Ultrastructure of Striated Muscle (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Ultrastructure of striated muscle
Striated muscle makes up the muscles in the body that are attached to the skeleton
'Striated' means it is striped/streaky in appearance
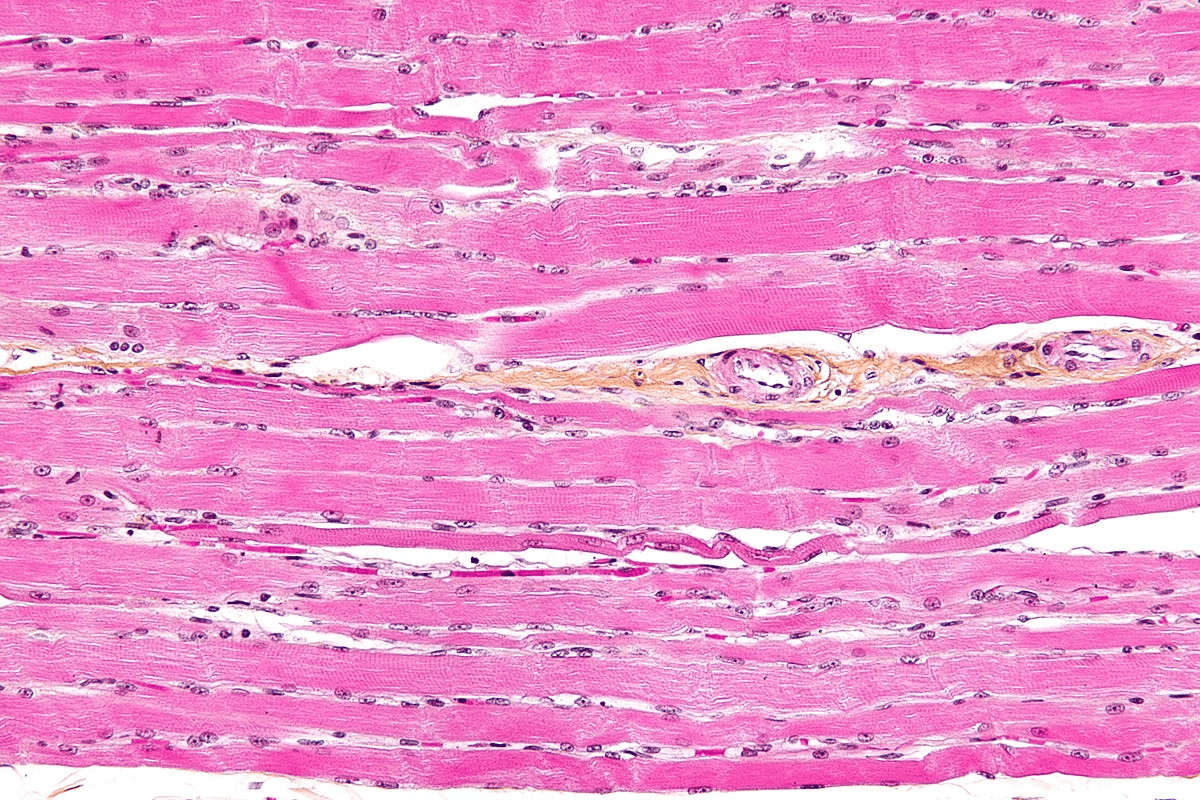
Striated muscle is made up of muscle fibres
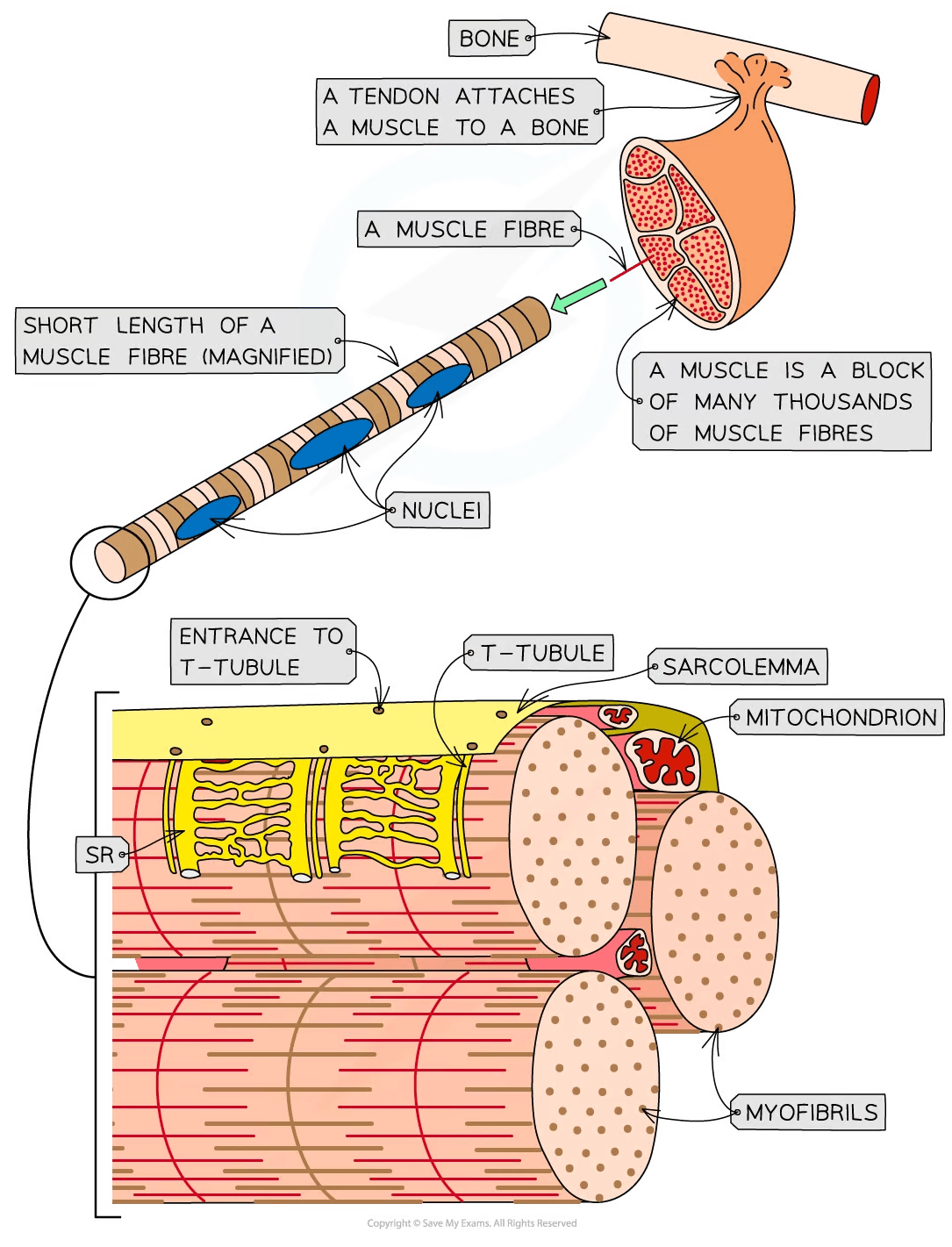
A muscle fibre is a highly specialised cell-like unit:
Each muscle fibre contains an organised arrangement of contractile proteins in the cytoplasm
Each muscle fibre is surrounded by a cell surface membrane
Each muscle fibre contains many nuclei—this is why muscle fibres are not usually referred to as cells
The different parts of a muscle fibre have different names from the equivalent parts of a normal cell:
Cell surface membrane = sarcolemma
Cytoplasm = sarcoplasm
The sarcoplasm contains mitochondria and myofibrils
The mitochondria carry out aerobic respiration to generate the ATP required for muscle contraction
Myofibrils are bundles of actin and myosin filaments, which slide past each other during muscle contraction
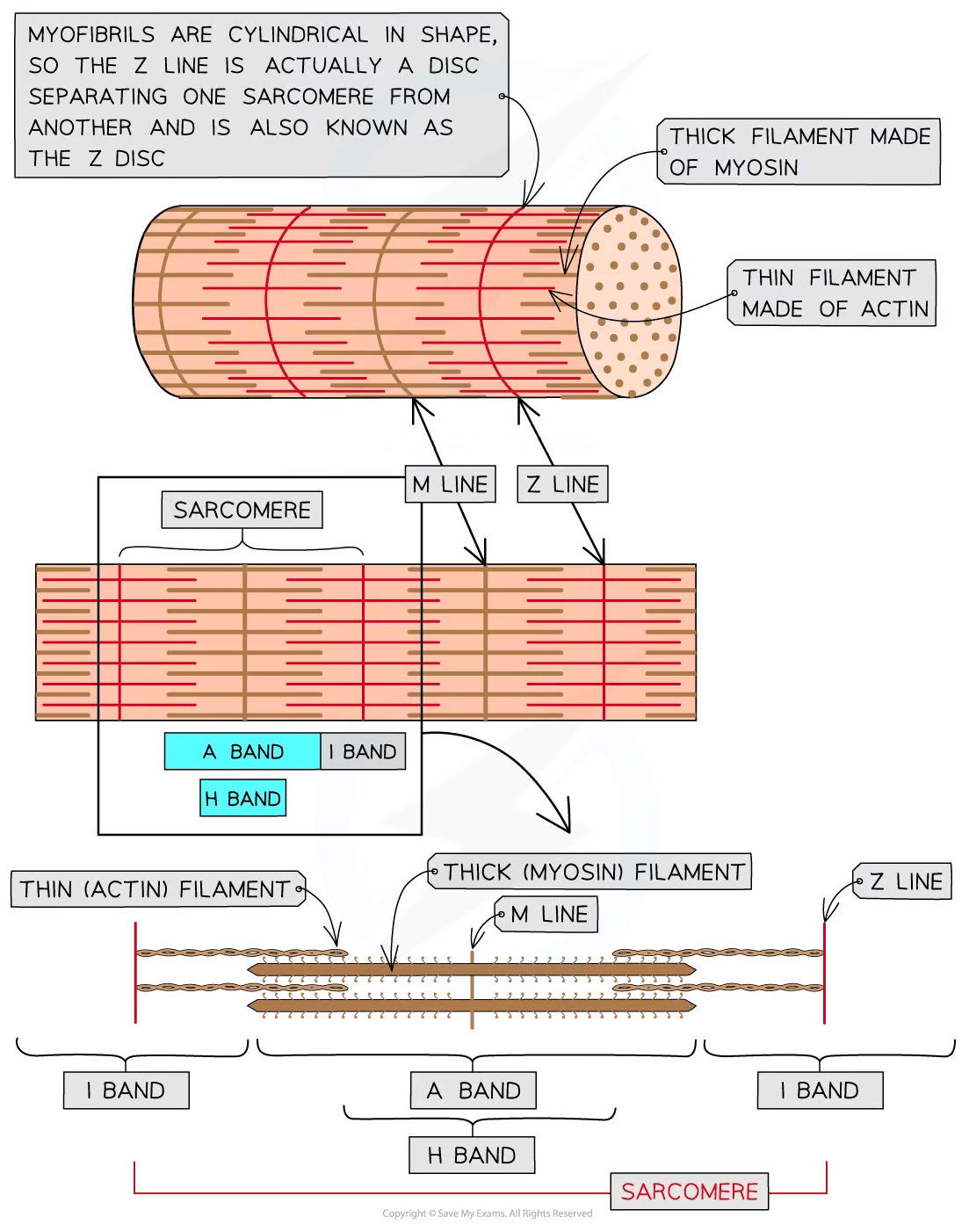
Myofibrils
Myofibrils are located in the sarcoplasm
Each myofibril is made up of two types of protein filament:
Thick filaments made of myosin
Thin filaments made of actin
These two types of filament are arranged in a particular order, creating different types of band and line
Part of myofibril | Description |
|---|---|
H band | Only thick myosin filaments present |
I band | Only thin actin filaments present |
A band | Contains areas where only myosin filaments are present and areas where myosin and actin filaments overlap |
M Line | Attachment for myosin filaments |
Z line | Attachment for actin filaments |
Sarcomere | The section of myofibril between two Z lines |

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
