Haemoglobin (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology) : Revision Note
The Molecular Structure of Haemoglobin
Structure
Haemoglobin is a globular protein which is an oxygen-carrying pigment found in vast quantities in red blood cells
It has a quaternary structure as there are four polypeptide chains. These chains or subunits are globin proteins (two α–globins and two β–globins) and each subunit has a prosthetic haem group
The four globin subunits are held together by disulphide bonds and arranged so that their hydrophobic R groups are facing inwards (helping preserve the three-dimensional spherical shape) and the hydrophilic R groups are facing outwards (helping maintain its solubility)
The arrangements of the R groups is important to the functioning of haemoglobin. If changes occur to the sequence of amino acids in the subunits this can result in the properties of haemoglobin changing
This is what happens to cause sickle cell anaemia
The prosthetic haem group contains an iron II ion (Fe2+) which is able to reversibly combine with an oxygen molecule forming oxyhaemoglobin and results in the haemoglobin appearing bright red
Each haemoglobin with the four haem groups can therefore carry four oxygen molecules (eight oxygen atoms)
Haemoglobin Diagram
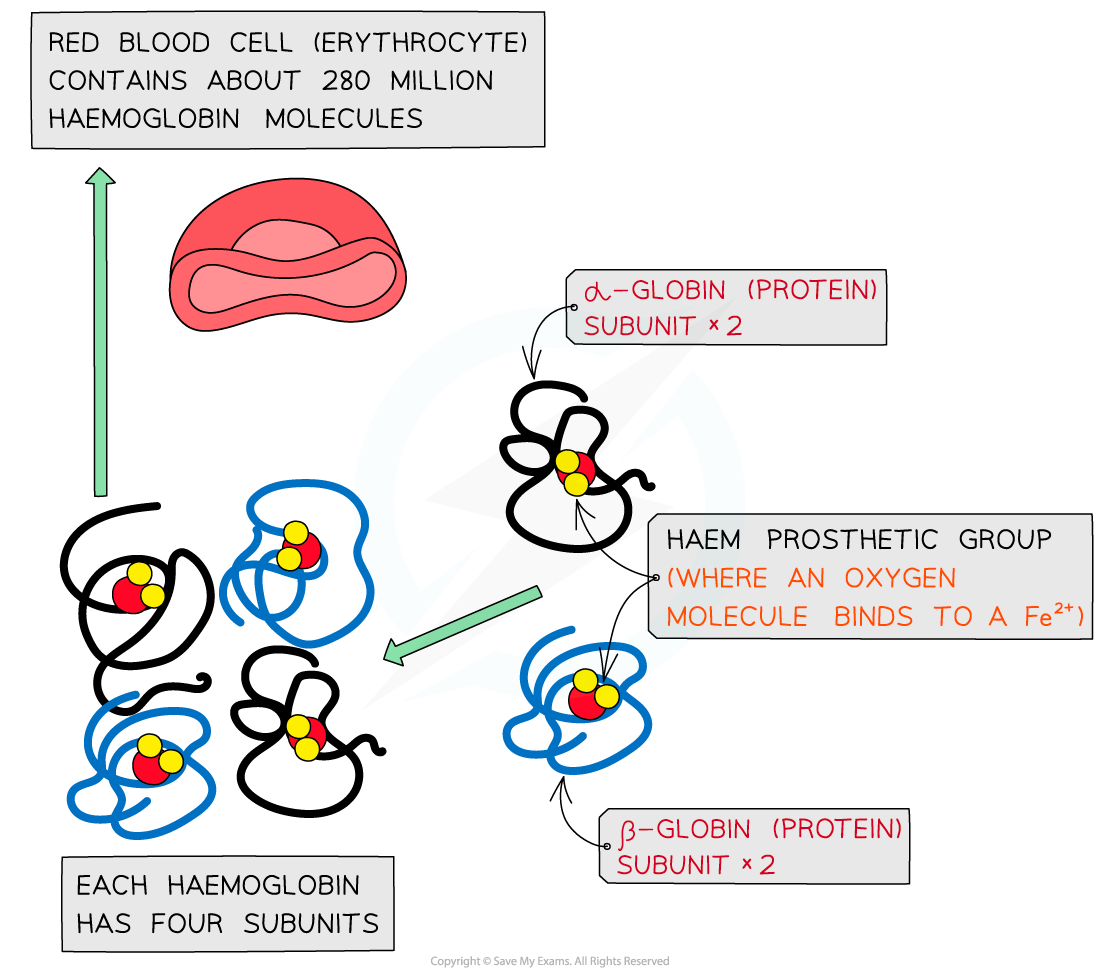
The structure of haemoglobin showing the α–globin and β–globin subunits, the prosthetic haem group with oxygen molecules bonded to form oxyhaemoglobin.
Function
Haemoglobin is responsible for binding oxygen in the lung and transporting the oxygen to tissue to be used in aerobic respiration
As oxygen is not very soluble in water and haemoglobin is, oxygen can be carried more efficiently around the body when bound to the haemoglobin
The presence of the haem group (and Fe2+) enables small molecules like oxygen to be bound more easily:
As each oxygen molecule binds, it alters the quaternary structure (due to alterations in the tertiary structure) of the protein which causes haemoglobin to have a higher affinity for the subsequent oxygen molecules and they bind more easily
The existence of the iron II ion (Fe2+) in the prosthetic haem group also allows oxygen to reversibly bind as none of the amino acids that make up the polypeptide chains in haemoglobin are well suited to binding with oxygen
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You need to know the structure of haemoglobin and how this relates to the function (its ability to transport oxygen).

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
