Neurones (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Neurones
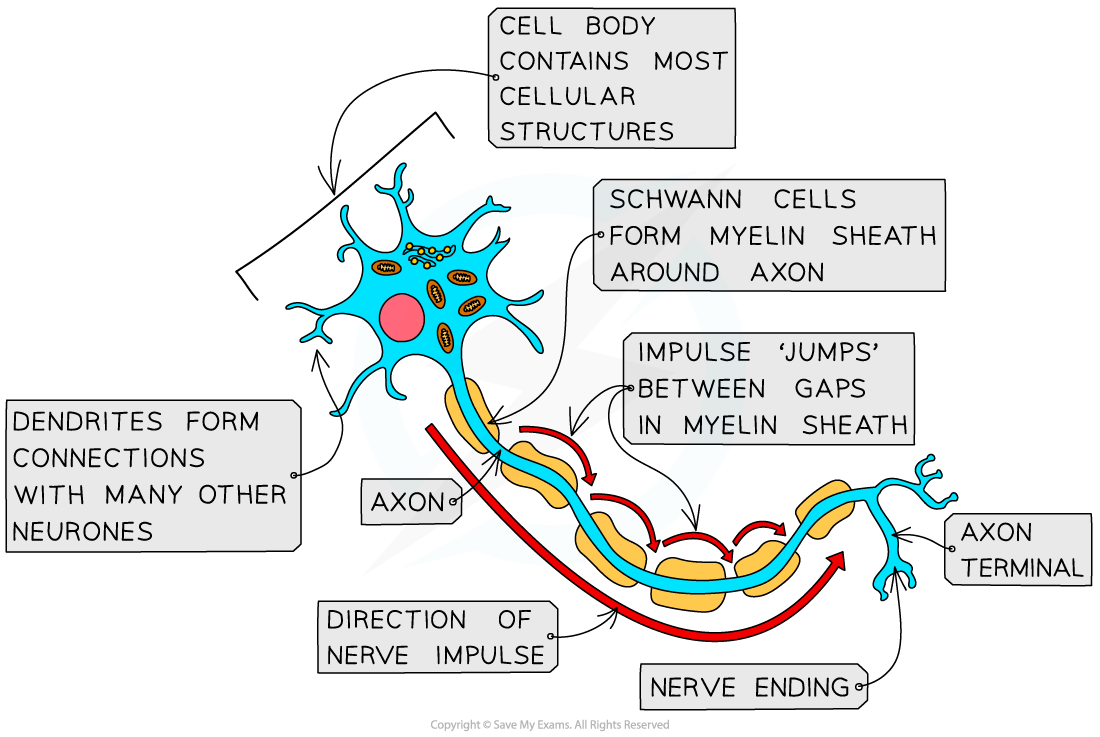
A neurones has a long fibre known as an axon
The axon is insulated by a fatty sheath with small, uninsulated sections along its length (called nodes of Ranvier)
The sheath is made of myelin, a substance that is made by specialised cells known as Schwann cells
Myelin is made when Schwann cells wrap themselves around the axon along its length
This means that the electrical impulse does not travel down the whole axon, but jumps from one node to the next
This means that less time is wasted transferring the impulse from one cell to another
Their cell bodies contain many extensions called dendrites
This means they can connect to many other neurones and receive impulses from them, forming a network for easy communication
There are three main types of neurone: sensory, relay and motor
Sensory neurones carry impulses from receptors to the CNS (brain or spinal cord)
Intermediate (aka relay) neurones are found entirely within the CNS and connect sensory and motor neurones
Motor neurones carry impulses from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)
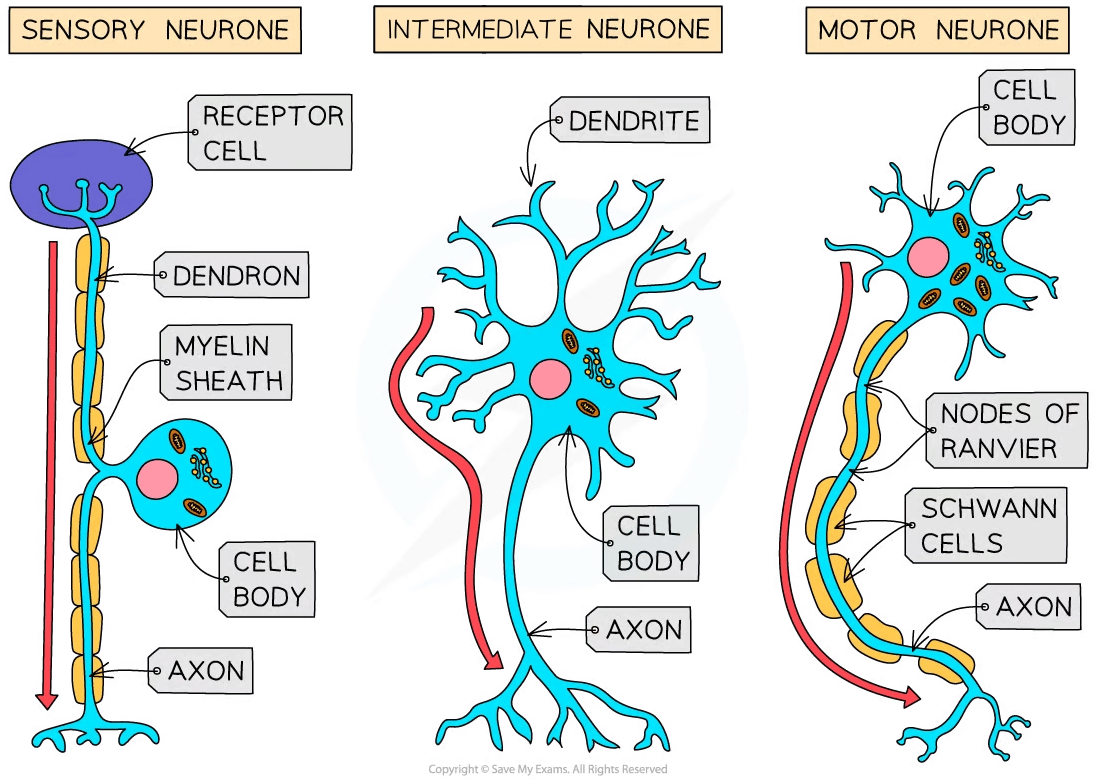
Each type of neurone has a slightly different structure
Motor neurones have:
A large cell body at one end, that lies within the spinal cord or brain
A nucleus that is always in its cell body
Many highly-branched dendrites extend from the cell body, providing a large surface area for the axon terminals of other neurones
Sensory neurones have the same basic structure as motor neurones, but have:
A cell body that branches off in the middle of the cell - it may be near the source of stimuli or in a swelling of a spinal nerve known as a ganglion
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You may be asked to identify the different types of neurone in a diagram. It can be helpful to memorise the key differences between them—such as the location and size of the cell body.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?