Types of Variation (OCR A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: H420
Types of Variation
The term variation refers to the differences between living organisms
Variation can be:
between different species or within a single species
continuous or discontinuous
caused be genetic and/or environmental factors
Interspecific vs intraspecific variation
Interspecific variation
Interspecific variation is that which exists between individuals of different species
Interspecific variation can be useful for classifying organisms into species groups
Different species may show clear phenotypic variation that can help differentiate them
Some species have such similar phenotypes that they can be very difficult to distinguish, meaning that genetic variation must be used for classification
Intraspecific variation
Intraspecific variation is that which exists between individuals of the same species
These differences are smaller than those found between individuals of different species
Variation within a species allows natural selection to occur
Discontinuous vs continuous variation
Discontinuous variation
Discontinuous variation refers to differences that fall into discrete and distinguishable categories with no intermediates
E.g. there are four possible ABO blood groups in humans; a person can only have one of them
Discontinuous variation can be represented using a bar chart with bars that are clearly distinct from each other

Blood type is an example of discontinuous varation
Continuous variation
Continuous variation refers to differences that show a range of values and can fall anywhere between two extremes
E.g. body mass and height are measured on a continuous scale
Continuous variation can be represented on a histogram with bars that touch each other, and will often show a characteristic bell-shaped curve
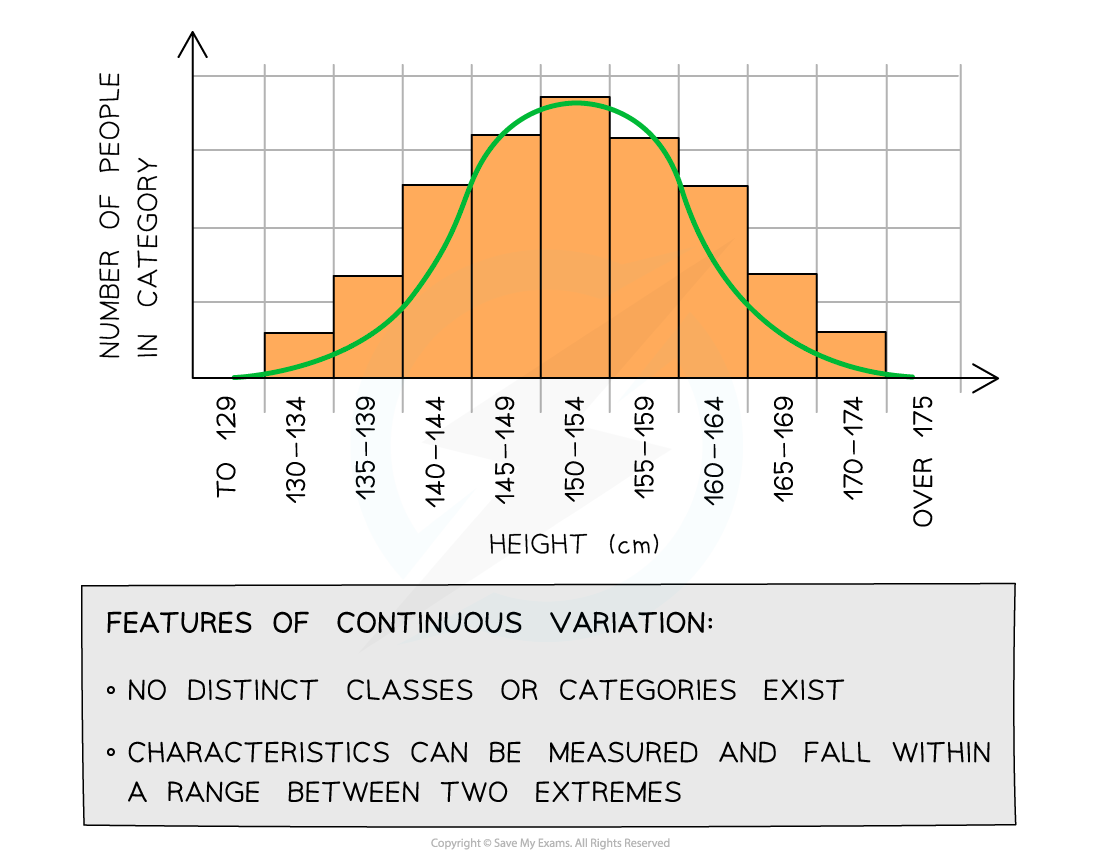
Height is an example of continuous variation
Causes of variation
Variation can be caused by genetic factors, environmental factors or a combination of the two
Causes of discontinuous variation
This type of variation occurs solely due to genetic factors
The environment has no direct effect
Phenotype = genotype
At the genetic level:
Different genes have different effects on the phenotype
Different alleles at a single gene locus have a large effect on the phenotype
Remember diploid organisms will inherit two alleles of each gene, these alleles can be the same or different
A good example of this is the F8 gene that codes for the blood-clotting protein Factor VIII
The different alleles at the F8 gene locus dictate whether or not normal Factor VIII is produced and whether the individual has the condition haemophilia
Causes of continuous variation
This type of variation is caused by an interaction between genetics and the environment
Phenotype = genotype + environment
At the genetic level:
Different alleles at a single locus have a small effect on the phenotype
Different genes can have the same effect on the phenotype and these add together to have an additive effect
If a large number of genes have a combined effect on the phenotype they are known as polygenes
Environmental factors
In some cases, phenotypic variation is explained by environmental factors alone
For example, clones of plants with exactly the same genetic information (DNA) will grow to different heights when grown in different environmental conditions
Different environments around the globe experience very different conditions in terms of the:
Length of sunlight hours (which may be seasonal)
Supply of nutrients (food)
Availability of water
Temperature range
Oxygen levels
Changes in the factors above can affect how organisms grow and develop
For example, plants with a tall genotype growing in an environment that is depleted in minerals, sunlight and water will not be able to grow to their full potential size determined by genetics
Variation in phenotype caused solely by environmental pressures or factors cannot be inherited by an organism’s offspring
Only alterations to the genetic component of gametes will ever be inherited
Other examples of environmental variation include:
An accident may lead to scarring on the body
Eating too much and not leading an active lifestyle will cause weight gain
Being raised in a certain country will cause you to speak a certain language with a certain accent

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?