Haploidy & Diploidy (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Haploid & diploid cells
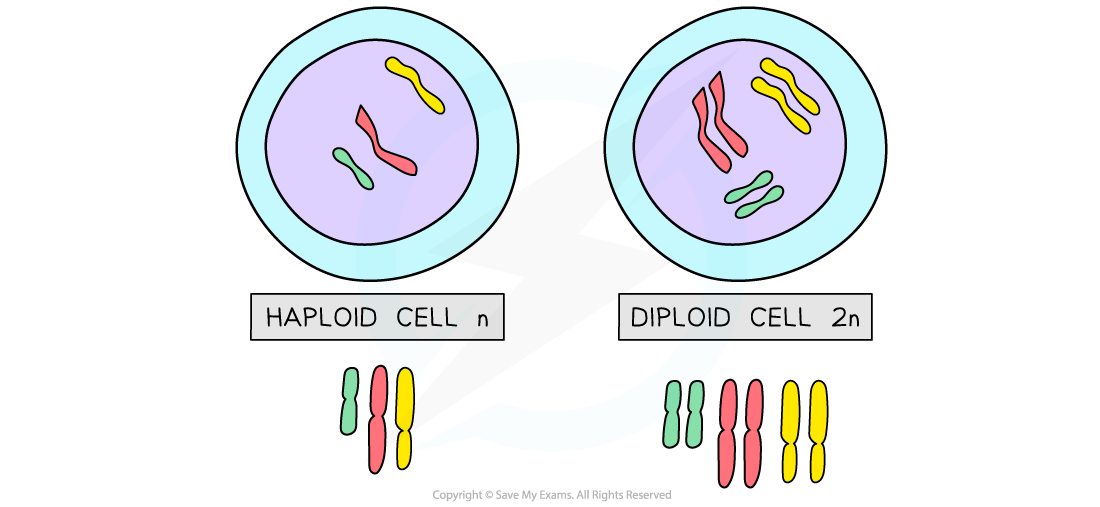
A diploid cell is a cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes (2n)
These chromosomes contain the DNA necessary for protein synthesis and cell function
Nearly all cells in the human body are diploid with 23 pairs (46 individual) of chromosomes in their nucleus
Haploid cells contain one complete set of chromosomes (n)
In other words they have half the number of chromosomes compared to diploid cells
Humans have haploid cells that contain 23 chromosomes (no pairs) in their nucleus
These haploid cells are called gametes and they are involved in sexual reproduction
For humans they are the female egg and the male sperm
Haploidy and diploidy are terms that can be applied to cells across different species
They describe the number of sets of chromosomes, not the total number of chromosomes
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Red blood cells are an exception when it comes to chromosome number as they don’t have a nucleus!
You may be asked to estimate the number of chromosomes that would be present in the haploid cell of any species. For example, dogs have 78 chromosomes in their diploid cells. When trying to find the number of chromosomes in their haploid cells simply remember that diploid is 2n and haploid is n, meaning you just need to divide the number of chromosomes by 2. So dogs have 39 chromosomes in their haploid cells!
The need for reduction division during meiosis
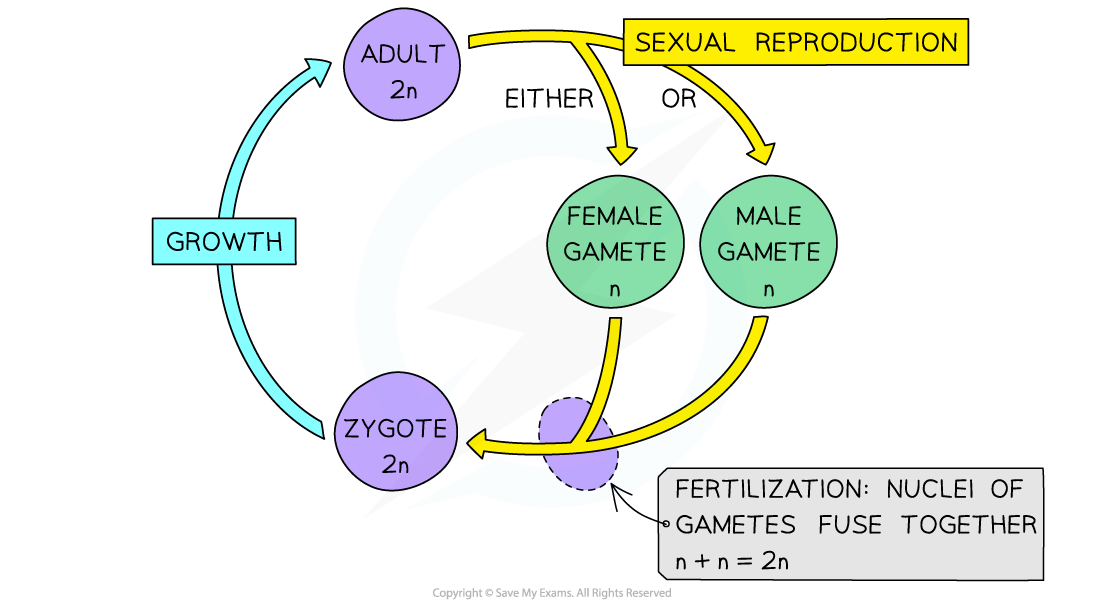
During fertilisation the nuclei of gametes fuse together to form the nucleus of the zygote
Both gametes must contain the correct number of chromosomes in order for the zygote to be viable. If a zygote has too many or too few chromosomes it may not survive
For a diploid zygote this means that the gametes must be haploid
n + n = 2n
Where n is the haploid number of chromosomes and 2n is the diploid number of chromosomes
Meiosis produces haploid gametes during sexual reproduction
The first cell division (this is not referring to the first stage) of meiosis is a reduction division
This is a nuclear division that reduces the chromosome number of a cell
In humans the chromosome number is reduced from 46 (diploid) to 23 (haploid)
The reduction in chromosome number during meiosis ensures the gametes formed are haploid

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
