Vmax & the Michaelis-Menten Constant (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Vmax & the Michaelis-Menten constant
Substrate concentration affects the rate of catalysis in an enzyme-substrate reaction
When the substrate concentration is fixed (and enzyme concentration is kept constant) the initial rate of reaction is fastest
As active sites become engaged, the reaction rate falls
The Michaelis-Menten model describes the kinetics of such enzyme catalysed reactions
In this model, two values are used to describe an enzyme catalysed reaction:
The maximal rate or maximal velocity (Vmax)
The Michaelis-Menten constant (Km)
These values are derived from the reaction rate at different substrate concentrations
The maximum rate of reaction (Vmax) is used to derive the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km)
This is then used to compare the affinity of different enzymes for their substrates
Michaelis-Menten enzyme kinetics
The Michaelis-Menten model is used to investigate the kinetics of enzyme catalysed reactions (enzyme kinetics is an area in biochemistry that studies how different variables affect reaction rates)
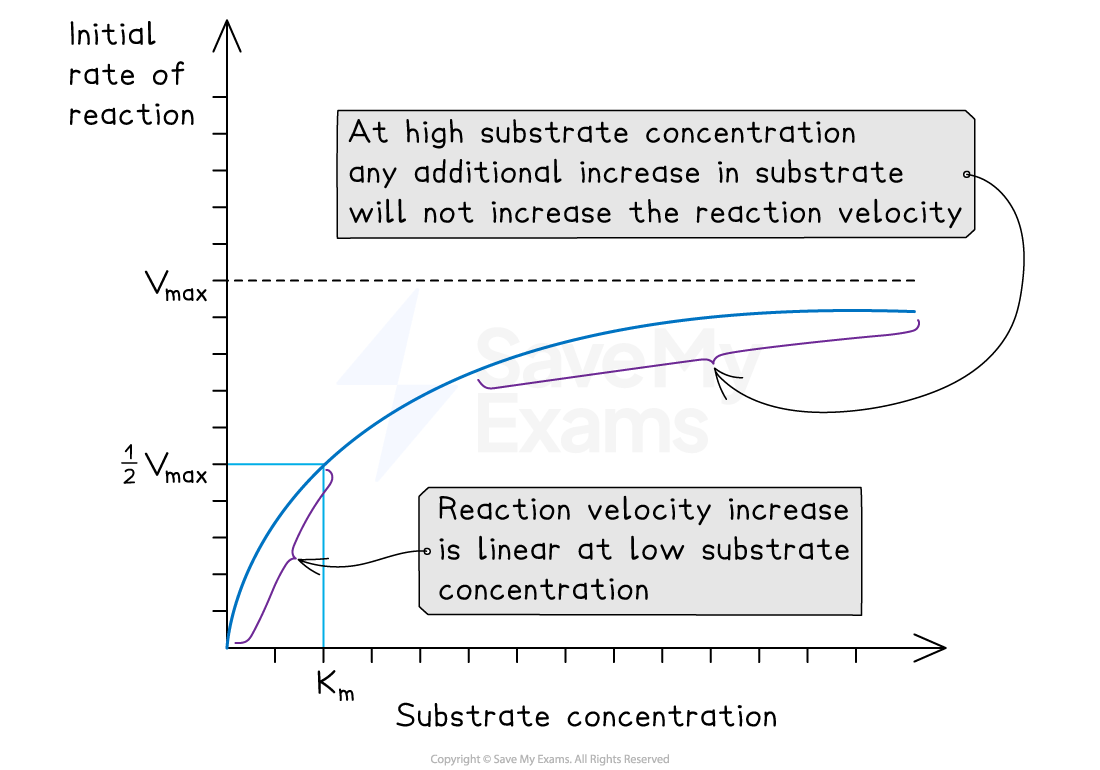
The rate of reaction is measured at different substrate concentrations, producing a graph like the one below
The two important values deduced are:
The Vmax (maximum rate of reaction at saturating substrate concentrations)
The Km, which is the substrate concentration at ½Vmax (this is also known as the Michaelis-Menten constant)
The Michaelis-Menten constant is the substrate concentration at which the enzyme works at half its maximum rate
At this point, half of the active sites of the enzyme are occupied by substrate molecules
The higher the affinity of the enzyme for the substrate, the lower the substrate concentration needed for this to occur
This is why the Michaelis-Menten constant is a measure of the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate
There is an inverse relationship between the Km and the affinity of an enzyme for its substrate
An enzyme with a high Km has a low affinity for its substrate and an enzyme with a low Km has a high affinity for its substrate
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you can identify the Vmax and the Km on a graph like the one above.

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
