Animal & Plant Cells (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
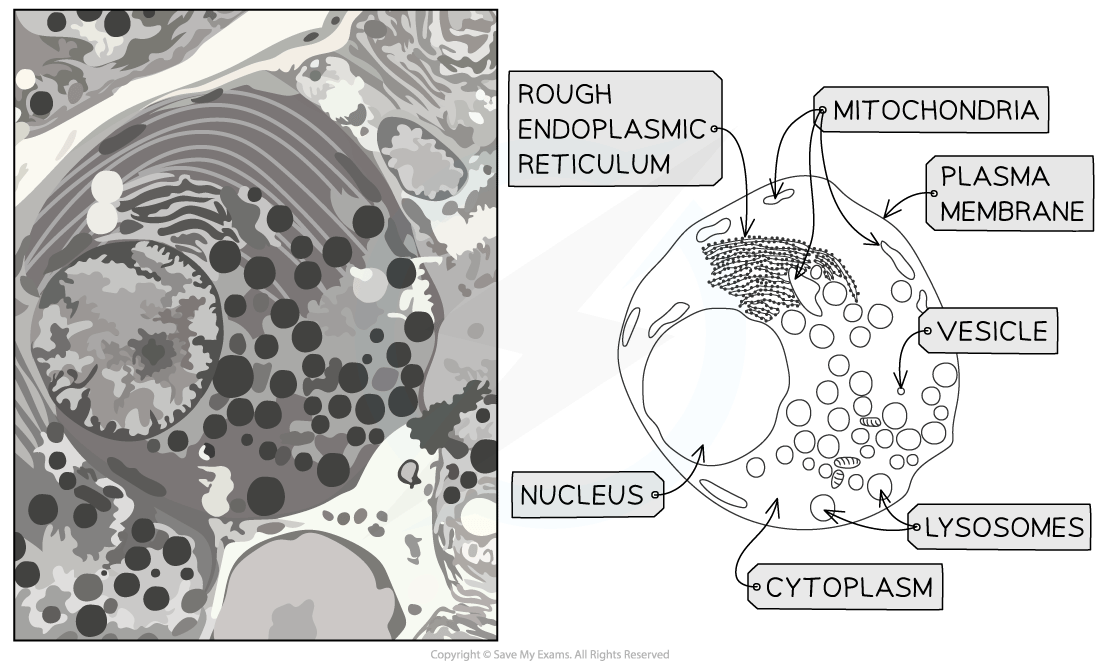
Electron micrographs: animal cells
Exam questions will not always contain neat diagrams of cellular structures, but may instead present images taken using microscopes
Such images are known as micrographs
It is possible to identify organelles in micrographs of animal cells on the basis of their shape, location, and size relative to other organelles, e.g.
The nucleus will always be the largest organelle
Mitochondria are the next largest, and are often cylindrical with a folded inner membrane
Note that mitochondria are not always cylindrical, but can also be circular; their shape will depend on their age, and on the angle at which they were sliced during specimen preparation
RER will be near the nucleus, and ribosomes can sometime be seen
Lysosomes and vesicles will be smaller than mitochondria
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be able to describe and interpret photomicrographs, electron micrographs and drawings of typical animal cells.
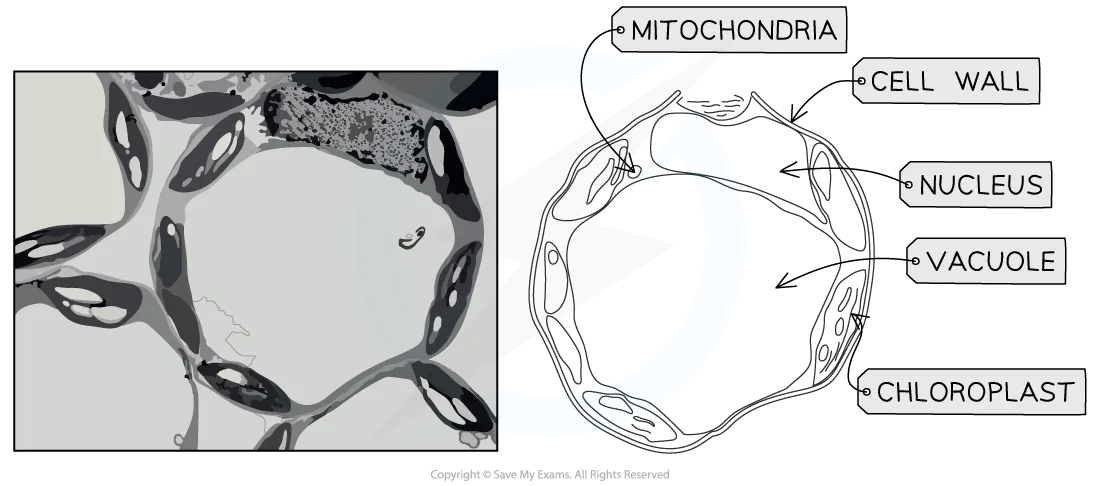
Electron micrographs: plant cells
Plant cell micrographs can be interpreted using the same techniques as animal cells
Large, seemingly empty spaces inside cells will be vacuoles
The nucleus will be the largest dark region in the cell
Chloroplasts are the next-largest organelles, and grana are often visible
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You should be able to describe and interpret photomicrographs, electron micrographs and drawings of typical plant cells.
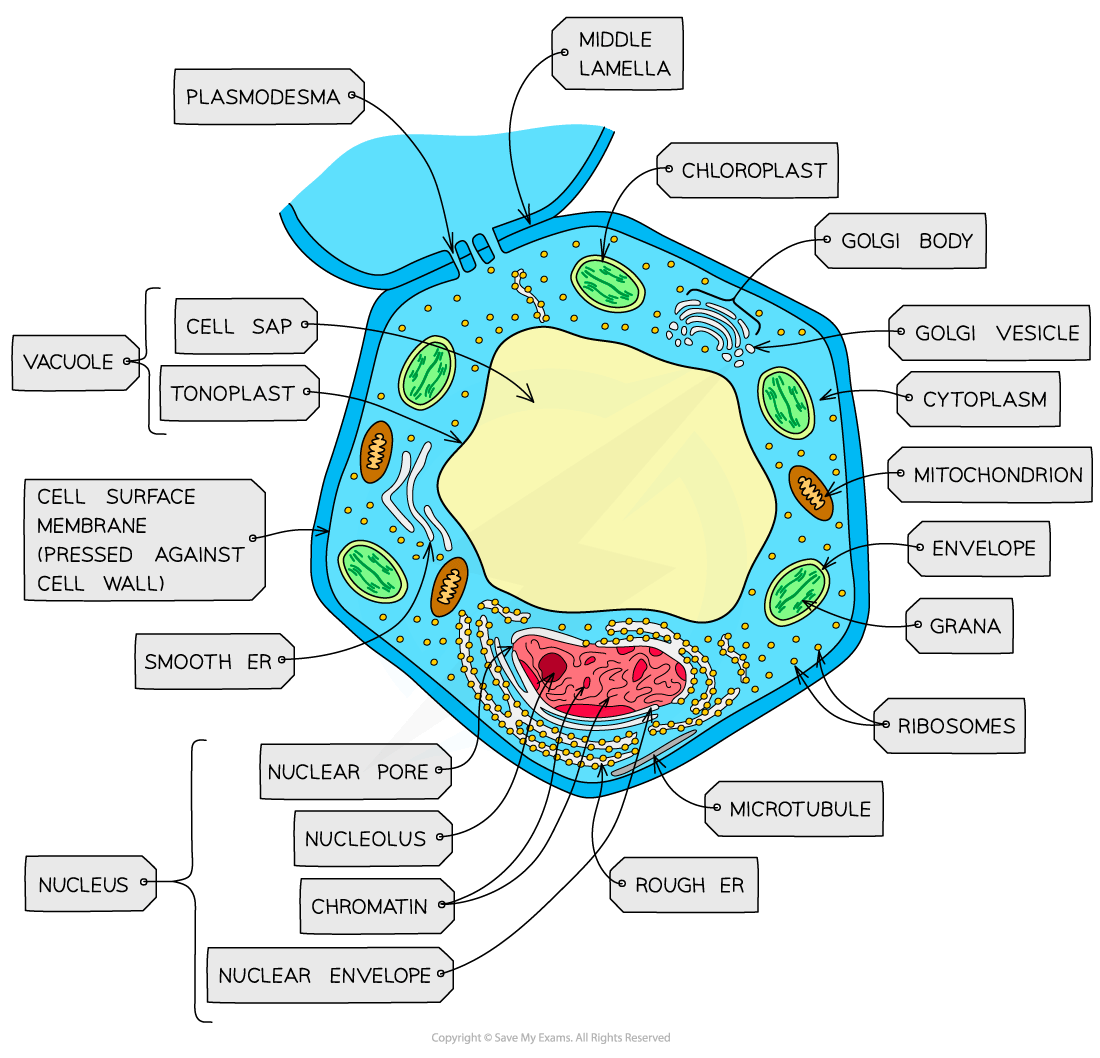
Structure of animal & plant cells
Animal and plant cells have many common structures:
Cell surface membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus
Mitochondria
Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi bodies
Vesicles and lysosomes
Ribosomes
Microtubules
Plant cells are larger and more regular in shape than animal cells, and have the following additional structures
Cellulose cell wall
Large permanent vacuoles
Chloroplasts
Plasmodesmata
The only structures found in animal cells but not plant cells are centrioles and microvilli


Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
