Amino Acids & Peptide Bonds (OCR A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: H420
Amino Acids
Proteins
Proteins are polypeptides (and macromolecules) made up of monomers called amino acids
The sequence, type and number of the amino acids within a protein determines its shape and therefore its function
Proteins are extremely important for cell growth, cell repair and structure
They form all of the following:
Enzymes
Cell membrane proteins (eg. carrier)
Hormones
Immunoproteins (eg. immunoglobulins)
Transport proteins (eg. haemoglobin)
Structural proteins (eg. keratin, collagen)
Contractile proteins (eg. myosin)
Amino acids
Amino acids are the monomers of polypeptides
There are 20 amino acids found in proteins common to all living organisms
The general structure of all amino acids is a central carbon atom bonded to:
An amine group -NH2
A carboxylic acid group -COOH
A hydrogen atom
An R group (which is how each amino acid differs and why amino acid properties differ e.g. whether they are acidic or basic or whether they are polar or non-polar)

The generalised structure of an amino acid
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You will be expected to recognise whether an unfamiliar molecule is an amino acid or protein so look for the functional groups (amine and carboxyl).
The Peptide Bond
Peptide bonds form between amino acids
Peptide bonds are covalent bonds and so involve the sharing of electrons
In order to form a peptide bond a hydroxyl (-OH) is lost from the carboxylic group of one amino acid and a hydrogen atom is lost from the amine group of another amino acid
The remaining carbon atom (with the double-bonded oxygen) from the first amino acid bonds to the nitrogen atom of the second amino acid
This is a condensation reaction so water is released
Dipeptides are formed by the condensation of two amino acids
Polypeptides are formed by the condensation of many (3 or more) amino acids
A protein may have only one polypeptide chain or it may have multiple chains interacting with each other
During hydrolysis reactions, the addition of water breaks the peptide bonds resulting in polypeptides being broken down to amino acids
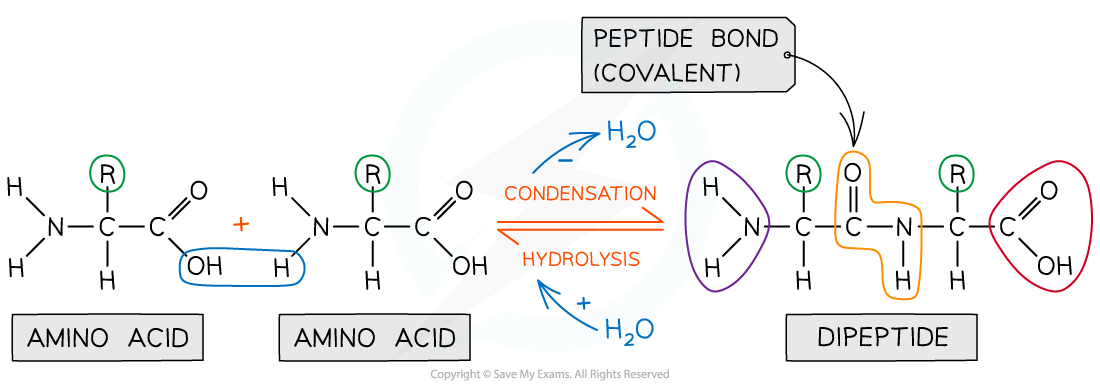
Amino acids are bonded together by covalent peptide bonds to form a dipeptide in a condensation reaction
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When asked to identify the location of the peptide bond, look for where nitrogen is bonded to a carbon which has a double bond with an oxygen atom, note the R group is not involved in the formation of a peptide bond.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?