirect, e.g. airlines competing with each other but also with other forms of transport, such as trains
Changing legislation; e.g. laws that strengthen environmental standards often create new markets
3. Innovation and market growth
Product innovation involves the adaptation or improvement of existing products, e.g. improved video cameras on laptops
Process innovation involves the adaptation or improvement of existing processes, e.g. just-in-time stock control
Market growth is the measurement of the change in the entire market, expressed as a percentage of the original size
A business's market share does not necessarily increase automatically as the entire market continues to grow
Market growth can be caused by numerous factors. For example:
Increasing population sizes can increase demand in certain markets
Increasing incomes can increase demand in certain markets
Changing tastes and preferences can cause the market to grow, e.g. the growth in the electric car market
Worked Example
Sales of electric vehicles were 267,203 in 2022. This was a 40% increase from the previous year.
Calculate the number of electric vehicles sold in the UK in 2021. Round your answer to the nearest whole car. You are advised to show your workings.
[4]
Step 1: Find the number of electric cars sold in 2022
[1]
Step 2: Reduce 267,203 by 40%
[2]
Step 3: Express your answer to the nearest whole number of vehicles
2021 UK sales = 190,859 electric vehicles [1]
4. Adapting to change
Recognising and adapting to market changes allows businesses to thrive in dynamic markets
Strategies to adapt to change include:
Create flexible business structures, especially in terms of operations and people management
Meet customer needs by carrying out market research and communicating with customers
Invest in staff training, new products and processes
Innovate so as to gain the first mover advantage
How competition affects the market
Competition occurs when at least two businesses are providing goods/services to the same target market
The more businesses in the market, the more intense the competition
Competition can be direct or indirect
Direct competition occurs when the business is targeting customers with the same product as a competitor
Indirect competition occurs when firms sell different products but compete with each other for customers' disposable income; e.g. cinema and theatre companies are in indirect competition
Competition results in many benefits for the customer, such as:
Businesses offer lower prices
Businesses produce better quality products
Businesses provide better customer service
The absence of competition reduces incentives for businesses to innovate, be efficient or offer consumers lower prices
The difference between risk and uncertainty
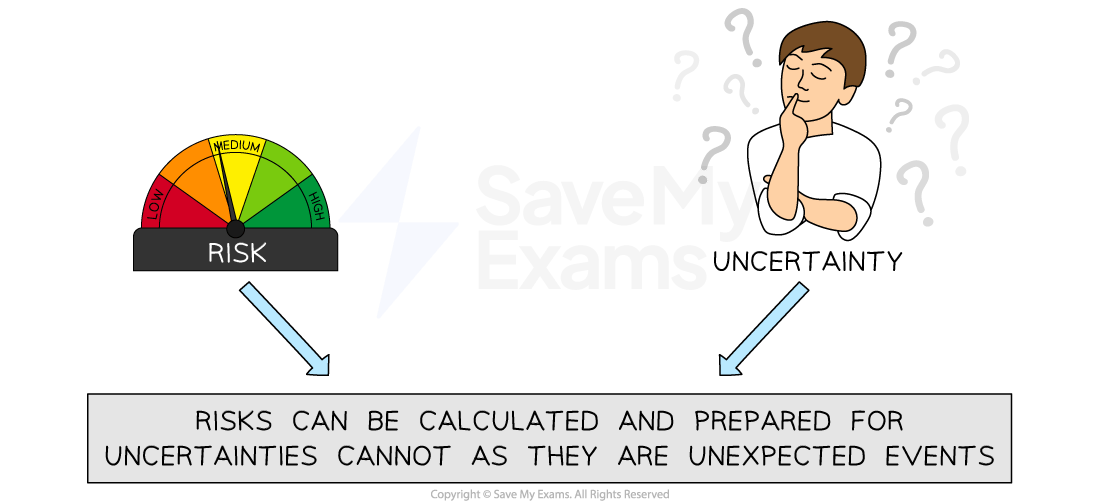
Risk is the potential threat to business success
Risks can be from inside the business (internal) or from outside the business (external)
Risks can be measured and prepared for using risk management
Uncertainty occurs when outcomes are difficult to predict
Examples of risk and uncertainty
Risk | Uncertainty |
|---|---|
|
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You can make use of the concepts of risk and uncertainty in strategy-focused questions. For example, when evaluating a particular strategy, you could explain the possible risks as well as the rewards associated with it.
Moreover, there are no certainties in business, so outlining potential uncertainties before making a recommendation at the end of an essay is a good way to demonstrate evaluation skills.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?