Mammalian Sensory Receptors (OCR A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: H420
Mammalian sensory receptors
A cell that responds to a stimulus is called a receptor cell
Receptor cells are transducers – they convert energy from one form (such as light, heat or sound) into energy in an electrical impulse within a sensory neurone
Each receptor will only respond to a specific stimulus

Receptors of the body act as transducers
Receptors of the Body and their Stimuli Table

Pacinian corpuscles
In any area of the skin, there are a range of different receptors present
The different receptors have different structures and positions within the skin
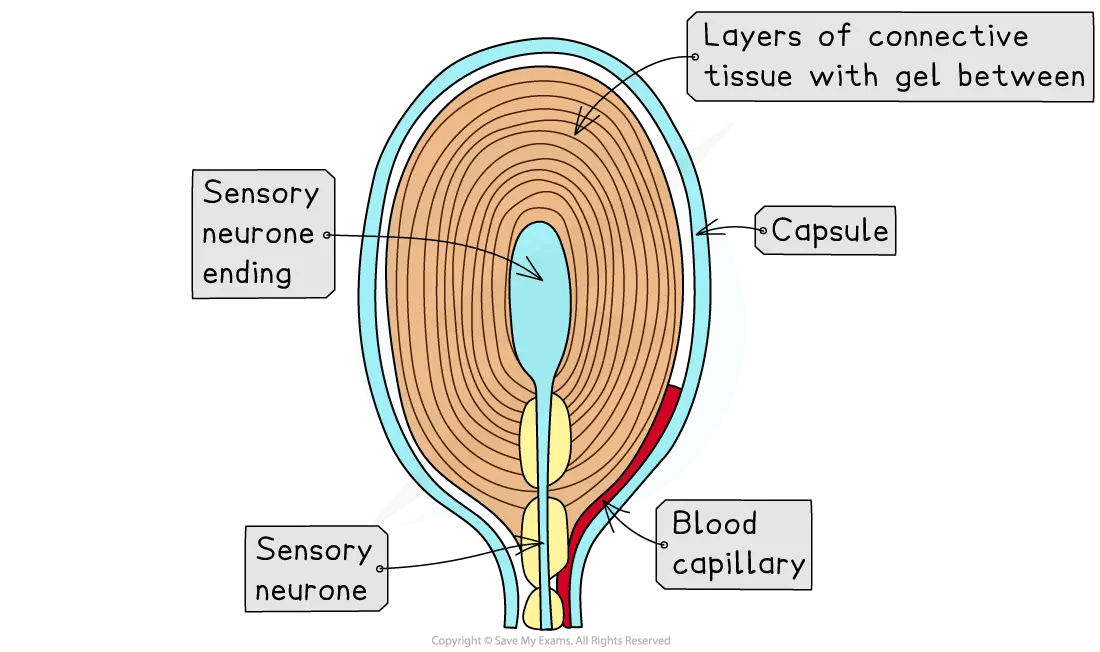
Pacinian corpuscles are a type of mechanoreceptor found deep in the skin
They are present in the skin of fingers, soles of the feet as well as in joints, tendons and ligaments
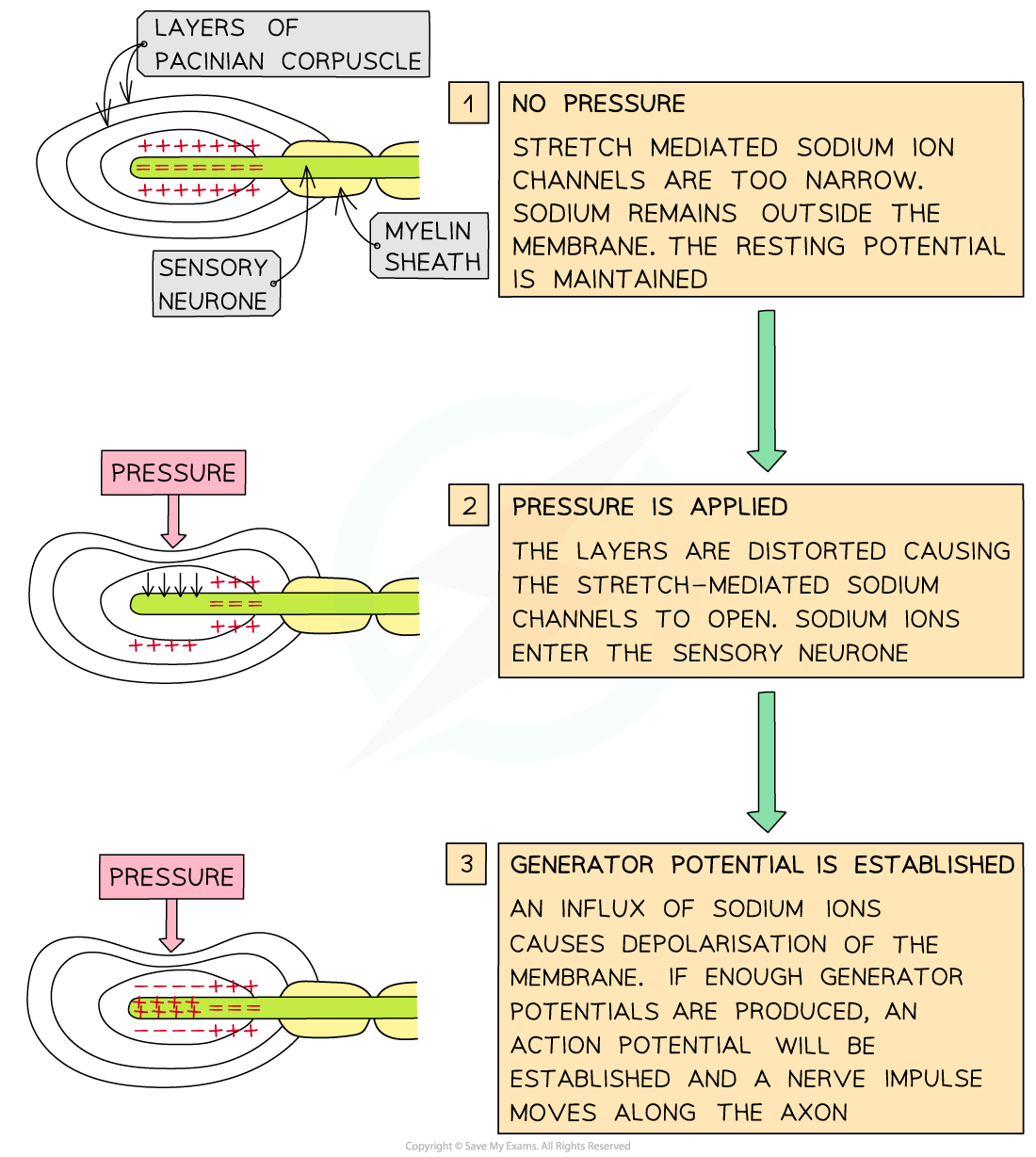
They respond to changes in pressure
When these receptors are stimulated by pressure on the skin it leads to the establishment of a generator potential

Pacinian corpuscles connect to sensory neurones
They consist of many layers of membrane around the end of the neurone
The layers are separated by a gel
The gel contains positively charged sodium ions (Na+)
The section of neurone surrounded by layers of membrane contains stretch-mediated sodium ion channels which open when sufficient pressure is applied
This allows (Na+) to flow into the neurone, so that an electrical potential difference is established across the cell membrane; this is a generator potential
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Receptors can be cells, specifically adapted parts of a cell (e.g. the Pacinian corpuscle) or proteins on the cell surface membrane.Many sensory receptors are found in sensory organs such as the eye or ear.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
