Endocytosis & Exocytosis (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology) : Revision Note
Endocytosis & Exocytosis
The processes of diffusion, osmosis and active transport are responsible for the transport of individual molecules or ions across cell membranes
However, the bulk transport of larger volumes of materials into or out of cells is also possible
Examples of these larger quantities of materials that might need to cross the membrane include:
Large molecules such as proteins or polysaccharides
Parts of cells
Whole cells eg. bacteria
Bulk transport into cells = endocytosis
Bulk transport out of cells = exocytosis
These two processes require energy input and are therefore forms of active transport
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is the process by which the cell surface membrane engulfs material, forming a small sac (or ‘endocytic vacuole’) around it
There are two forms of endocytosis:
Phagocytosis:
This is the bulk intake of solid material by a cell
Cells that specialise in this process are called phagocytes
The vacuoles formed are called phagocytic vacuoles
An example is the engulfing of bacteria by phagocytic white blood cells
Pinocytosis:
This is the bulk intake of liquids
If the vacuole (or vesicle) that is formed is extremely small then the process is called micropinocytosis
Phagocytosis Diagram

The process of phagocytosis of a bacterium by a phagocyte (white blood cell)
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is the process by which materials are removed from, or transported out of, cells (the reverse of endocytosis)
The substances to be released (such as enzymes, hormones or cell wall building materials) are packaged into secretory vesicles formed from the Golgi body
These vesicles then travel to the cell surface membrane
Here they fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents outside of the cell
An example is the secretion of digestive enzymes from pancreatic cells
Exocytosis Diagram
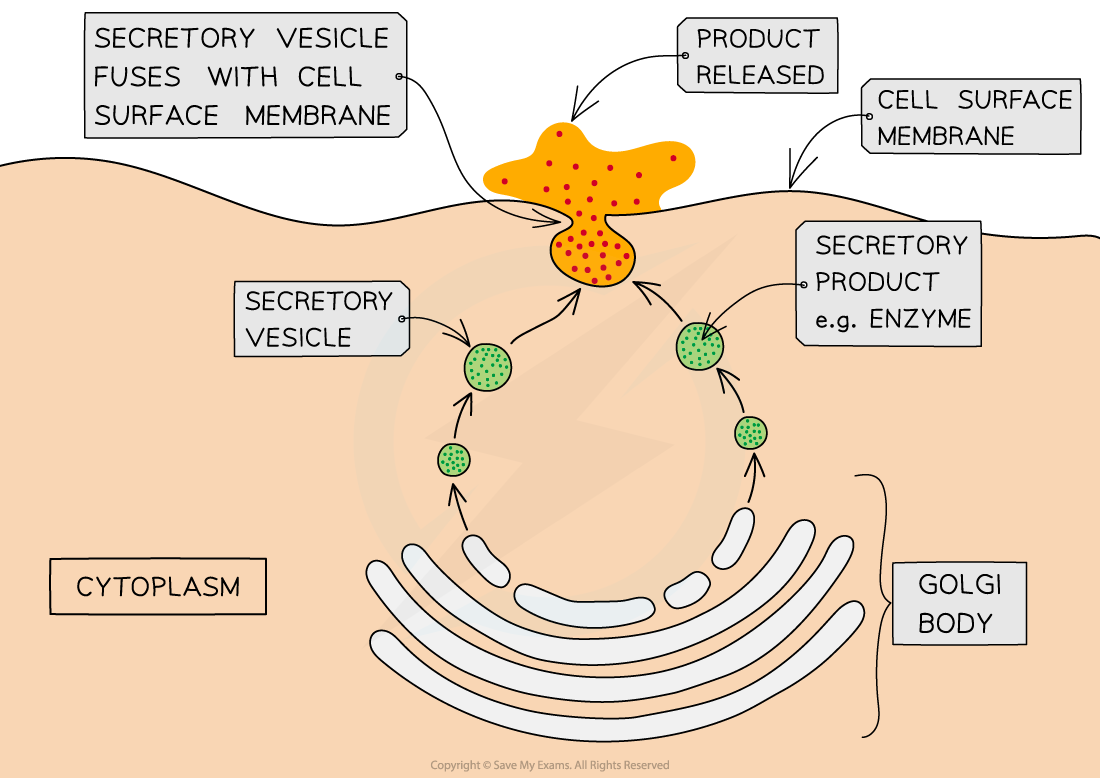
The process of exocytosis.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember – active transport, endocytosis and exocytosis all require the input of energy. This energy is provided by the hydrolysis of ATP produced during respiration.To get the mark in the exam you have to specifically state 'exocytosis' for bulk transport out of the cell and 'endocytosis' (or even better: phagocytosis, pinocytosis, micropinocytosis, macropinocytosis) for bulk transport into the cell. Simply stating 'bulk transport' is not specific enough, the examiner will want to know what type of bulk transport and for this you need to state the scientific name!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
